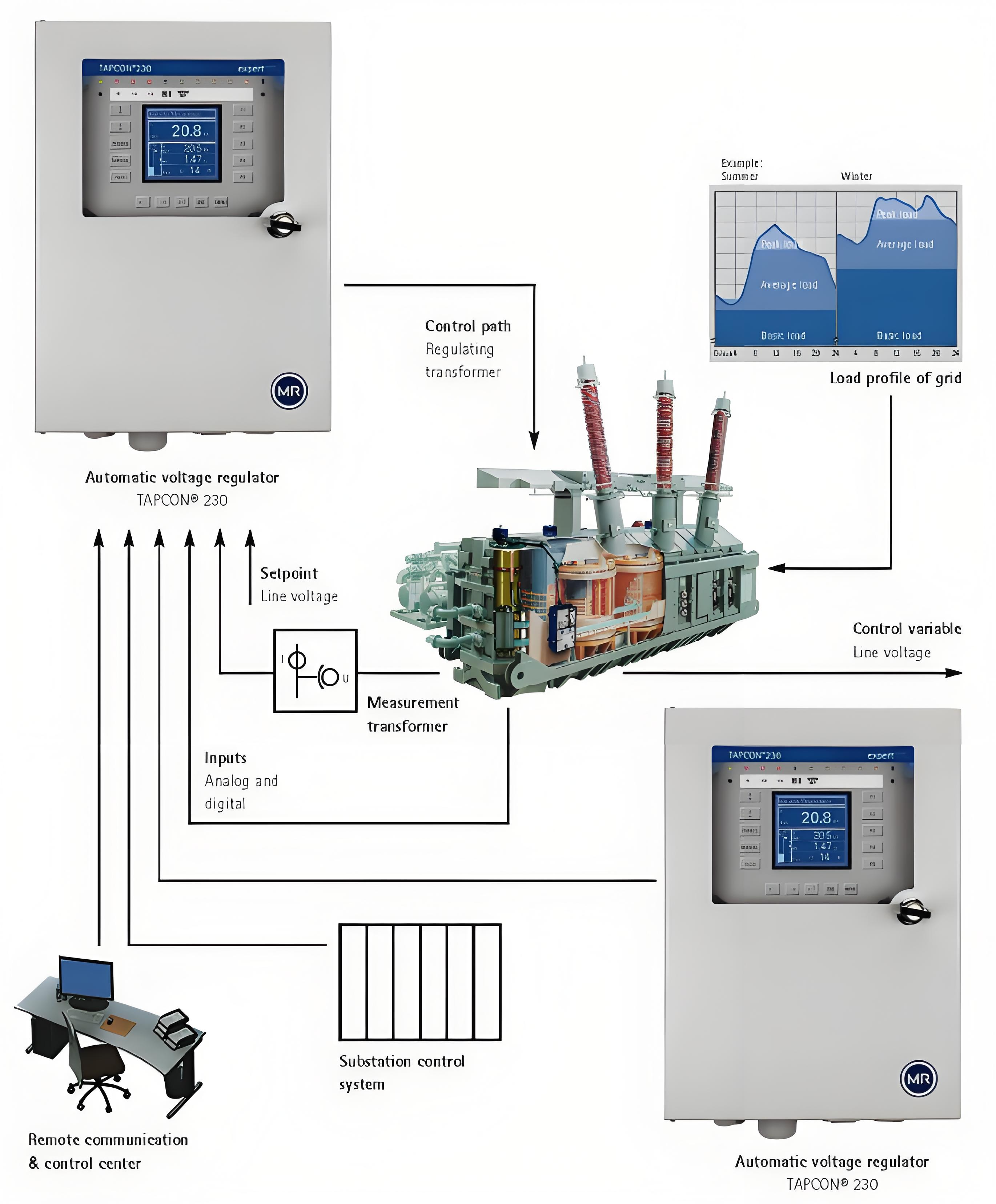
Voltage regulation and tapping arrangements also demand precise specification. This ensures that the transformer can adapt its output voltage in response to network fluctuations. On - load tap changers (OLTC) and off - load tap changers (DETC) serve to maintain voltage within predefined limits. To uphold voltage stability, the specification must distinctly detail the number of tapping steps, the voltage adjustment range, and the type of tap changer.
When formulating transformer specifications, environmental and site - specific conditions necessitate meticulous consideration.
Elements like installation altitude, ambient temperature, humidity, pollution levels, and seismic activity have a direct bearing on transformer design and operational performance. For applications in extreme conditions, transformers call for additional design deliberations, including high - altitude insulation adjustments, the use of corrosion - resistant materials, or the implementation of advanced cooling systems.
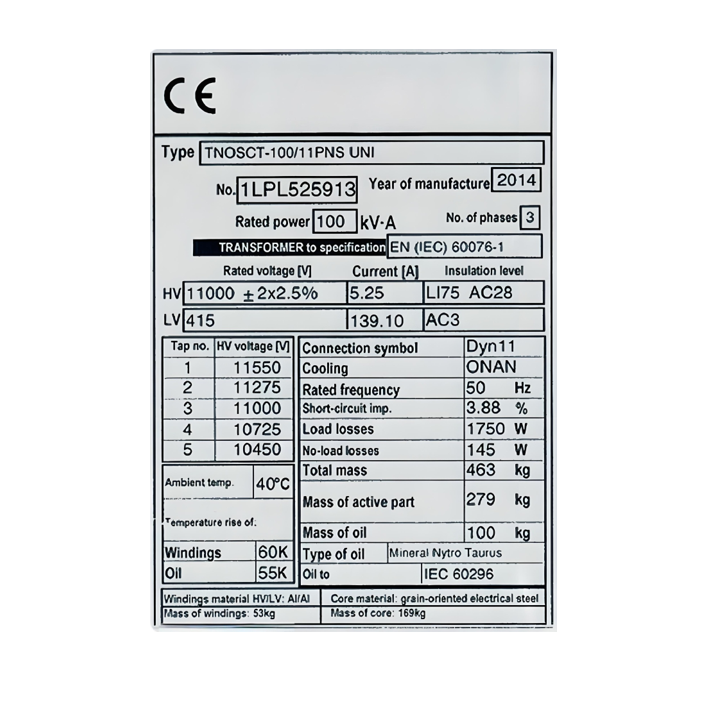
The transformer specification ought to incorporate details of the rating plate and nameplate as well. These offer vital information for identification, operation, and maintenance purposes. The rating plate should encompass particulars such as the transformer type, rated power, primary and secondary voltages, connection symbol, cooling method, insulation class, impedance, and manufacturer - related information.
In the formulation of transformer specifications, aspects concerning transport, installation, and maintenance must not be disregarded. Transformers, being large and heavy - duty equipment, demand specialized handling, transportation, and installation protocols. The specification should clearly stipulate weight limits, lifting arrangements, and storage conditions.
Moreover, it is essential to outline guidelines for preventive maintenance, oil analysis, and periodic inspections. This ensures the long - term reliability of the transformer.