What is a Rectifier Ammeter?
Meters are generally designed to measure specific quantities. For example, the unit of current is the ampere, and the device used to measure current is called an ammeter. A rectifier ammeter employs a moving coil in conjunction with a rectifier to measure current. The primary function of the rectifier is to convert alternating current into direct current. This conversion is necessary because the moving - coil mechanism in the rectifier ammeter is typically designed to operate based on direct current. By converting the alternating current to direct current, the rectifier ammeter can accurately measure the magnitude of the current, providing a reliable reading of the electrical current flowing through a circuit.A rectifier ammeter is composed of four rectifier elements that are arranged in the form of a bridge, along with a moving - coil ammeter. The circuit diagram of these bridge - configured rectifier elements is presented in the figure below.
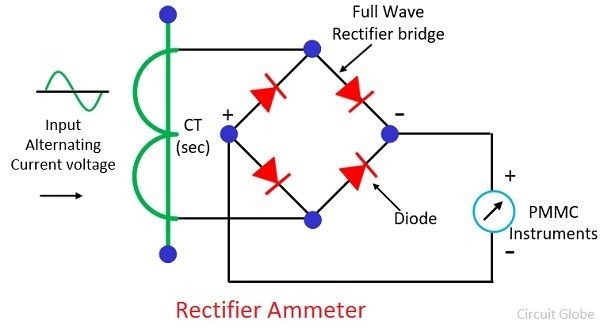
In a DC moving - coil instrument, a shunt is utilized to safeguard the moving - coil mechanism from heavy currents. However, in the case of a rectifier ammeter, using a shunt is not feasible. This is because the current passing through the moving - coil instrument varies continuously due to the resistance of the rectifier.
Advantages of the Rectifier Ammeter
The advantages of the rectifier ammeter are elaborated in detail as follows:
Wide Frequency Range: The frequency range of this instrument can be easily extended from 20Hz up to high audio frequencies.
Low Operating Current Requirement: The rectifier ammeter demands a very low operating current.
Uniform Scale: It features a uniform scale, which simplifies reading and interpretation.
Acceptable Accuracy: Under normal operating conditions, the accuracy of the instrument is within ±5%.
Factors Affecting the Performance of the Rectifier Ammeter
The following factors have an impact on the performance of the rectifier ammeter:
Waveform Influence: The waveform of the current and voltage significantly affects the operation of the rectifier instrument. Different waveforms can lead to inconsistent rectification and inaccurate current measurements.
Rectifier Resistance: The rectifier elements possess some inherent resistance. This resistance can distort the current flow through the instrument and thus impact its performance.
Temperature Sensitivity: Variations in temperature can also affect the working of the instrument. Temperature changes may alter the resistance of the rectifier elements and other components, leading to measurement errors.
Rectifier Capacitance: The rectifier has some capacitance associated with it, and this capacitance can influence the operation of the instrument. Capacitance can cause phase shifts and transient effects, which may affect the accuracy of current measurement.
AC vs. DC Sensitivity: The instrument has a relatively lower sensitivity for AC compared to DC. This is due to the rectification process, which can introduce losses and reduce the overall responsiveness to AC signals.
Small - Sized Transformer Usage: A small - sized transformer is used in the instrument because of its low burden. The low - burden characteristic of the transformer helps in maintaining the accuracy of the instrument while minimizing power consumption.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













