What is the Thomson Effect?
What is the Thomson Effect?
Thomson effect definition
The Thomson effect is an important part of the phenomenon of thermoelectricity, which describes the phenomenon of heat absorption or release in a conductor (or semiconductor) in the presence of a temperature gradient when an electric current is passed through the conductor.
Working principle
When an electric current passes through a conductor with a temperature gradient, the electrons (or other charge carriers) experience a different thermal environment during their movement. Because carriers have different energy states at different temperatures, they release some energy (exothermic) when they move from the high temperature region to the low temperature region, and absorb energy (endothermic) when they move from the high temperature region. This phenomenon can be described by the Thomson coefficient (
T) to quantify, which defines the change in heat generated when a unit of current passes through a unit temperature gradient.
Thomson effect formula
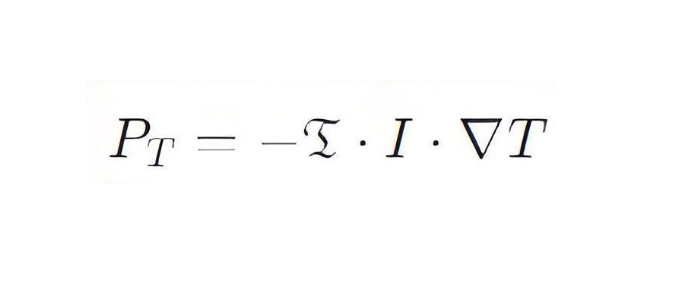
P T is the thermal power per unit length;
Σ is a Thomson coefficient
I∇ is the current intensity
∇T is the temperature gradient
Apply
Thermoelectric coolers: Although primarily based on the Paltier effect, understanding the Thomson effect is very important for designing efficient thermoelectric coolers.
Thermoelectric generators: The Thomson effect is also a factor to consider when developing thermoelectric generators for converting waste heat into electricity.
Research on thermoelectric materials: The Thomson effect provides an important theoretical basis for the development of new thermoelectric materials.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













