What is Admittance?
What is Admittance?
Admittance Defined
Admittance measures how easily current flows through a circuit and is measured in siemens.
Impedance Relation
Admittance is the inverse of impedance, demonstrating opposite functionality in allowing current flow.

Admittance is also a complex number as impedance which is having a real part, Conductance (G) and imaginary part, Susceptance (B).

(it is negative for capacitive susceptance and positive for inductive susceptance)
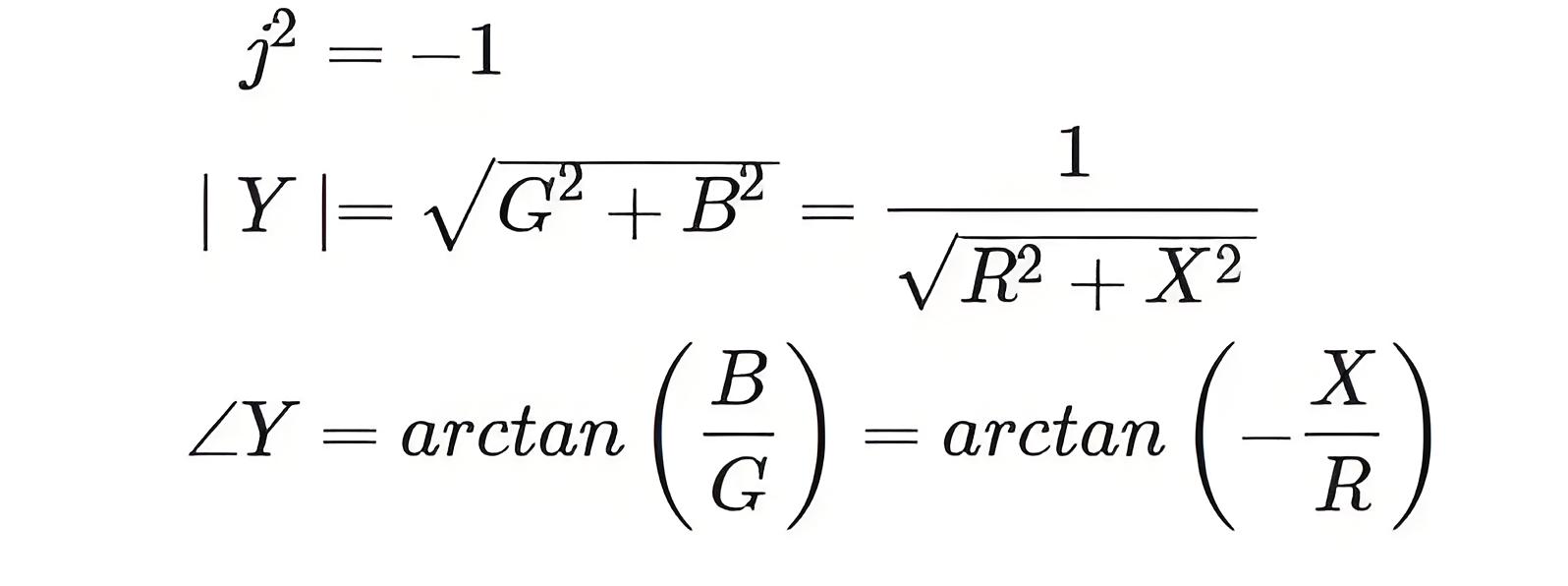
Admittance Components
It includes conductance, which facilitates current flow, and susceptance, which affects the circuit’s response to AC signals.
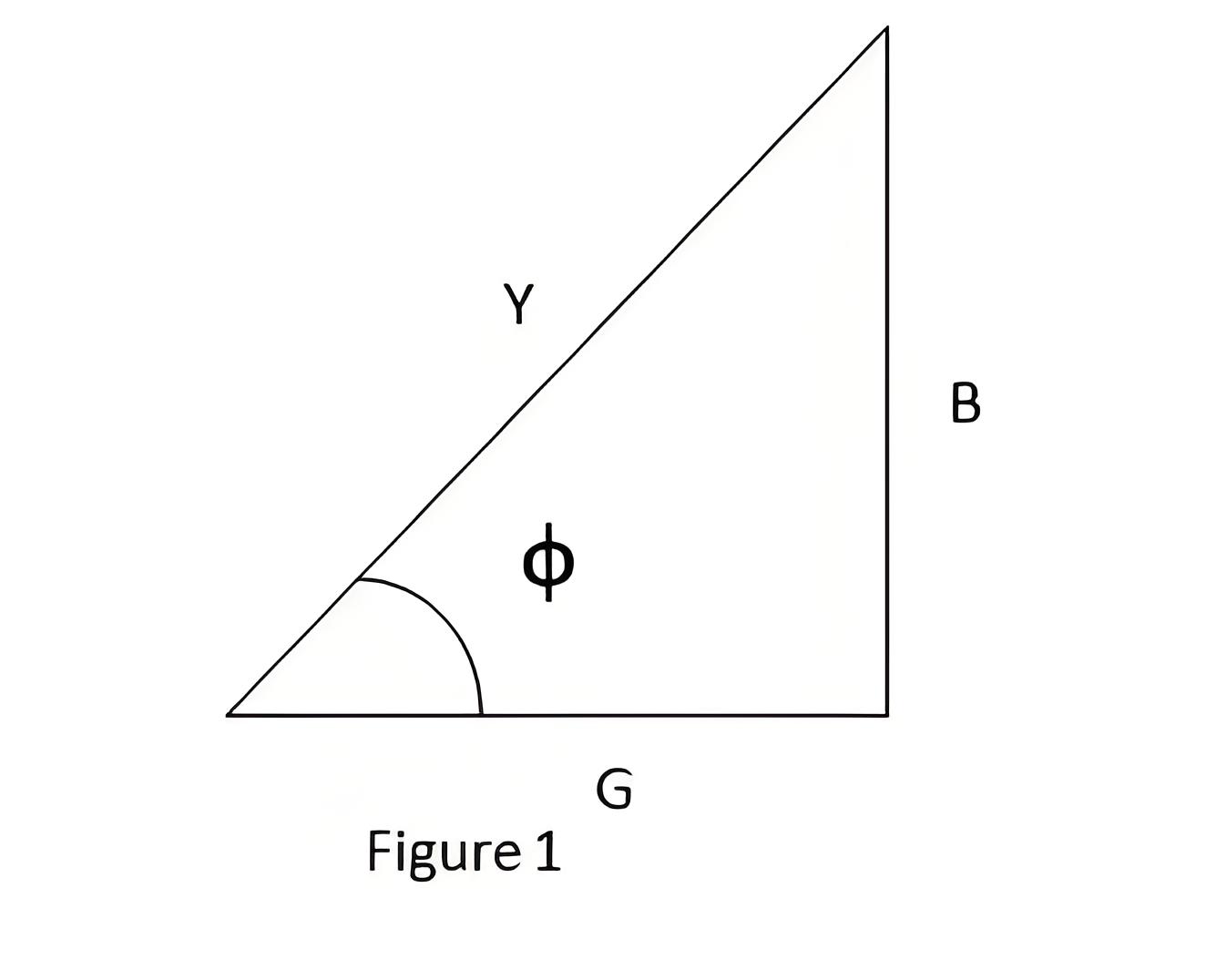
From admittance triangle,
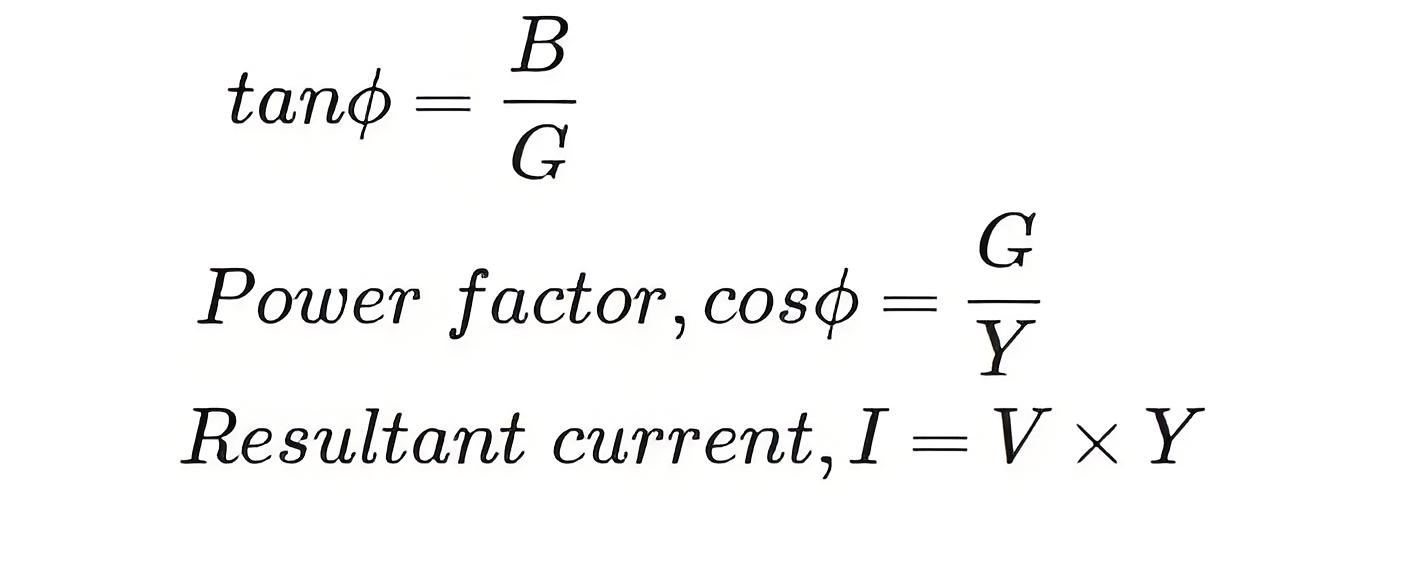
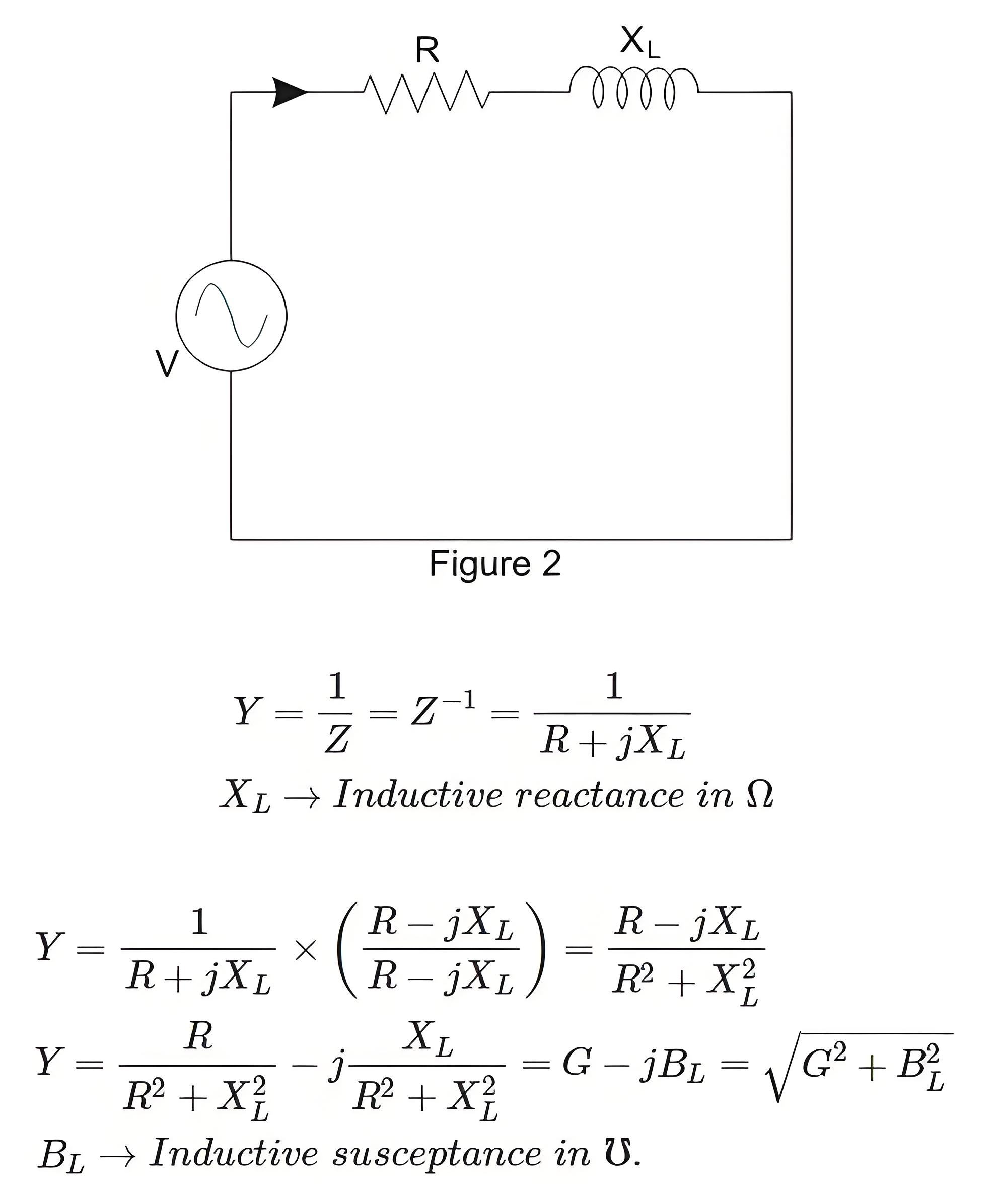
Admittance of a Series Circuit
When a circuit consist of Resistance and Inductance reactance in series is considered as shown below.
When the circuit consist of Resistance and Capacitive reactance in series is considered as shown below.
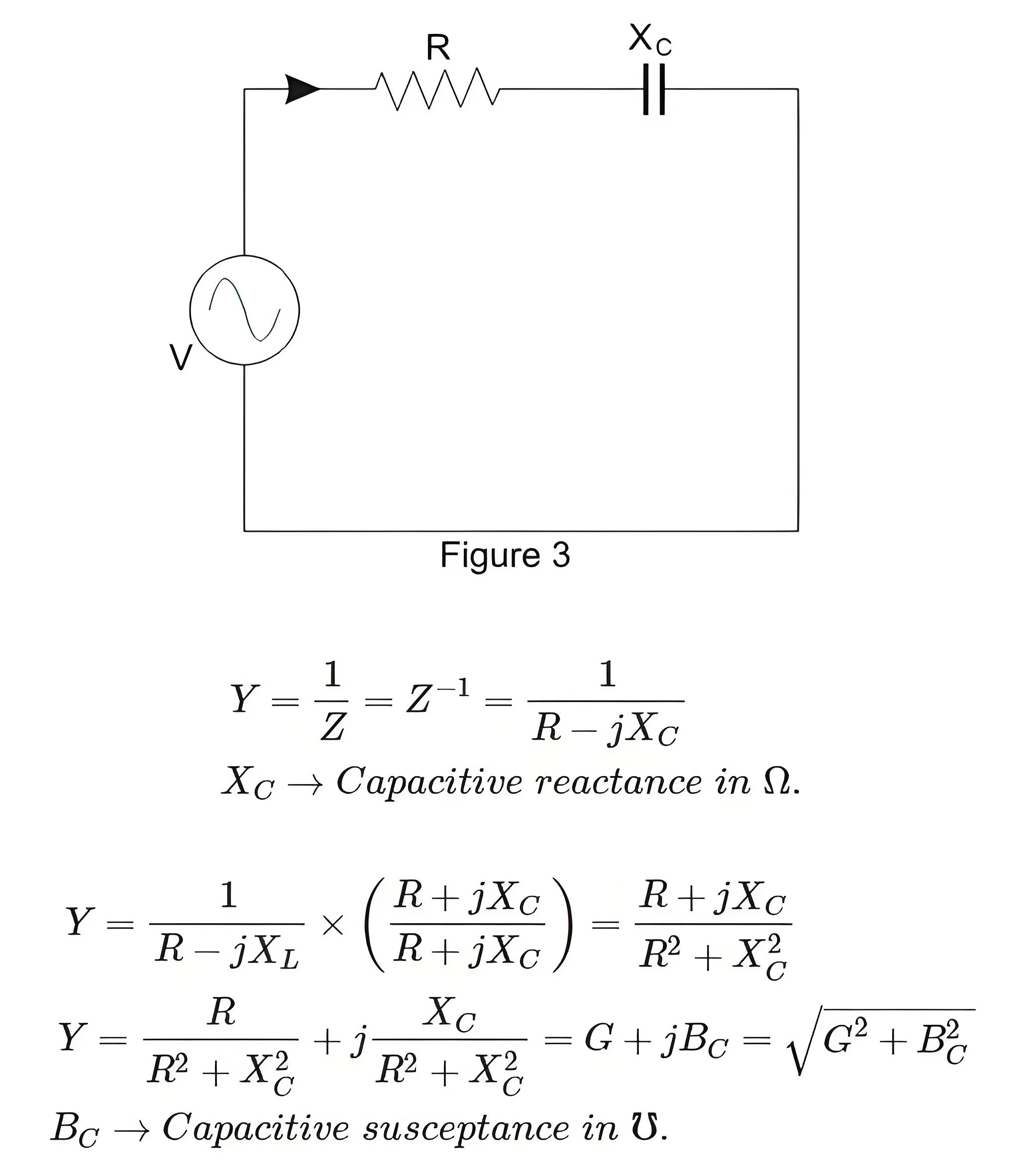
Series and Parallel Circuits
Understanding admittance in these configurations helps predict how circuits will behave under different setups.
Consider a parallel circuit with two branches, A and B. Branch A includes an inductive reactance (XL) and a resistance (R1), while B includes a capacitive reactance (XC) and another resistance (R2). A voltage (V) is applied across the circuit.
For Branch A
For Branch B
So, if the admittance of a circuit is known, then the total current and power factor can be obtained easily.
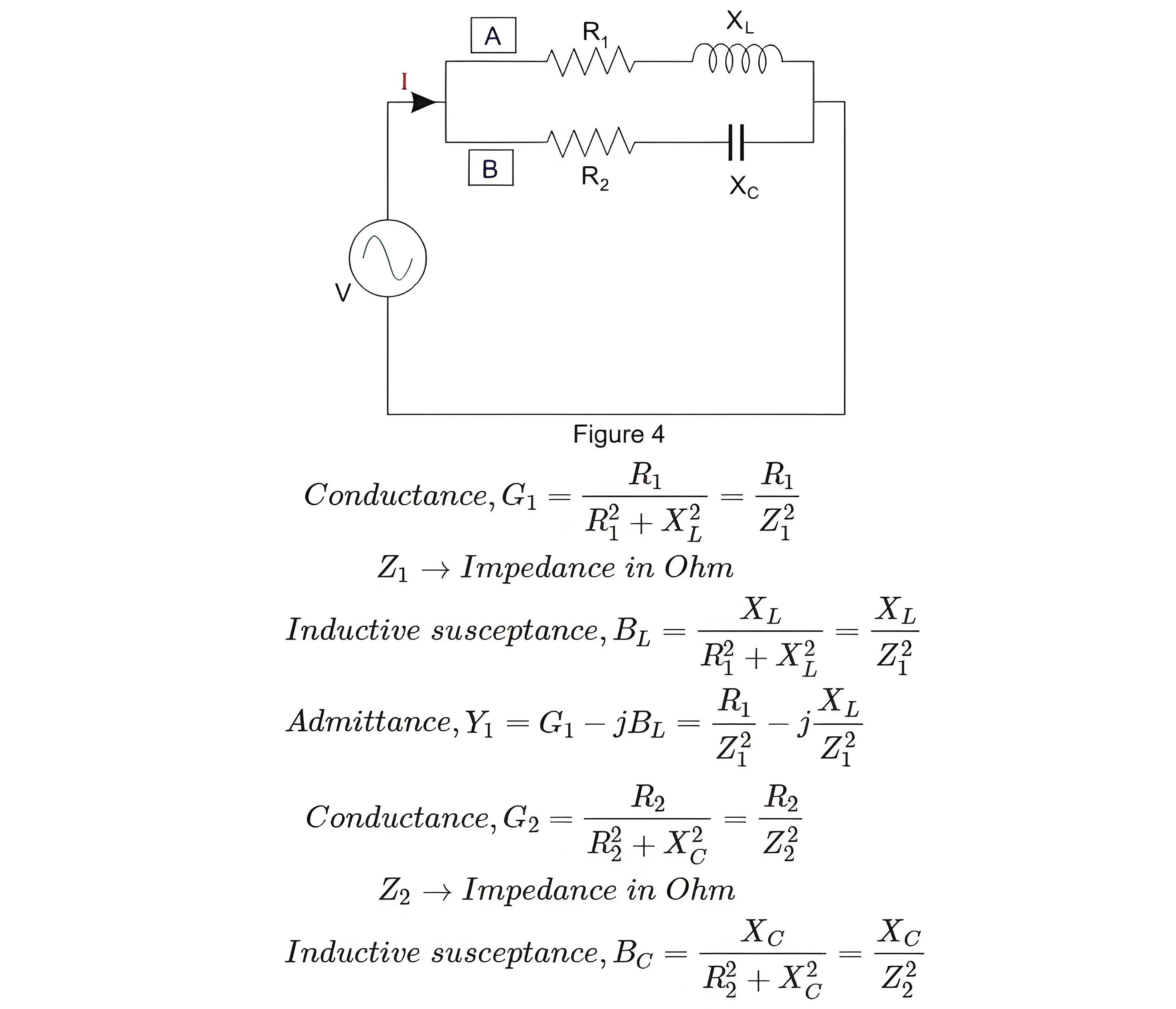
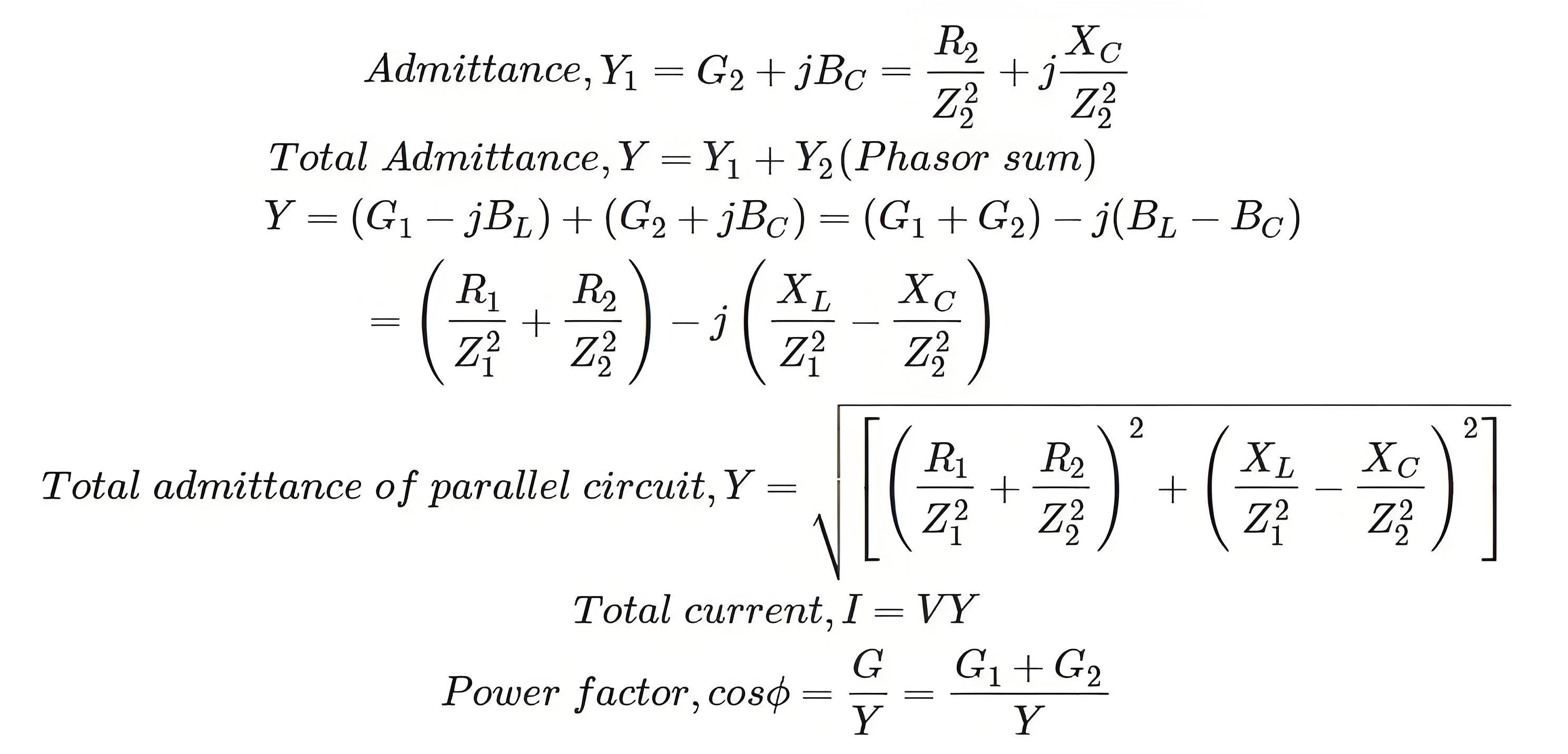
Practical Use
Knowing admittance allows engineers to calculate the necessary parameters like total current and the circuit’s power factor.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













