What is the Carnot Cycle?
What is the Carnot Cycle?
Carnot efficiency definition
Carnot efficiency refers to the maximum thermal efficiency that an ideal heat engine can achieve when working between a heat source and a cold source. It is an important concept in thermodynamics, and the Carnot efficiency is the theoretical limit, beyond which the efficiency of any practical heat engine will not exceed this limit.
Carnot efficiency formula
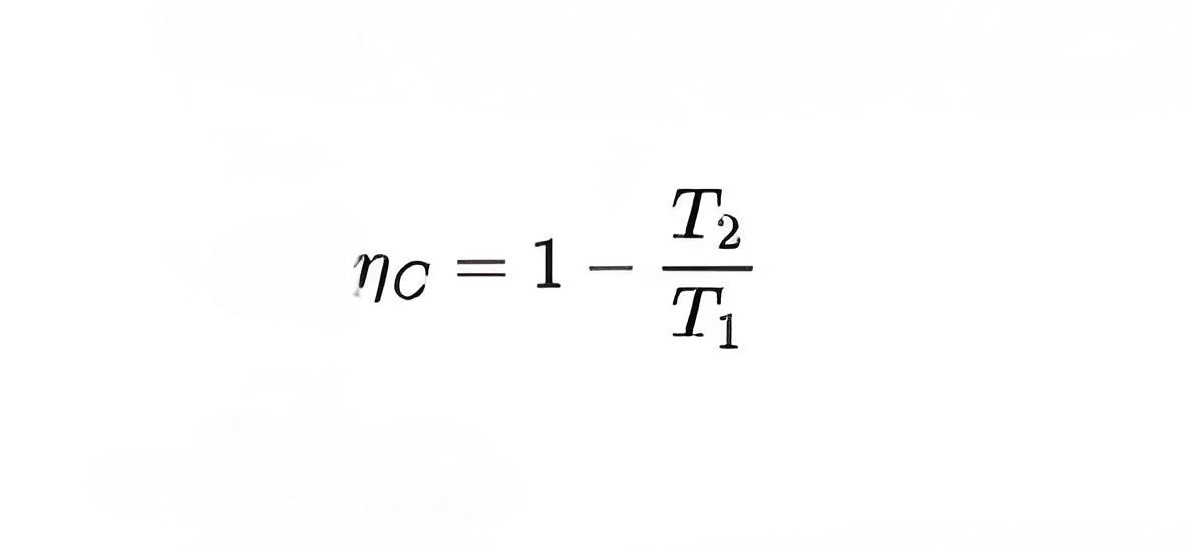
Peculiarity
Maximum efficiency: The Carnot efficiency gives the maximum possible efficiency of a heat engine between two fixed temperatures.
Ideal conditions: The Carnot cycle is carried out under ideal conditions, and the efficiency of the actual heat engine is always lower than the Carnot efficiency due to the existence of friction and other irreversible processes.
Temperature dependent: Carnot efficiency depends only on the temperature of the two heat sources, independent of the type of working medium.
Theoretical limit: The efficiency of any practical heat engine cannot exceed the Carnot efficiency, which reflects the requirements of the second law of thermodynamics.
Apply
Engine design: Carnot efficiency provides a theoretical upper limit of efficiency when designing heat engines such as internal combustion engines and steam turbines.
Refrigeration and heat pumps: In the design of refrigeration and heat pump systems, Carnot efficiency similarly provides a theoretical upper limit on efficiency.
Teaching Thermodynamics: Carnot efficiency is an important concept in the teaching of thermodynamics, helping students understand the first and second laws of thermodynamics.
Energy Efficiency Assessment: Carnot efficiency provides a benchmark when evaluating the efficiency of various energy conversion systems.
Significance
Theoretical limit: The Carnot efficiency provides a theoretical upper limit for the efficiency of a real heat engine. It indicates the highest efficiency that a heat engine can achieve over a given temperature range, and the efficiency of any actual heat engine is unlikely to exceed the Carnot efficiency.
Guidance and improvement: By analyzing Carnot efficiency, we can understand the gap between the actual heat engine and the ideal situation, and provide guidance for improving the heat engine efficiency. For example, the efficiency of the actual heat engine can be improved by increasing the temperature of the high temperature heat source, reducing the temperature of the low temperature heat source, and reducing the irreversible loss.
Fundamentals of thermodynamics: Carnot efficiency is one of the important applications of the Second Law of thermodynamics, which played a key role in the development of thermodynamic theory. The concept of Carnot efficiency helped people better understand the nature and limitations of energy conversion, and laid the foundation for further research in thermodynamics.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













