25 Top Power Plant Electrical Interview Questions
1). What are the energy sources for electric power generation?
Energy sources fall into two categories:
Non-conventional primary sources, such as geothermal energy, solar energy, ocean tides & waves, wind, and so on.
Conventional secondary sources include fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, as well as hydraulic and nuclear energy.
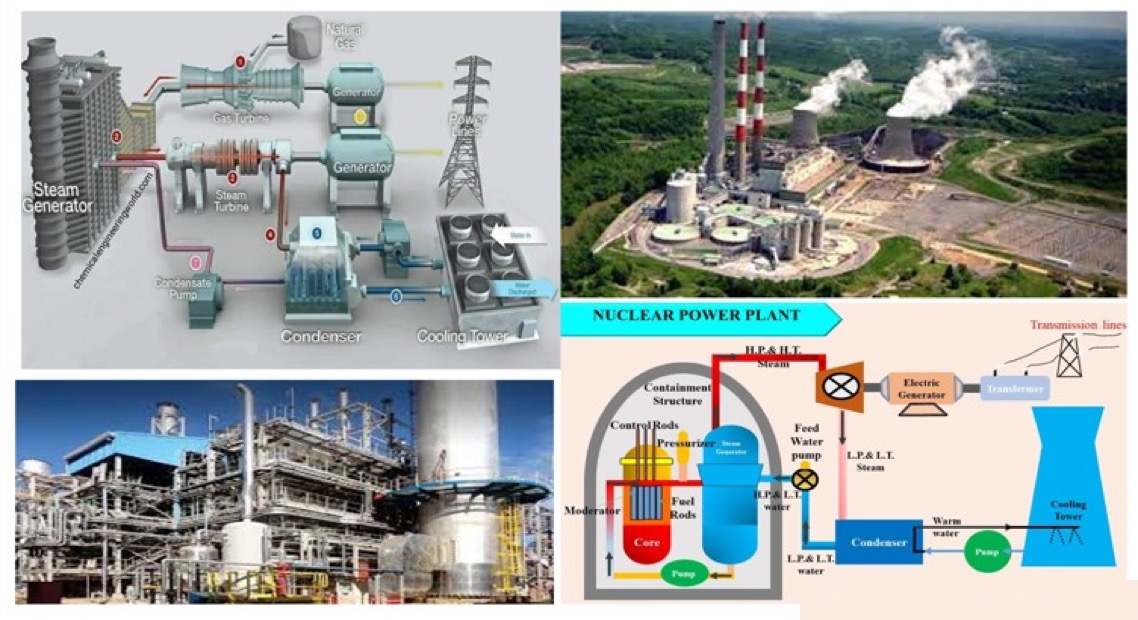
2). What are the different types of power stations?
Thermal power station
Hydroelectric power station
Diesel power station
Nuclear power station
Gas-turbine power station
Magnetohydrodynamic power station.
3). What is the working principle of a thermal power plant?
A thermal power plant burns fuel (which include coal or gas) to generate heat, which is then converted into steam. The steam propels a turbine, which in turn powers a generator to generate electricity.
4). Name the 4 major circuits in a steam power plant.
Coal & ash circuit
Air & flue gas circuit
Feed water & steam circuit
Cooling water circuit.
5). What is known as prime mover?
The equipment that drives the electric generator or provides mechanical power to the generator is known as a prime mover.
6). What are the components of the air and flue gas circuit?
The air and flue gas circuit includes
Forced draught fan,
Air pre-heater,
Boiler,
Furnace,
Super heater,
Economizer,
Dust collector,
Induced draught fan, and
Chimney.
7). What is the feed water & steam flow circuit in steam power?
The feed water & steam flow circuit consists of a
Feed pump,
Economizer
Boiler drum super heater,
Turbine, and
Condenser.
8). Which nuclear fuel is used?
Uranium,
Plutonium, and
Thorium
are among the most regularly utilized fuels.
It could be U-235, U-238, Pu-236, or Th-232.
Uranium is widely selected due to its high melting point.
9). How can a grid-connected solar power system work?
Solar panels in a grid-connected solar power system convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. Inverters convert the DC electricity into AC power, which is then delivered into the electrical grid. The electricity generated may be utilized directly by the consumer (or) fed into the grid.
10). Explain the principle of load dispatch in power systems.
Load dispatching is the process of optimizing and controlling power generation & transmission to fulfill electricity demand. It comprises assessments on unit commitment, economic dispatch, & load frequency control.
11). How is a supercritical power plant different from a subcritical power plant?
Supercritical power plants run at higher pressures & temperatures, resulting in greater efficiency than subcritical power plants. They use improved steam characteristics to maximize thermal efficiency.
12). What are the primary performance parameters for a power plant?
Heat rate,
Efficiency,
Availability,
Capacity factor, and
Pollution levels
are key performance indicators for power plants.
13). How do hydroelectric power plants operate?
A hydroelectric power plant uses the potential energy of water contained in a dam. The water flows through turbines, which turn generators to generate power.
14). What are the advantages & disadvantages when utilizing coal as a fuel source in power plants?
Advantages: Coal’s abundance & low cost make it a desirable fuel source.
Disadvantages: Limitations include environmental pollution, emissions, & the requirement for improved emission control systems.
15). Describe the concept of synchronized generators and its usefulness in power systems.
A synchronized generator is one that runs in parallel with other generators in a power system. It is essential for ensuring grid stability, load sharing, & a consistent power supply.
16). What are the primary components of a solar photovoltaic (PV) system.
A solar PV system includes
Solar panels,
Inverters,
Mounting structure,
Electrical wiring, &
Monitoring system.
17). How are gas turbine power plants operated?
A gas turbine power plant compresses air, mixes it with fuel, and burns it in a combustion chamber. The hot gases flow through a turbine, causing a generator to generate energy.
18). Describe the combined cycle power plant concept.
A combined cycle power plant uses both the Brayton cycle (gas turbine) & the Rankine cycle (steam turbine) to increase overall efficiency. Waste heat from gas turbine is utilized to generate steam, which powers a steam turbine.
19). What are the advantages & disadvantages of utilizing wind energy?
Advantages: Wind energy has the advantage of being renewable and emitting minimal levels of greenhouse gases.
Disadvantages: The disadvantages include inconsistent generation, visual impact, & the necessity for appropriate wind resources.
20). How do nuclear power plants create electricity?
Nuclear fission generates heat in a nuclear power plant, converting water into steam. The steam drives a turbine, which generates energy. Nuclear reactors burn uranium (or) plutonium as fuel.
21). What type of power generation technology are employed in cogeneration systems?
Cogeneration systems generate electricity and useable thermal energy concurrently by utilizing technologies including
Waste heat recovery,
Trigeneration, and
Combined heat & power (CHP).
22). Explain the principle of load flow analysis in the power systems.
Load flow analysis is a computer method for determining the steady-state operating (operational state) conditions of the power system.
It computes
Voltage magnitudes,
Phase angles, and
Power flows in the network.
23). What are the advantages & disadvantages of implementing a distributed control system (DCS) in power plants?
Advantages: The advantages of distributed control system (DCS) include centralized control, increased automation, and greater monitoring capabilities.
Disadvantages: The disadvantages include a higher initial cost & the requirement for specialized personnel for maintenance.
24). How does a generator’s excitation system work?
A generator’s magnetic field is controlled by an excitation system, which enables the generator to generate energy. An exciter, an automated voltage regulator (AVR), and related control devices are usually included.
25). Describe the importance of the load frequency control concept.
Real-time power generation & load demand balance is maintained through the use of load frequency control. It supports
Consistent power supply,
Frequency control, and
Grid stability.
Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
Hobo is an electrical engineer with 10 years of work experience, mainly responsible for designing, developing and maintaining electrical systems and equipment.