What is Megger ?
What is Megger ?
Megger Definition
A megger is defined as a device used to measure the insulation resistance of electrical components and systems, crucial for ensuring operational safety and functionality.
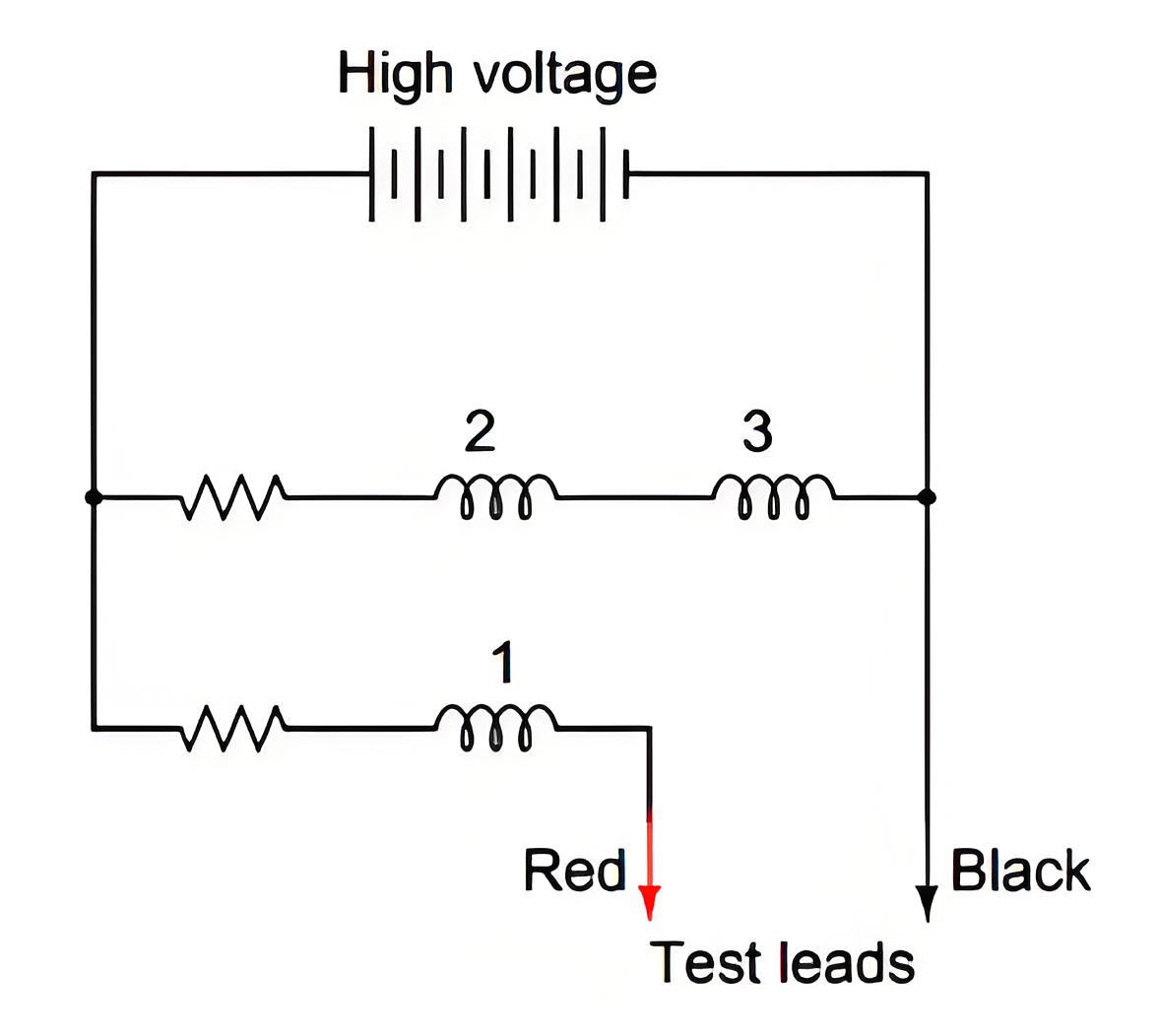
Working Principle
Meggers generate a testing voltage (either via a hand-cranked generator or battery) that creates a torque proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to current, helping measure the electrical resistance.
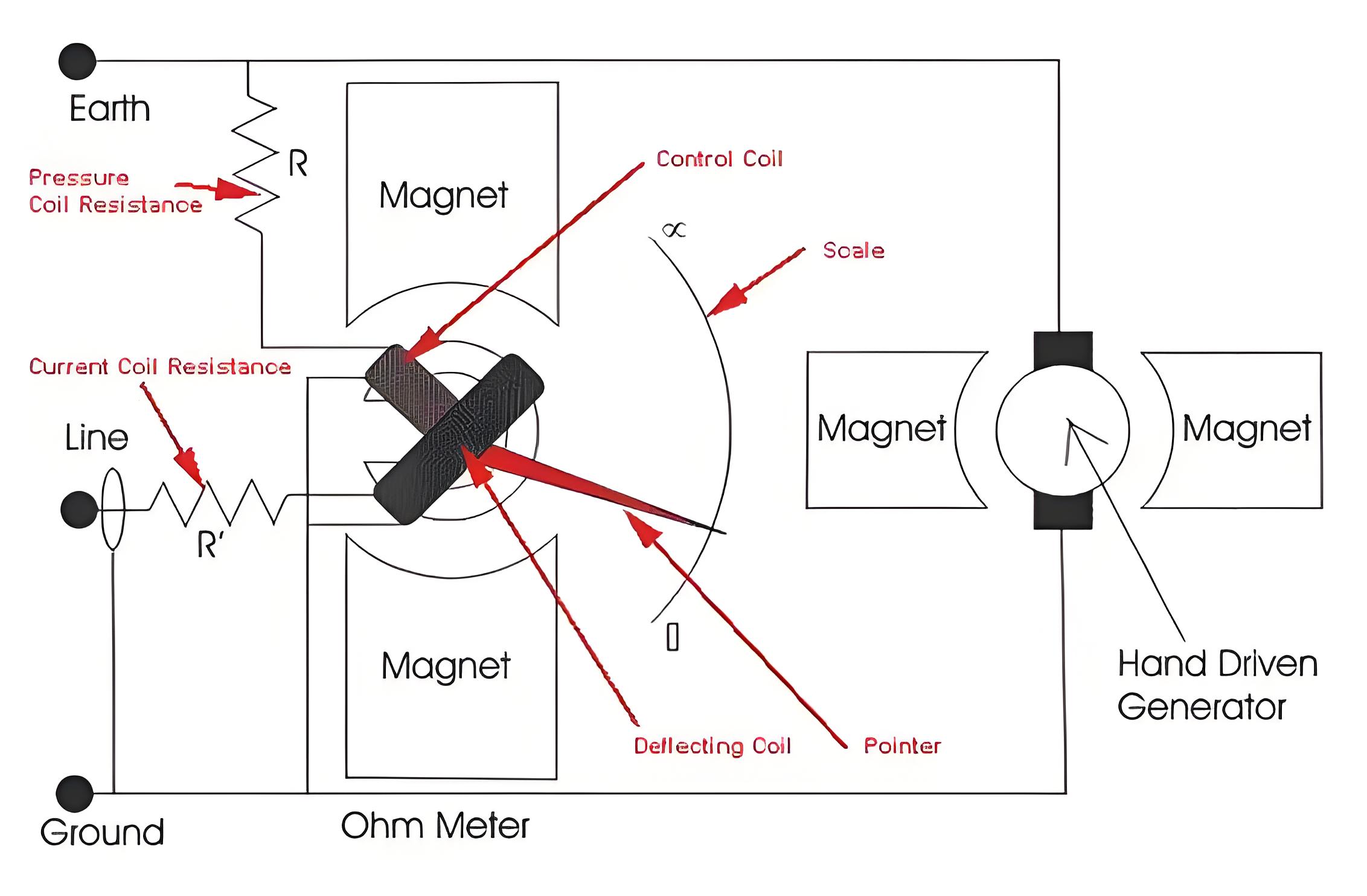
Types of Meggers
Electronic
Advantages
Level of accuracy is very high.
IR value is digital type, easy to read.
One person can operate very easily.
Works perfectly even at very congested space.
Very handy and safe to use.
Disadvantages
Require an external source of energy to energies i.e. Dry cell.
Costlier in market.
Manual
Advantages
Still keeps important in such high-tech world as it’s an oldest method for IR value determination.
No external source required to operate.
Cheaper available in market.
Disadvantages
At least 2 person required to operate i.e. one for rotation of crank other to connect megger with electrical system to be tested.
Accuracy is not up to the level as it’s varies with rotation of crank.
Require very stable placement for operation which is a little hard to find at working sites.
Unstable placement of tester may impact the result of tester.
Provides an analog display result.
Require very high care and safety during use of the same.
Uses of Megger
Meggers are essential for testing the electrical insulation level of various devices, helping detect potential failures due to electrical leakage or insulation breakdown.
Historical Context
First used in 1889 and becoming widely popular in the 1920s, Meggers have evolved significantly in design and functionality while maintaining their fundamental purpose.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













