Space Charge: Definition, Examples, and Effects
A space charge is defined as a region of space where electric charges accumulate, either in free space or in a dielectric material. The electric charges can be either positive or negative, and they can be either mobile or immobile. The space charge can affect the electric field, the electric potential, and the current flow in the region.
Examples of Space Charge
Space charge can occur in various situations, such as:
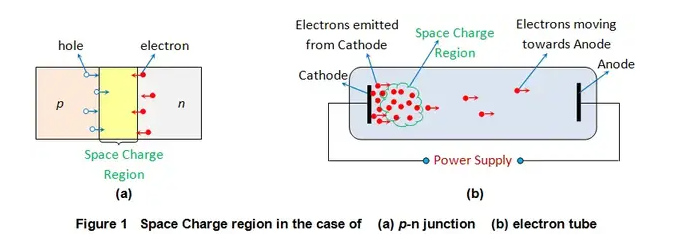
Semiconductor junctions: When a p-type semiconductor (which has excess holes) is brought in contact with an n-type semiconductor (which has excess electrons), the electrons and holes near the junction recombine, leaving behind immobile ions. This creates a space charge region that is depleted of mobile charge carriers and has an electric field that opposes further diffusion of charges. This region is also called the depletion layer or the depletion zone.
Electron tubes: When an electron tube (such as a vacuum tube or a thermionic converter) is supplied with power, electrons are emitted from the cathode (the negative electrode) and move toward the anode (the positive electrode). However, the electrons take some finite time to travel across the tube, and they can form a cloud of negative charges near the cathode. This creates a space charge region that repels the emitted electrons and reduces the current flow. This region is also called the cathode fall or the virtual cathode.
Space charge can have both positive and negative effects on various devices and applications, such as:
Thermionic converters: Thermionic converters are devices that convert heat into electricity by using thermionic emission, which is the emission of electrons from a hot metal surface. Space charge reduces the efficiency and power output of thermionic converters by creating an additional barrier for the emitted electrons. To overcome this barrier, higher temperatures or lower voltages are required, which increase the heat loss or decrease the voltage output.
Amplifiers: Amplifiers are devices that increase the amplitude of an input signal by using an electron tube or a transistor. Space charge can improve the performance of amplifiers by creating a negative voltage on some tubes, which is equivalent to providing a negative bias to them. This bias helps to control the amplification process and reduce distortion.
Shot noise: Shot noise is a type of noise that arises from the random fluctuations of electric current due to discrete charges. Space charge can reduce shot noise by affecting the movement of charges along their path. This reduces the number of charges that arrive randomly at a given point, thereby reducing their statistical variation, which is shot noise.
Conclusion
Space charge is a phenomenon that occurs when electric charges accumulate in a region of space, either in free space or in a dielectric material. It can have various causes, such as thermionic emission, semiconductor junctions, dielectric breakdown, or water trees. It can also have various effects, such as reducing thermionic conversion efficiency, improving amplifier performance, or reducing shot noise.
Source: Electrical4u
Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
Electrical4U is dedicated to the teaching and sharing of all things related to electrical and electronics engineering.