Temperature Transducer
Definition: A temperature transducer is an electrical device that converts thermal energy into physical quantities such as displacement, pressure, or an electrical signal. Its primary function is to enable the automatic measurement of temperature. The fundamental principle underlying a temperature transducer is to detect heat and then convert this information into a readable format for transmission.
Characteristics of the Temperature Transducer
- The input is invariably a thermal quantity.
- Transducers typically convert the thermal quantity into an alternating quantity.
- They are used for measuring the temperature and heat flow within devices.
Sensing Element
The sensing element employed in a temperature transducer must possess the property of having its characteristics change in response to temperature variations. For instance, in a resistance thermometer, platinum metal serves as the sensing element. Key requirements for the sensing element are as follows:
- The temperature - sensing element converts temperature into heat.
- There should be a significant change in resistance with respect to temperature.
- The sensing element must have high resistivity.
Types of Temperature Transducers
Temperature transducers are mainly classified into two broad types:
Contact Temperature Sensor Devices
In this type of transducer, the sensing element is directly connected to the heat source. Heat transfer occurs through the phenomenon of conduction, which is the process by which heat is transferred from one substance to another without the movement of the substances themselves.
Non - contact Type Temperature Sensor Devices
Here, the sensing element does not come into direct contact with the heat source. Instead, they rely on the convection phenomenon for heat transfer. Convection is the process in which heat is transferred by the
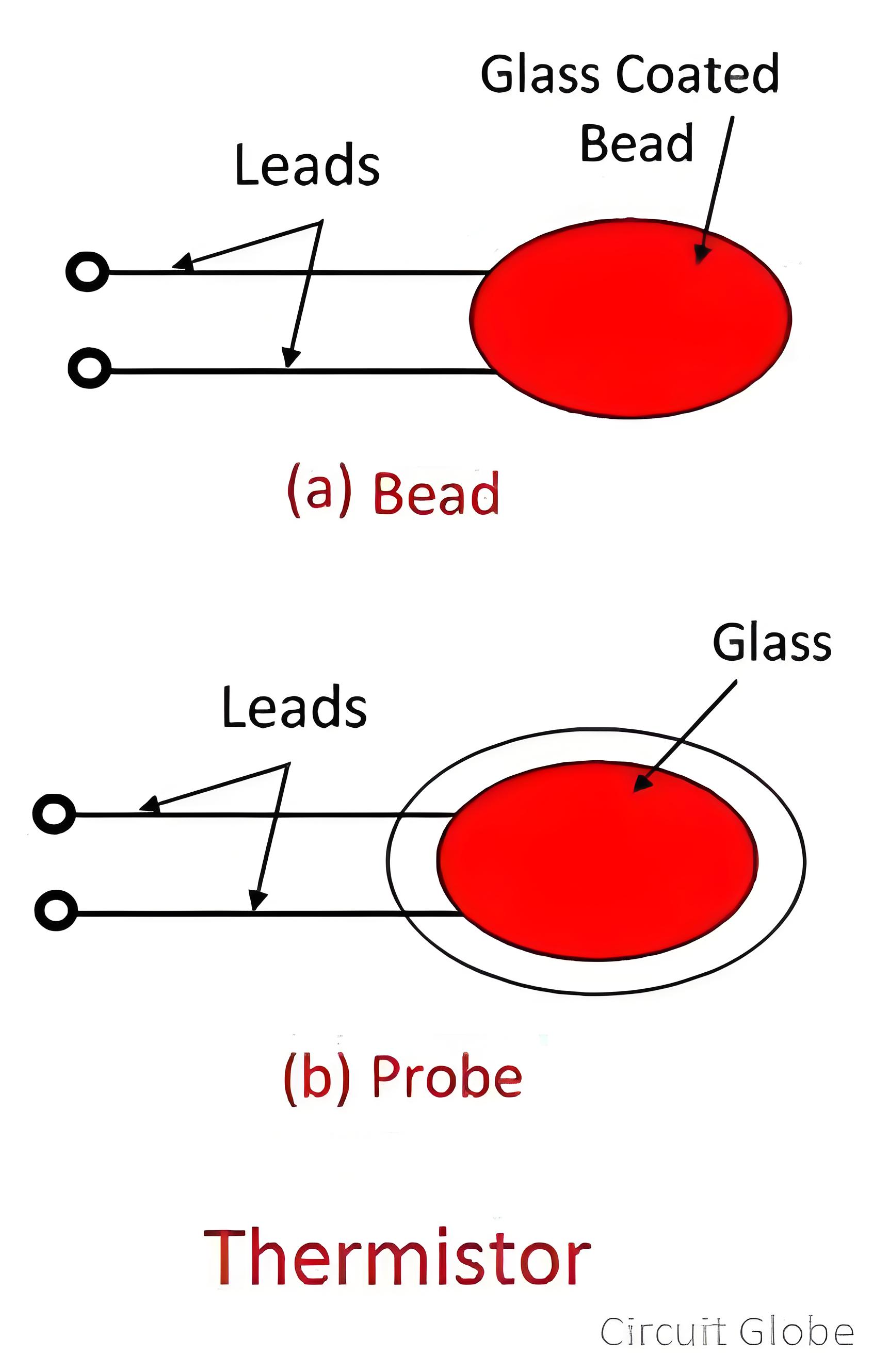
Resistance thermometers are classified into two main types:
- Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) Resistance Thermometers: These are primarily used for temperature sensing. As the name implies, the resistance of an NTC thermistor decreases as the temperature rises. This characteristic makes them highly effective in accurately detecting temperature changes.
- Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) Resistance Thermometers: PTC thermometers are mainly utilized for current control. When the temperature increases, the resistance of a PTC thermistor also increases. This property allows them to regulate the flow of electric current in various applications.
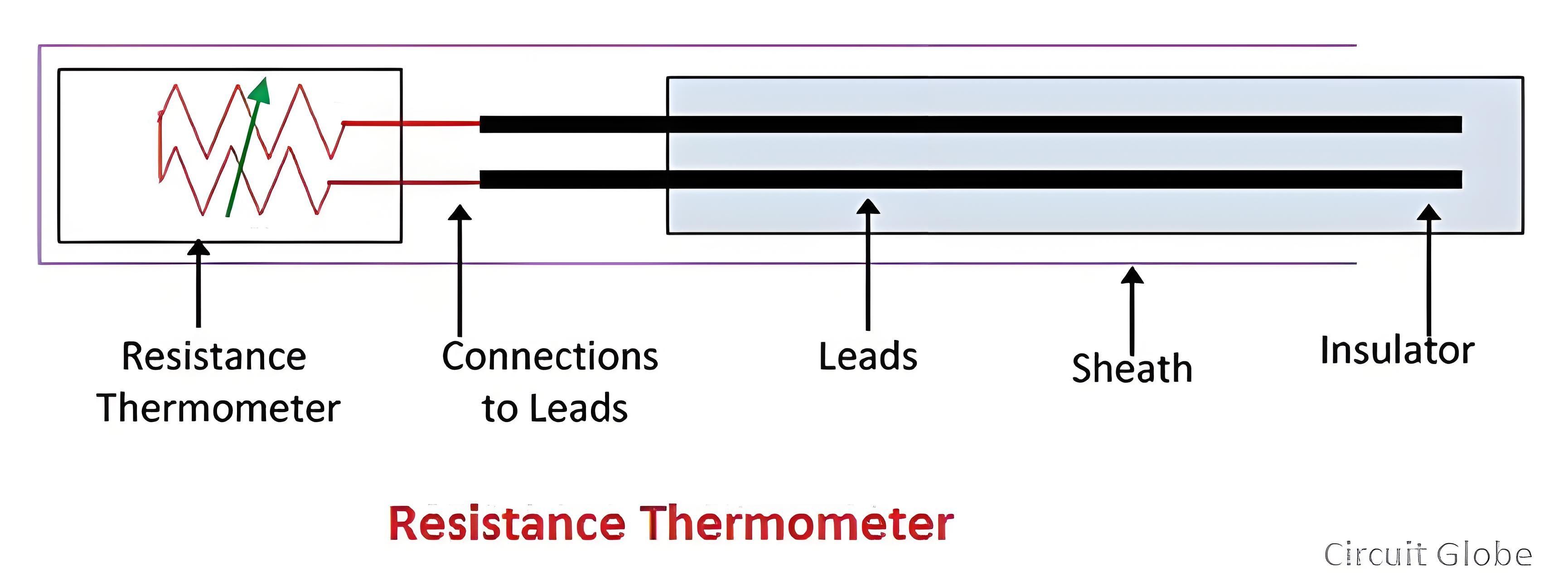
- Operating Principle of Resistance Thermometers: Metals exhibit a property where their resistance varies with temperature. Resistance thermometers leverage this principle for temperature measurement. Platinum is commonly employed as the sensing element in high - precision resistance thermometers. Due to platinum's stable and predictable resistance - temperature relationship, these thermometers can accurately measure the surrounding temperature. By measuring the resistance of the platinum element, the corresponding temperature can be precisely determined, making resistance thermometers a reliable choice for a wide range of temperature - monitoring applications.
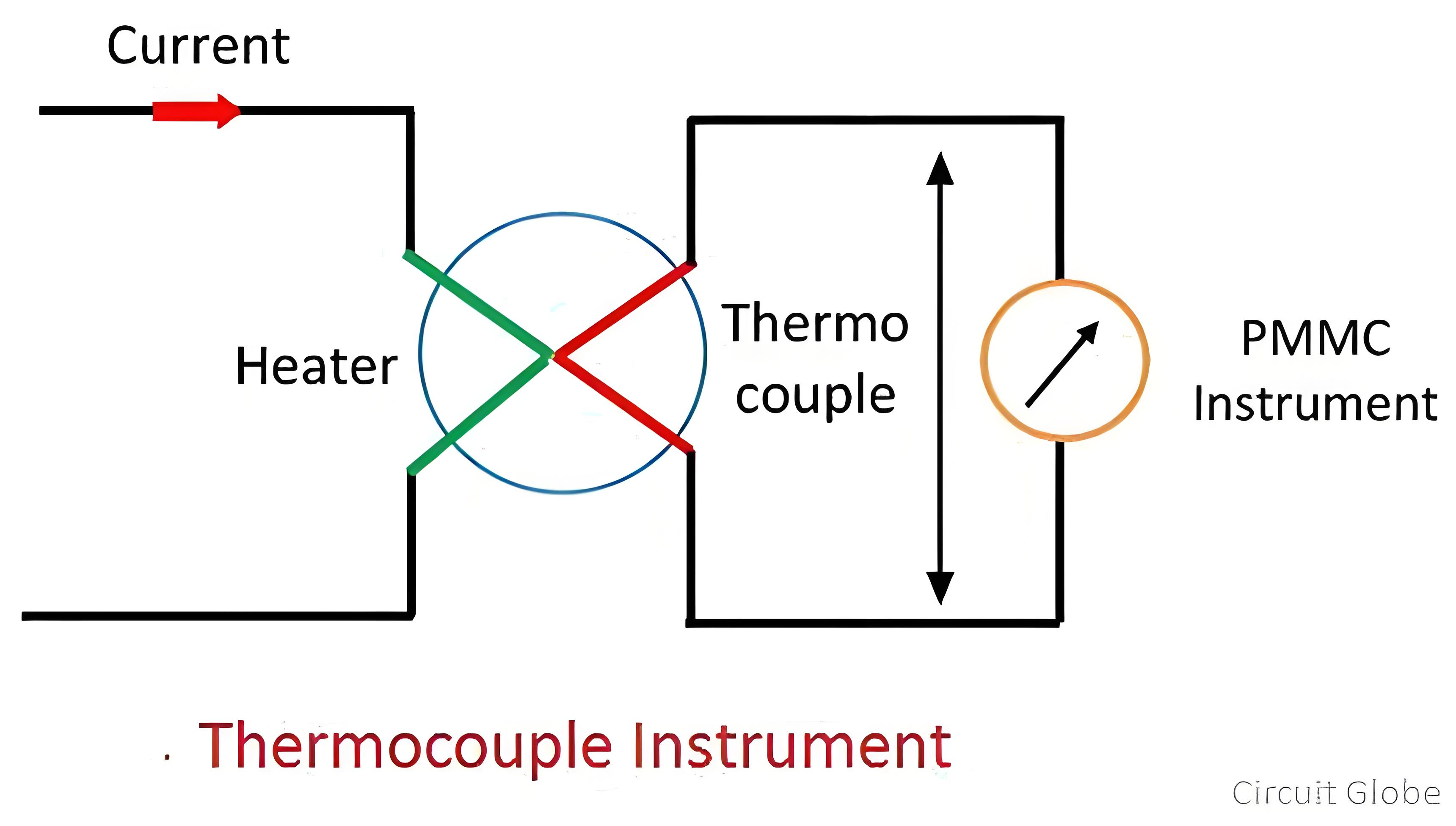
Thermocouples: A thermocouple is a device that converts temperature into electrical energy at the contact point. It operates based on the principle that different metals possess distinct temperature coefficients. When two dissimilar metals are joined together to form a junction, a phenomenon known as the Seebeck effect occurs. As the temperature at the junction changes, a voltage is induced across the junction. Significantly, this induced voltage is directly proportional to the temperature difference between the junction and a reference point. This linear relationship between the generated voltage and temperature allows thermocouples to be highly effective in accurately measuring temperature. They are widely used in various industrial, scientific, and domestic applications, where precise temperature monitoring and control are crucial, such as in furnaces, ovens, and industrial process control systems.
Integrated Circuit Temperature Transducer: An integrated circuit (IC) temperature transducer employs a combination of a temperature - sensing element and an electronic circuit to measure temperature. This type of transducer is characterized by its linear response, which simplifies the process of converting the sensed temperature into an electrical output that can be easily interpreted. However, one of the notable drawbacks of the integrated temperature transducer is its relatively narrow operating range. It typically functions within a temperature span of 0°C to 200°C. This limited range restricts its applicability in certain high - temperature or low - temperature environments where broader temperature coverage is required.
Despite this shortcoming, IC temperature transducers are widely used in numerous applications such as consumer electronics, where their compact size, linearity, and relatively simple interfacing make them a preferred choice for temperature monitoring within the specified temperature range.movement of the substance. Non - contact type transducers can be further sub - categorised, with one example being the thermistor. A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance changes with temperature. Its resistance is measured by passing a small, measured direct current, which in turn causes a voltage drop across the resistance.













