What is Arc Interruption Theory?
What is Arc Interruption Theory?
Arc Interruption Theory Definition
Arc interruption theory is defined as the process of stopping electrical arcs that occur when circuit contacts open.
Methods of Arc Interruption
There are two main methods: the high resistance method, which increases resistance to zero current, and the low resistance method, which uses the natural zero point of AC current.
Restriking Voltage
Restriking voltage is the voltage across breaker contacts at the moment an arc is extinguished.
Energy Balance Theory
When the circuit breaker contacts are about to open, the restriking voltage is zero, so no heat is generated. When fully open, the resistance is infinite, again producing no heat. Thus, the maximum heat generated is between these points. The energy balance theory states that if heat dissipation between contacts is faster than heat generation, the arc can be extinguished by cooling, lengthening, and splitting the arc.
Voltage Race Theory
The arc is due to the ionization of the gap between the contact of the circuit breaker. Thus the resistance at the initial stage is very small i.e. when the contact are closed and as the contact separates the resistance starts increasing. If we remove ions at the initial stage either by recombining them into neutral molecules or inserting insulation at a rate faster than the rate of ionization, the arc can be interrupted. The ionization at zero current depends on the voltages known as restriking voltage.
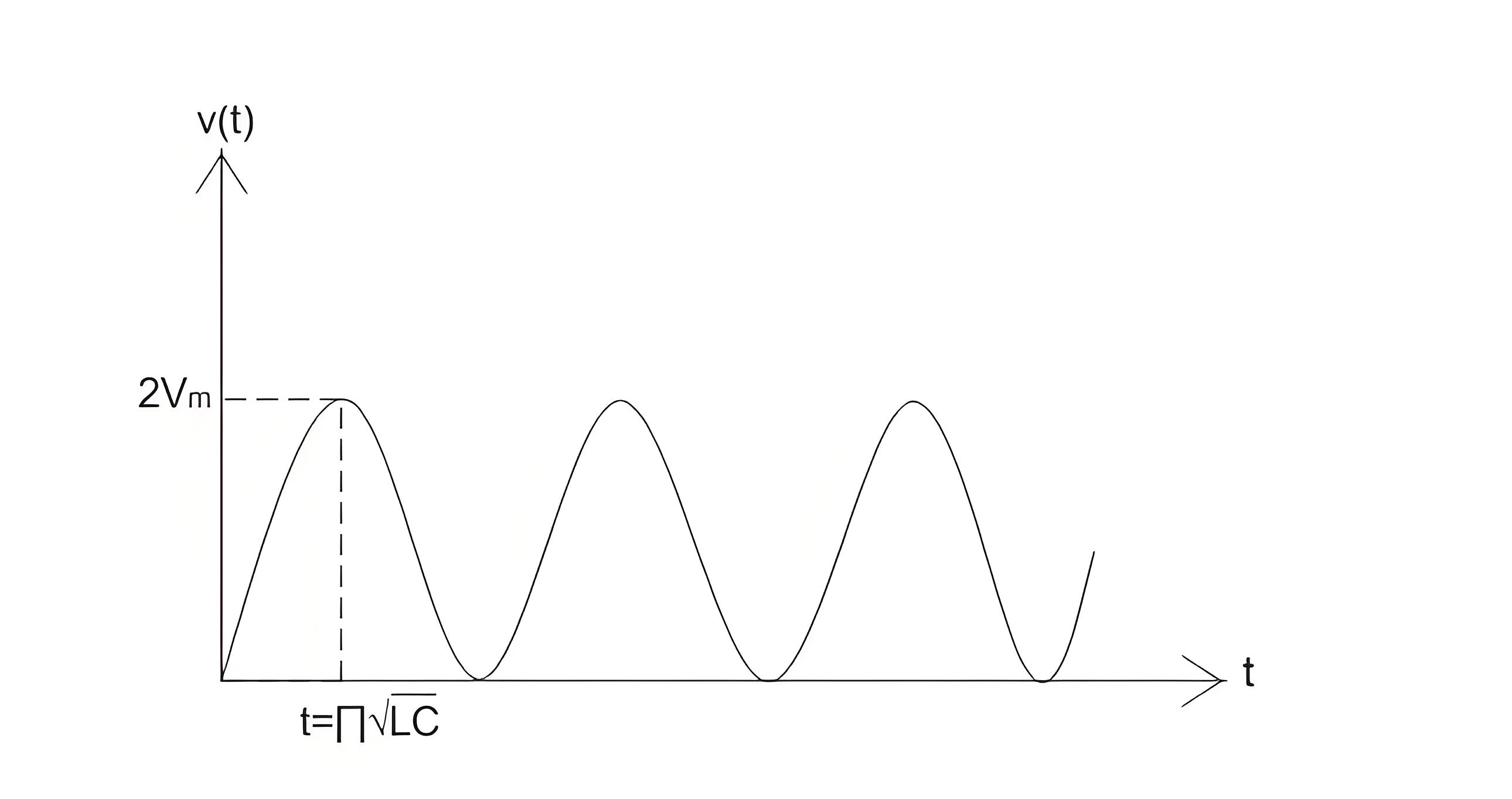
Let us define an expression for restriking voltage. For loss-less or ideal system we have,
Here, v = restriking voltage.
V = value of voltage at the instant of interruption.
L and C are series inductor and shunt capacitance up to fault point.
Thus from above equation we can see that lower the value of product of L and C, higher the value of restriking voltage.
The variation of v versus time is plotted below:
Now let us consider a practical system, or assume there finite loss in the system. As figure shown below, in this case the restriking voltage is damped out due to the presence of some finite resistance. Here it is assumed that the current lags behind the voltage by an angle (measured in degrees) of 90. However in practical situation angle may varies depending upon time in cycle at which the fault is occurred.
Let us consider the effect of arc voltage, if arc voltage is included in the system, there is an increment in the restriking voltage. However this is offset by another effect of an arc voltage which opposes the current flow and making change in the phase of current, thus bringing it more into phase with the applied voltages. Hence the current is not at its peak value when voltage passes through zero value.
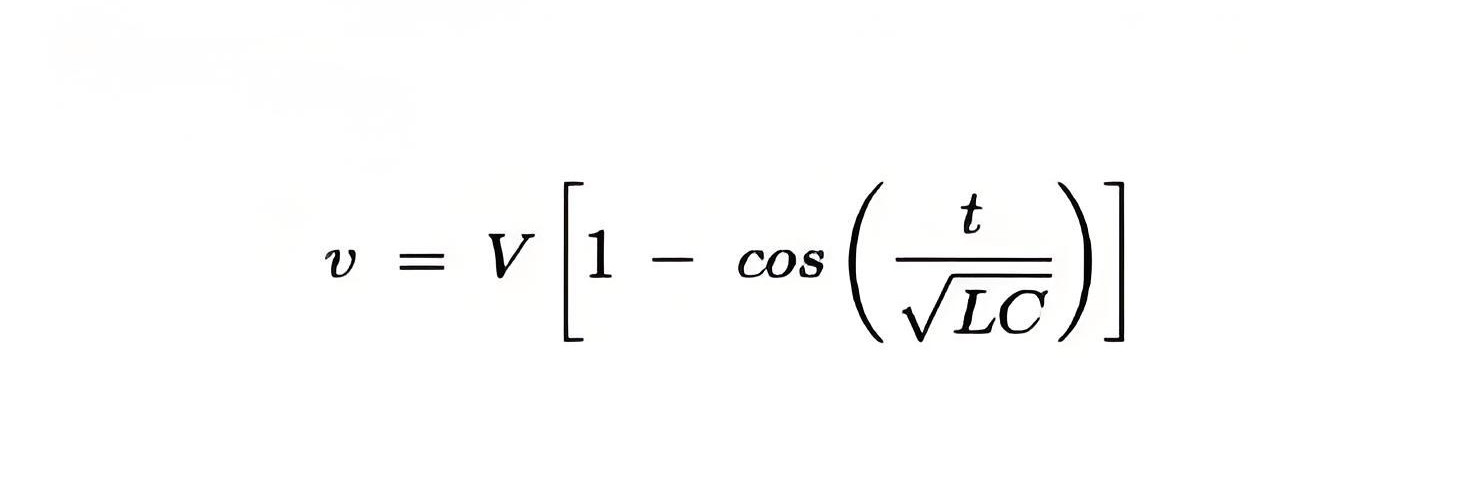
Rate of Rise of Restriking Voltage (RRRV)
It is defined as the ratio of peak value of restriking voltage to time taken to reach to peak value. It is one of the most important parameter as if the rate at which the dielectric strength developed between the contacts is greater than RRRV, and then the arc will be extinguishes.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













