Differential Protection of a Transformer
Differential Protection of a Transformer
Transformers are among the key components in power systems. As static, fully - enclosed, and typically oil - immersed devices, faults on them are relatively infrequent. However, even a rare fault can have severe consequences for a power transformer. Thus, safeguarding power transformers against potential faults is of utmost importance.
Faults on transformers are mainly categorized into two types: external faults and internal faults. External faults are swiftly cleared by the relay system outside the transformer to prevent any harm to the transformer from such faults. For internal faults in this type of transformer, a differential protection system is employed.
Differential protection schemes are predominantly utilized to guard against phase - to - phase and phase - to - earth faults. The differential protection for power transformers is grounded in the Merz - Prize circulating current principle. Such protection is generally applied to transformers with a rating exceeding 2 MVA.
Connection for Transformer Differential Protection
Power transformers are star - connected on one side and delta - connected on the other. The current transformers (CTs) on the star - connected side are delta - connected, while those on the delta - connected side are star - connected. The neutrals of both the current transformer star connection and the power transformer star connection are grounded.
A restraining coil is connected between the secondary windings of the current transformers. This restraining coil regulates the sensitivity of the system. The operating coil is positioned between the tapping point of the restraining coil and the star point of the current transformer secondary windings.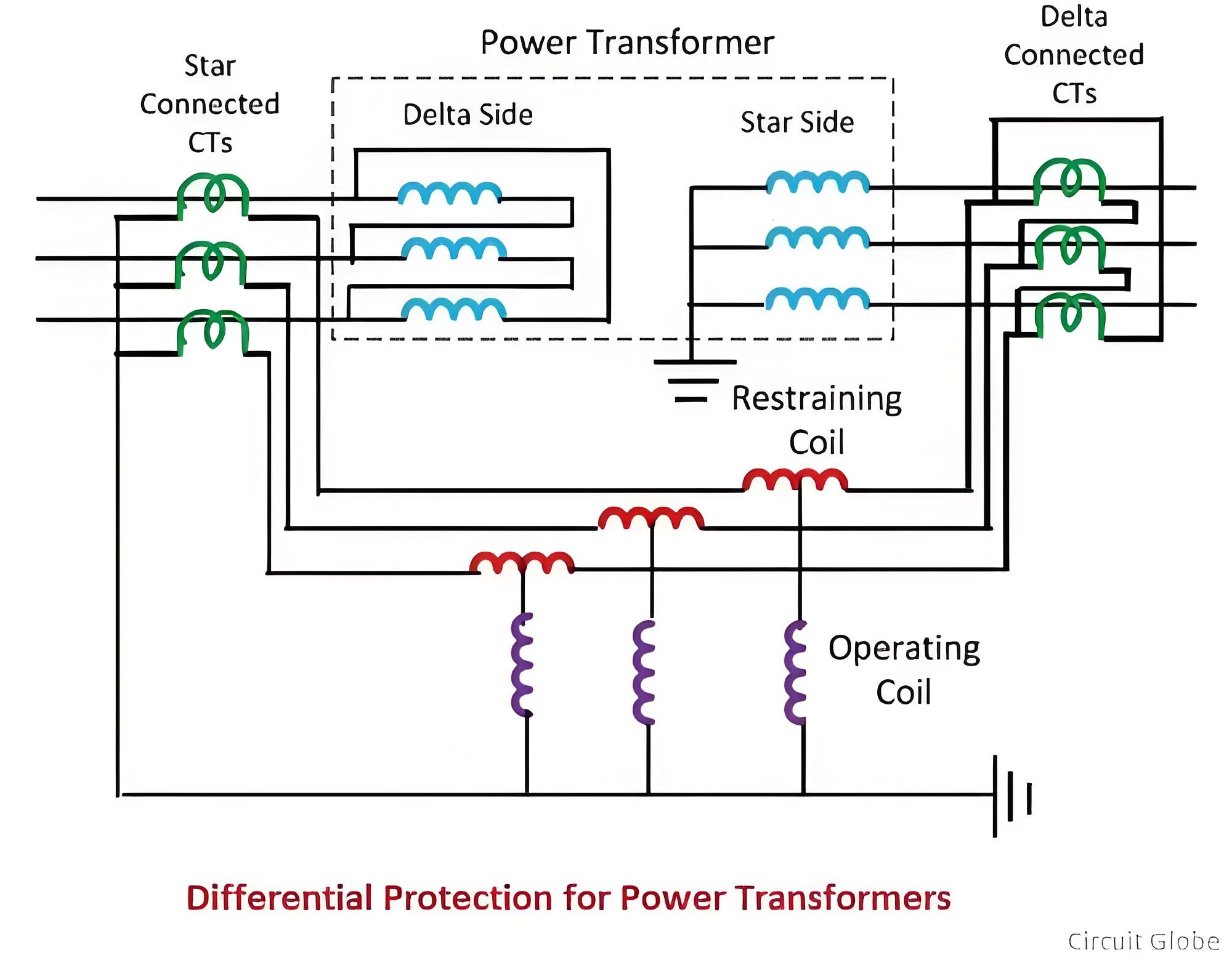
Operation of the Differential Protection System
Under normal circumstances, the operating coil carries no current since the currents on both sides of the power transformer are in balance. However, when an internal fault occurs within the power transformer windings, this balance is disrupted. Consequently, the operating coils of the differential relay carry a current that corresponds to the difference in current between the two sides of the transformer. As a result, the relay trips the main circuit breakers on both sides of the power transformer.
Issues with the Differential Protection System
When a transformer is energized, a transient inrush of magnetizing current flows through it. This current can be as much as 10 times the full - load current and decays over time. This magnetizing current flows in the primary winding of the power transformer, causing a discrepancy in the output of the current transformers. This, in turn, can cause the differential protection of the transformer to operate incorrectly.
To address this issue, a kick fuse is placed across the relay coil. These fuses are of the time - limit type with an inverse characteristic and do not operate during the brief duration of the inrush surge. When a fault occurs, the fuses blow, allowing the fault current to flow through the relay coils and activate the protection system. This problem can also be mitigated by using a relay with an inverse and definite minimum characteristic instead of an instantaneous - type relay.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













