What is a Thermal Relay?
What is a Thermal Relay?
Thermal relay definition
A thermal relay is defined as a device that uses unequal expansion rates of metals in a bimetallic strip to detect overcurrent conditions.
Working principle
Thermal relays work by heating a bimetallic strip, causing it to bend and close the normally open contact, which triggers the circuit breaker.
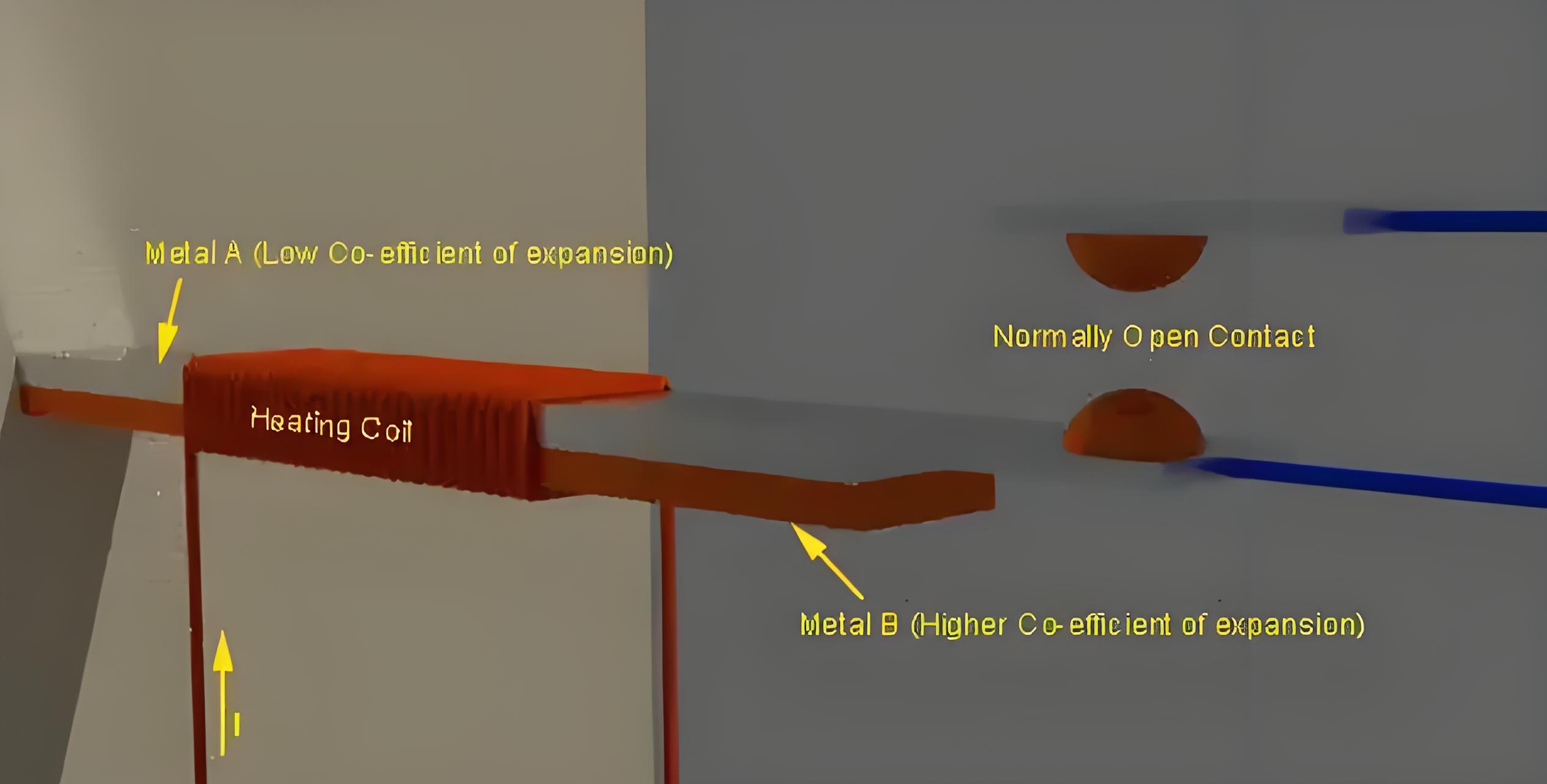
Construction of thermal relay
It consists of a bimetallic strip, metal with different expansion coefficients, a heating coil and contacts.
Technical parameter
Rated voltage
Rated current
Rated frequency
Set the current range
Delay function
The heating effect of the relay follows Joule's law, resulting in a delay in operation, allowing temporary overload without tripping.
Install
When the thermal relay is installed with other electrical appliances, it should be installed under the electrical appliances and more than 50mm away from other electrical appliances, so as not to be affected by the heating of other electrical appliances.
Routine maintenance
It takes a certain amount of time to reset the thermal relay after operation, the automatic reset time should be completed within 5 minutes, and the manual reset button can be pressed after 2 minutes.
After a short circuit fault occurs, check whether the thermal element and bimetal sheet are deformed
Thermal relays in use should be checked once a week
The thermal relay in use should be serviced once a year
Apply
Thermal relays are used for overload protection, especially in electric motors, where they prevent tripping due to short-term overload.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













