How Dose a Lead Acid Battery Work?
How Dose a Lead Acid Battery Work?
Lead Acid Battery Defined
A lead acid battery is defined as a rechargeable storage device where electrical energy is transformed into chemical energy during charging, and vice versa during discharging.
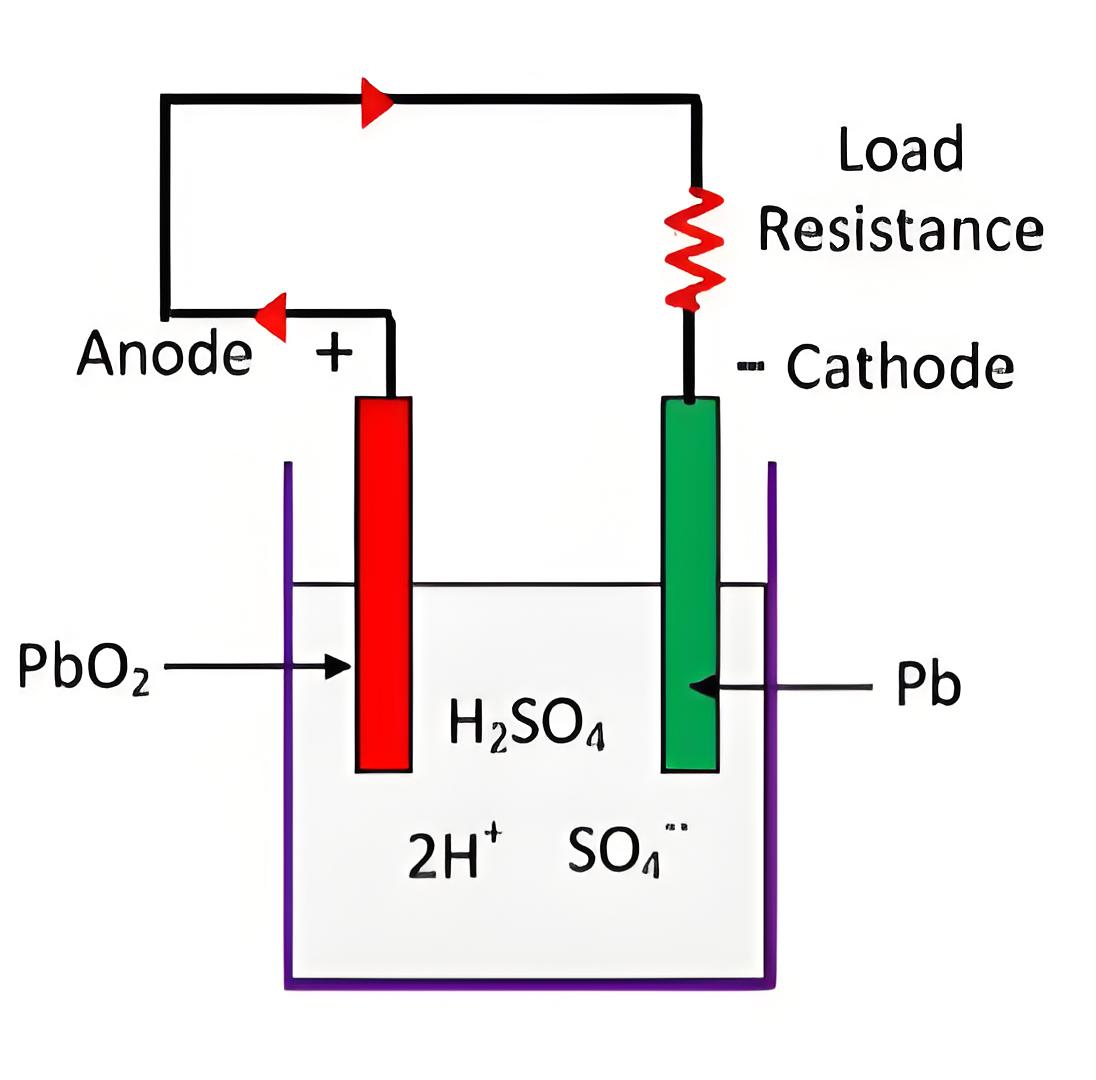
Materials and Composition
Essential materials include lead peroxide and sponge lead, used in the positive and negative plates respectively, submerged in dilute sulfuric acid.
Working of Lead Acid Battery
The battery operates by converting stored chemical energy into electrical energy through a series of electron exchanges between its lead plates during discharge.
Chemical Changes
Key reactions involve hydrogen and sulfate ions interacting with lead plates to form lead sulfate, dictating the flow of electrons and hence current through the battery.
Charging Process
Recharging the battery reverses the chemical reactions, converting lead sulfate back into lead peroxide and pure lead, thus restoring and enhancing battery capacity.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













