What is a Transducer ?
What is a Transducer ?
Transducer Definition
A transducer is a device that converts physical quantities into proportional electrical signals, which can be used for further control or display.
Types of Transducers
Types of Transducer based on Quantity to be Measured
Temperature transducers (e.g. a thermocouple)
Pressure transducers (e.g. a diaphragm)
Displacement transducers (e.g. LVDT)
Oscillator transducer
Flow transducers
Inductive Transducer
Types of Transducer based on the Principle of Operation
Photovoltaic (e.g. a solar cell)
Piezoelectric transducer
Chemical
Mutual induction
Electromagnetic
Hall effect
Photoconductors
Types of Transducer based on Whether an External Power Source is required or not
Active Transducers
These transducers do not need external power and work by directly converting physical inputs into electrical signals.
Passive Transducers
Passive transducers require external power and typically convert physical changes into signals via resistance, capacitance, or other electrical changes.
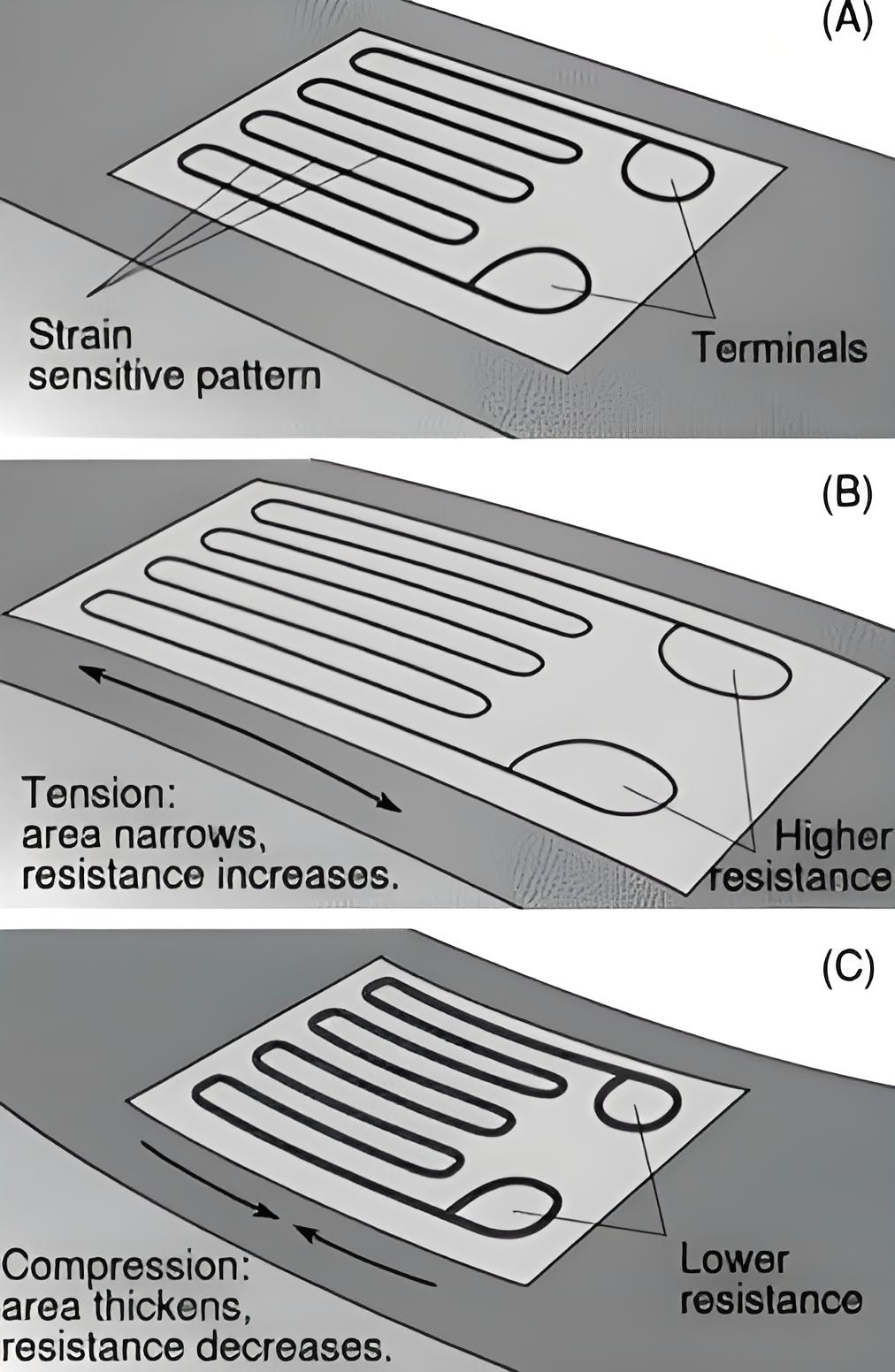
Application in Instrumentation
Transducers are crucial in instrumentation systems, which are central to controlling industrial processes by measuring various variables.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













