What is a Suspension Insulator?
Suspension insulators serve to isolate line conductors and provide electrical support for them. They are composed of multiple porcelain insulator units that are interconnected by metal links, forming a flexible string. The conductor is attached to the bottom of this string. A diagram of the suspension insulator is presented as follows.
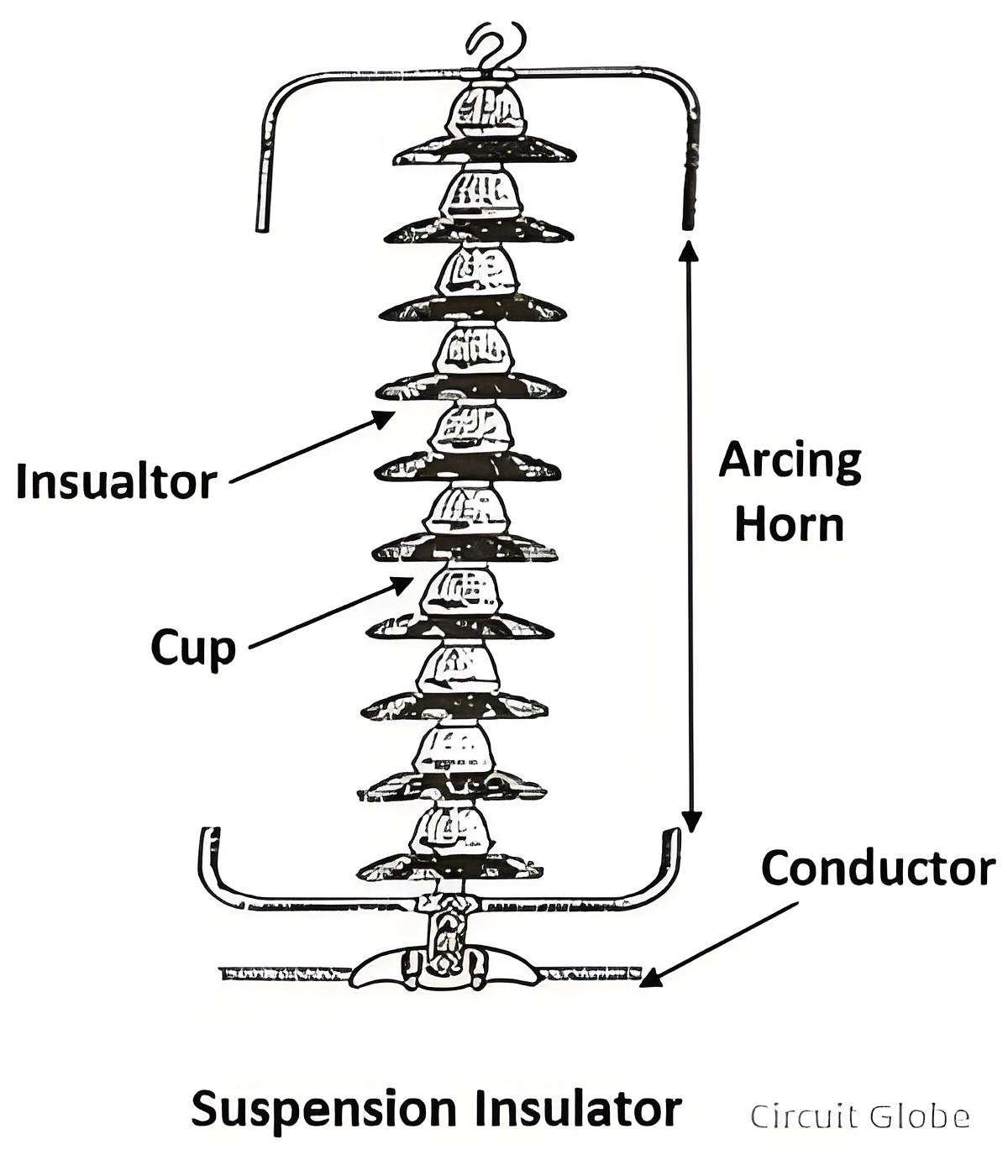
Suspension type insulators offer several benefits, as detailed below:
- Voltage Adaptability: Each unit can withstand approximately 11 kV of voltage. Thus, based on the overall line voltage, the appropriate number of insulator discs can be connected in series within the string. This modular approach allows for easy customization to different voltage requirements.
- Maintenance Ease: In the event that one unit within the string gets damaged, it can be replaced individually with a new one. There is no need to replace the entire string, which significantly reduces maintenance costs and downtime.
- Mechanical Flexibility: The insulator string is designed to be able to swing freely in any direction. This provides a high degree of flexibility to the transmission line, allowing it to better adapt to environmental factors such as wind and mechanical vibrations.
- Lightning Protection: Since the conductors are positioned beneath the suspension insulators, they receive partial protection from lightning strikes. This helps in reducing the risk of damage to the conductors and maintaining the integrity of the power transmission system.
Suspension insulators are primarily categorized into two main types:
- Cap and Pin Type
- Hewlett or Interlink Type
The following sections provide a detailed explanation of the cap - and - pin type and Hewlett (Interlink) type insulators.
In a cap - and - pin type insulator, a galvanized cast iron or forged steel cap is connected to a galvanized forged - steel pin, with porcelain serving as the insulating material. The individual units are joined together using either ball - and - socket or clevis - pin connections. These connection methods ensure a secure yet flexible link between the units, enabling the insulator string to function effectively under various mechanical stresses.
The interlink type insulator unit features porcelain with two curved channels that are oriented at right angles to each other. U - shaped, leveled, and covered steel links are passed through these channels, and they are used to connect the units.
One of the significant advantages of the Interlink type insulators is their superior mechanical strength compared to the cap - and - pin type units. In the event that the porcelain between the links breaks, the metallic link remains in place and continues to support the power line. As a result, the electrical supply is not interrupted, enhancing the reliability of the power transmission system.
However, the Hewlett (Interlink) type insulator has a drawback. The porcelain between the links is highly stressed electrically. Consequently, its puncture stress is lower compared to other insulator types. This means that it is more vulnerable to electrical breakdown under certain high - voltage conditions, which needs to be carefully considered during its installation and use in power transmission systems.














