What is electric current?
What is electric current?
Current definition
In electromagnetism, the amount of electricity passing through any cross section of the conductor in unit time is called the current intensity, referred to as current, the current symbol is I, the unit is amperes, referred to as "ampere".
The cause of current formation
A current is formed when the free charge in a conductor moves in a regular direction under the action of an electric field force.
Direction of current
The direction of positive charge directional flow is defined as the direction of current in electricity.
Current expression
The ratio of the amount of charge Q that passes through a cross section of a conductor to the time t that passes through these charges is called the current, also called the current intensity. So I=Q/t If the amount of charge passing through the cross section of a conductor in 1s is 1C, the current in the conductor is 1A.
Three effects of electric current
Thermal effect: the heating phenomenon when the conductor is energized is called the thermal effect of current.
Magnetic effect: Oster found that any wire with current can generate a magnetic field around it, which is called the magnetic effect of current.
Chemical effect: Due to the participation of ions in the current, the substance has changed, and this effect is called the chemical effect of the current.
Classification
Alternating current
The magnitude and direction of the current change periodically. Ac is widely used in family life and industrial production, and the domestic voltage 220V and the general industrial voltage 380V are all dangerous voltages.
Direct current
The direction does not change with time. Direct current is generally widely used in all kinds of small appliances, because these power supply voltage will not exceed 24V, so it is a safe power supply.
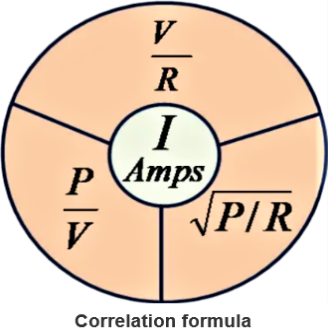
Current formula
The relationship between current, voltage and resistance.
The relationship between current, power and voltage.
The relationship between current, power and resistance.
Measuring instrument: Amperemeter
Usage
When connecting the AC ammeter, it should be connected to the electrical appliance in series in the circuit and the measured current should not exceed the range of the ammeter, and zero should be calibrated before use. DC ammeter wiring, should pay attention to its positive and negative polarity, ammeter positive wire pile to the direction of the actual current (the positive pole of the power supply, that is, the high potential point), ammeter negative wire pile to the direction of the actual current outflow (the negative pole of the power supply, that is, the low potential point).

Compared with AC meters, DC meters have simpler structure, higher measurement accuracy and smaller volume.

We aim to gather electrical knowledge and share it with others.













