Basic Construction of Wind Turbine
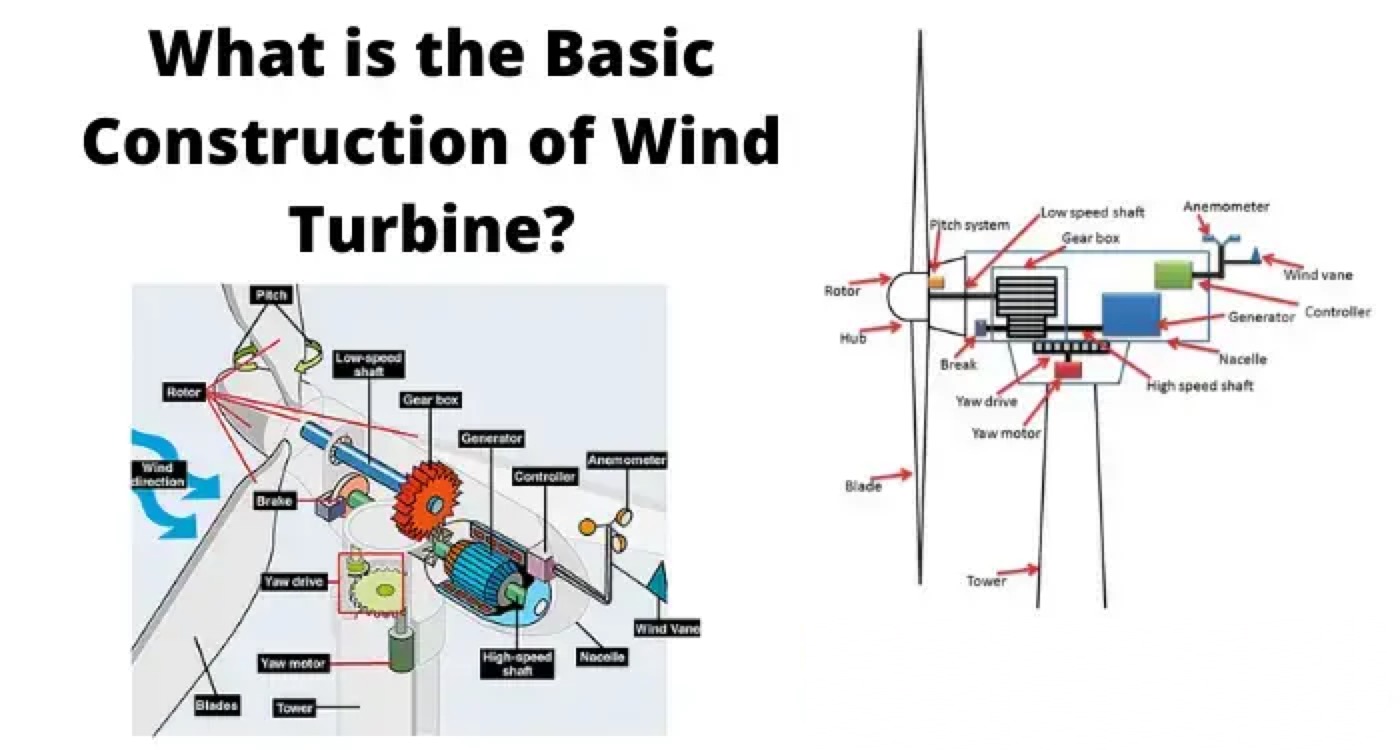
Major Parts of Wind Turbine
Tower of Wind Turbine
Tower is very crucial part of wind turbine that supports all the other parts. It not only supports the turbine but raises the turbine to sufficient height so that its blades tips would be at safe height during rotation. Not only that, we have to maintain the height of the tower, so that it can get sufficiently strong wind. The height of tower ultimately depends on the power capacity of wind turbines. The tower of the turbines in commercial wind power plants usually ranges from 40 meters to 100 meters. These towers may be either tubular steel towers, lattice towers, or concrete towers. We use a tubular steel tower for a large wind turbine. These are normally manufactured in a section of 30 to 40 meters in length. Each section has flanges with holes. Such sections are fitted together by nut bolts at the site to form a complete tower. The complete tower is slight conical shape to provide better mechanical stability. We assemble a lattice tower by different members of steel or GI angles or tubes. All members are bolted or welded together to form a complete tower of desired height. The cost of these towers are much less than that of steel tubular tower, but it aesthetically looks not as good as steel tubular tower. Although, transportation, assembling, and maintenance are quite easy but still use of lattice tower is avoided in modern wind turbine plant due to its aesthetic look. There is another type of tower used for small wind turbines, and this is guyed pole tower. Guyed pole tower is a single vertical pole supported by guy wired from different sides. Because of numbers of guy wires, it is difficult to access the footing area of the tower. Because of that, we avoid this type of tower in the agricultural field.
Each section has flanges with holes. Such sections are fitted together by nut bolts at the site to form a complete tower. The complete tower is slight conical shape to provide better mechanical stability. We assemble a lattice tower by different members of steel or GI angles or tubes. All members are bolted or welded together to form a complete tower of desired height. The cost of these towers are much less than that of steel tubular tower, but it aesthetically looks not as good as steel tubular tower. Although, transportation, assembling, and maintenance are quite easy but still use of lattice tower is avoided in modern wind turbine plant due to its aesthetic look. There is another type of tower used for small wind turbines, and this is guyed pole tower. Guyed pole tower is a single vertical pole supported by guy wired from different sides. Because of numbers of guy wires, it is difficult to access the footing area of the tower. Because of that, we avoid this type of tower in the agricultural field.
There is another type of wind turbine tower used for small plant, and this is a hybrid type tower. Hybrid type tower is also a guyed type tower, but the only difference is that instead of using a single pole in the middle it uses a thin and tall lattice type tower. Hybrid type tower is hybrid of both lattice type and guyed type tower.
Nacelle of Wind Turbine
The nacelle is a big box or kiosk that sits on the tower and houses all the components of a wind turbine. It houses an electrical generator, power converter, gearbox, turbine controller, cables, a yaw drive.

Rotor Blades of Wind Turbine
Blades are the main mechanical parts of a wind turbine. The blades convert wind energy into usable mechanical energy. When the wind strikes on the blades, the blades rotate. This rotation transfers its mechanical energy to the shaft. We design the blades like airplane wings. The wind turbine blades can be 40 meters to 90 meters long. The blades should be mechanically strong enough to withstand strong wind even during the storm. At the same time, the wind turbine blades should be made as light as possible to facilitate smooth rotation of the blades. For that, we make the blades with fiberglass and carbon fiber layers on synthetic reinforce.
In a modern turbine, normally three identical blades are fitted to a central hub using nut bolts. Each identical blades are aligned at 120o to each other. The process makes a better distribution of mass and gives the system more smooth rotation.
Shaft of Wind Turbine
The shaft directly connected to the hub is a low-speed shaft. When the blades rotate, this shaft spins with the same rpm as the rotating hub. We couple this shaft directly to the electrical generator in case of a low-speed generator. But in most cases, the low-speed main shaft is geared with a high-speed shaft through a gearbox. In this way, the rotor blades transfer its mechanical energy to the shaft which ultimately enters into an electrical generator.
Gearbox
The wind turbine does not rotate at high speed rather it rotates gently at low speed. But most of the electrical generators require high-speed rotation, to generate electricity at a desired voltage level. So there must be some speed multiplication arrangement to achieve the high speed of the generator shaft. The gearbox of the wind turbine does this. Gearbox increases the speed to much higher value. For example, if the gearbox ratio is 1:80 and if the rpm of a low-speed main shaft is 15, the gearbox will increase the speed of generator shaft to 15 × 80 = 1200 rpm.
Generator
The generator is an electrical device that converts mechanical energy received from the shaft into electrical energy. Normally, we use induction generators in modern wind turbines. Previously, synchronous generators were popular for this purpose. Permanent Magnet DC generator also used in some wind turbines. The speed of the shaft can be made high by using gearbox assembly, but we can not make the shaft speed constant. There may be a fluctuation in shaft speed since it depends on wind speed. So, the speed of the rotor also varies. This variation affects the frequency, voltage of the generated electric power. To, overcome these issues, we normally use an induction generator for the purpose.
Because the induction generator always produces electric power synchronized to the connected grid irrespective of the speed of the rotor. If we use the three-phase synchronous generator, then we first rectify the output power to DC and then convert it to AC of desired voltage and frequency using inverter circuit. Because the alternating power generated by the synchronous generator is not constant in voltage and frequency, rather it varies with speed of the rotor. Because, for the same reason, in some cases, we use a DC generator for the purpose. In these cases, the output DC power from generator inverted to AC of desired voltage and frequency, before feeding it to the grid.
Power Converter
Because wind is not always constant, so electrical potential generated from a generator is not constant, but we need a very stable voltage to feed the grid. A power converter is an electrical device that stabilizes the alternating output voltage transferred to the grid.
Turbine Controller
Turbine controller is a computer (PLC) that controls the entire turbine. It starts and stops the turbine and runs self diagnostic in case of any error in the turbine.
Anemometer
It measures the wind speed and passes the speed information to PLC to control the turbine power.
Wind Vane
It senses the direction of the wind and passes the direction to PLC then PLC faces the blades in such a way that it cuts the maximum wind.
Pitch Drive
Pitch drive motors control the angle of blades whenever the wind changes it rotates the angle of blades to cut the maximum wind, which is called pitching of blades.
Yaw Drive
Blades and other components in wind turbine are housed in a nacelle, whenever any change in wind direction is there, the nacelle has to face in the direction of the wind to extract the maximum energy from wind. For this purpose yaw drive, a motor is used to rotate the nacelle. It is controlled by PLC that uses the wind vane information to sense the wind direction.
Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
Electrical4U is dedicated to the teaching and sharing of all things related to electrical and electronics engineering.













