What are Alkaline Battery?
What are Alkaline Battery?
Alkaline Battery Definition
An alkaline battery is defined as a type of battery that uses zinc and manganese dioxide as electrodes and potassium hydroxide as the electrolyte.
Working Principle
Alkaline batteries work based on the reaction between zinc (Zn) and manganese dioxide (MnO2), facilitated by the potassium hydroxide electrolyte.
Construction
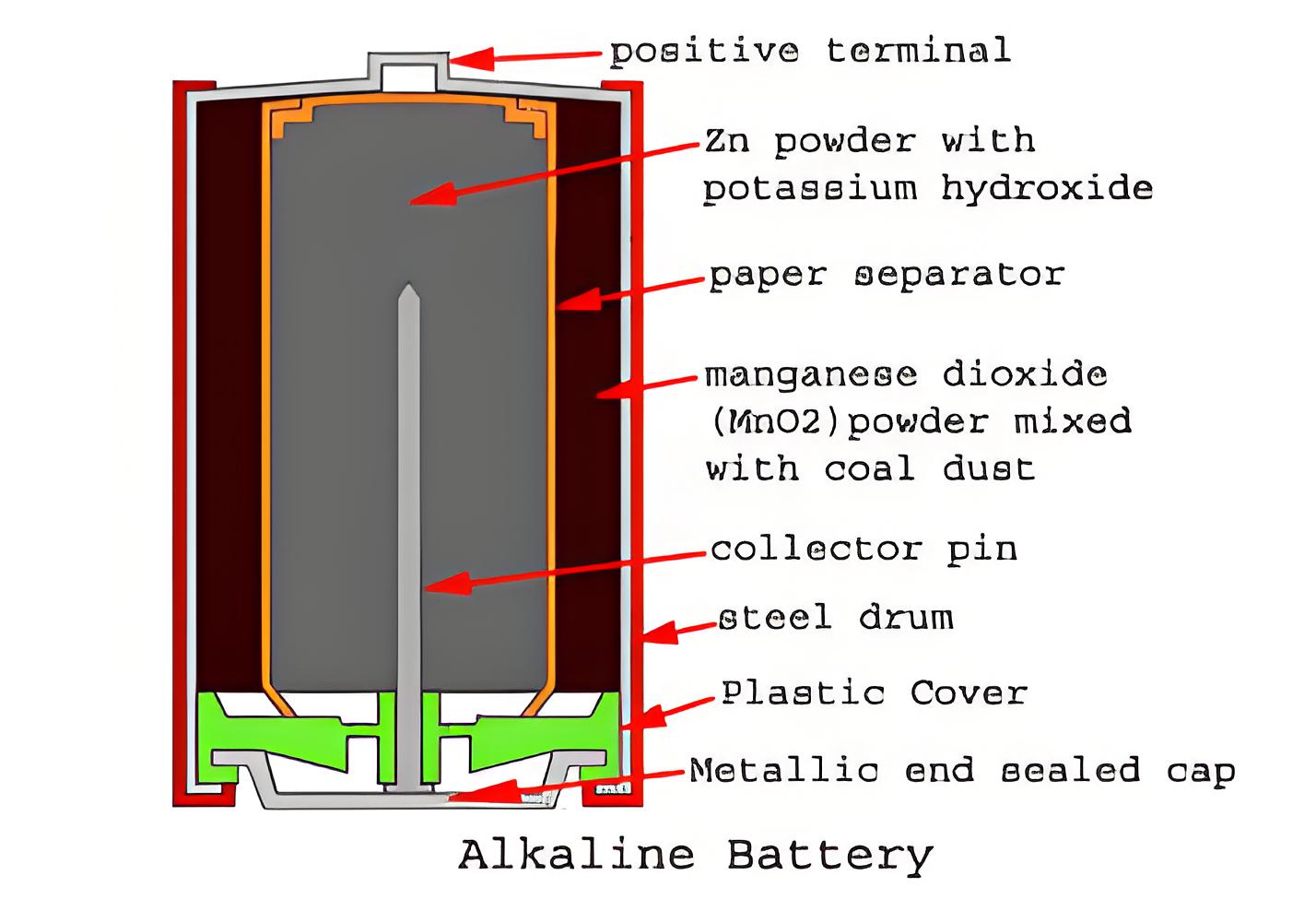
The construction of an alkaline battery involves a steel drum cathode, zinc powder anode, manganese dioxide cathode mixture, a paper separator, and a negative collector pin.
Advantages
high energy density
This battery performs equally well in both continuous and intermittent applications
This performs equally well in low and as well as high rate of discharge
This also performs equally well at ambient temperature as well as at low temperature
Alkaline battery has also low internal resistance
Enough longer self life
Leakage is low in this battery
Better dimensional stability
Disadvantage
High cost
Applications
Alkaline batteries are used in various applications, including industrial trucks, mine locomotives, air conditioning systems, commercial airlines, and military airplanes.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













