What is an Instantaneous Relay ?
What is an Instantaneous Relay ?
Instantaneous Relay Definition
An instantaneous relay is defined as a relay that operates with no intentional delay when the current exceeds a set threshold.
No Intentional Delay
Instantaneous relays activate without any added delay, making them very fast in operation.
Inherent Delays
These relays still have minor delays due to electrical and mechanical factors, but they are not intentionally introduced.
Types of Instantaneous Relays
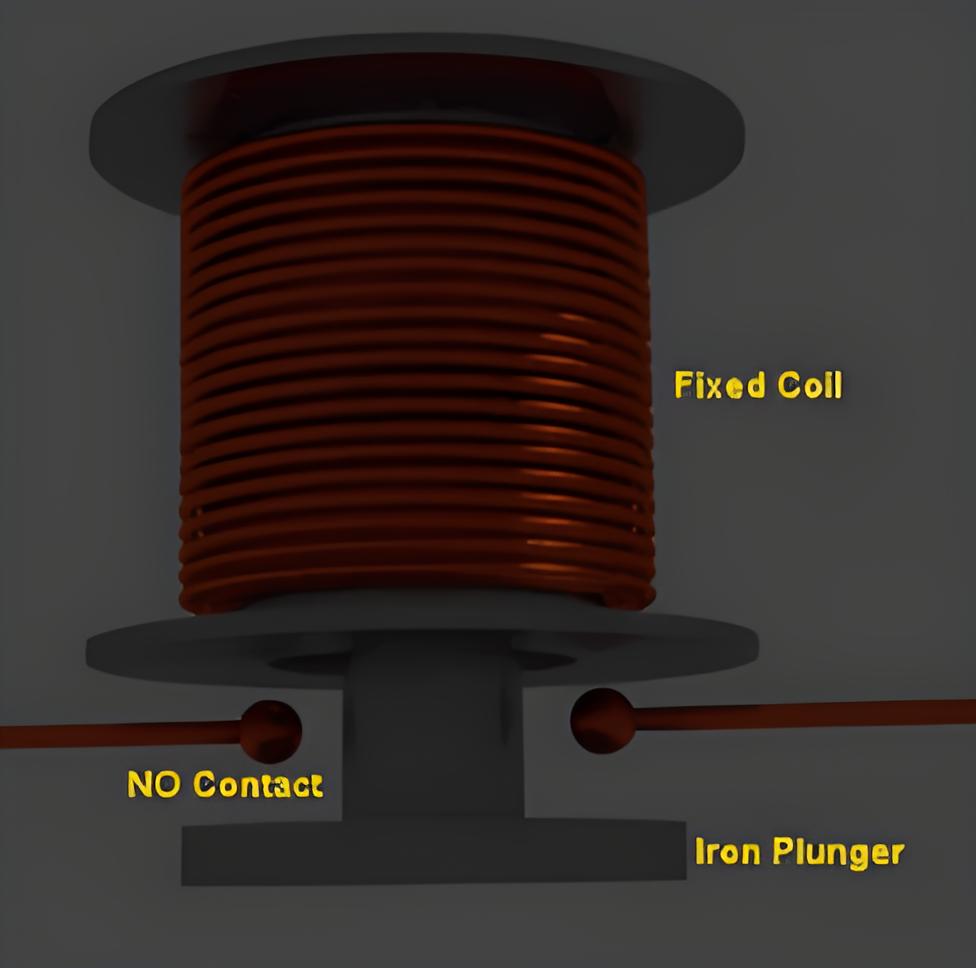
Examples include attracted armature relays, solenoid type relays, and balance beam relays.
Operation Mechanism
These relays rely on electromagnetic attraction to move a plunger or beam to close the relay contacts quickly.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













