What is an Atom ?
What is an Atom ?
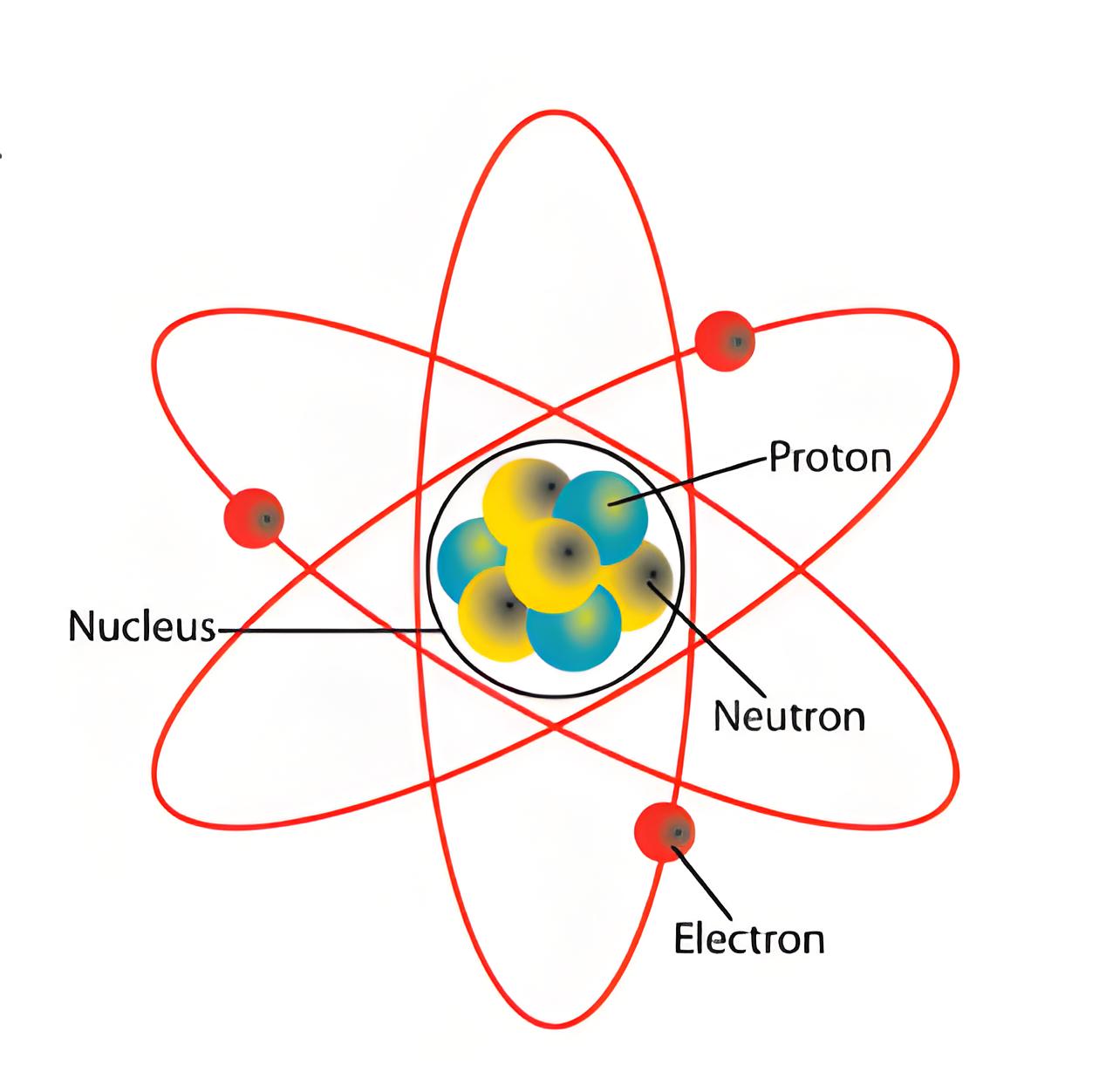
Atom Definition
An atom is defined as the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element.
Nucleus Composition
The nucleus contains protons and neutrons and is the core where most of an atom’s mass is concentrated.
Proton
Protons are positively charged particles. Charge on each proton is 1.6 × 10-19 Coulomb. The number of protons in nucleus of an atom represents the atomic number of atom.
Neutron
Neutrons do not have any electrical charge. Means, neutrons are electrically neutral particles. The mass of each neutron is equal to mass of the proton.
The nucleus is positively charged due to the presence of positively charged protons. In any material, the weight of the atom and radioactive properties are associated with the nucleus.
Electrons
An electron is a negatively charged particle present in the atoms. Charge on each electron is – 1.6 × 10 – 19 Coulomb. These electrons surround the nucleus.
Electron Dynamics
Electrons orbit the nucleus in energy levels, with their arrangement influencing the chemical properties of the atom.
Quantum Theory
Modern atomic theory explains atoms using quantum mechanics, describing electrons as both particles and probabilistic waves.
Valence Electrons
The electrons in the outermost shell determine an atom’s reactivity and are crucial for chemical bonding.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













