Horizontal and Vertical Axis Wind Turbines: A Comparison
Wind energy is a renewable and clean source of power that can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and fossil fuel dependence. Wind turbines are machines that convert the kinetic energy of the wind into electrical energy. There are two main types of wind turbines based on the orientation of their axis: horizontal and vertical.
What is a Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine?
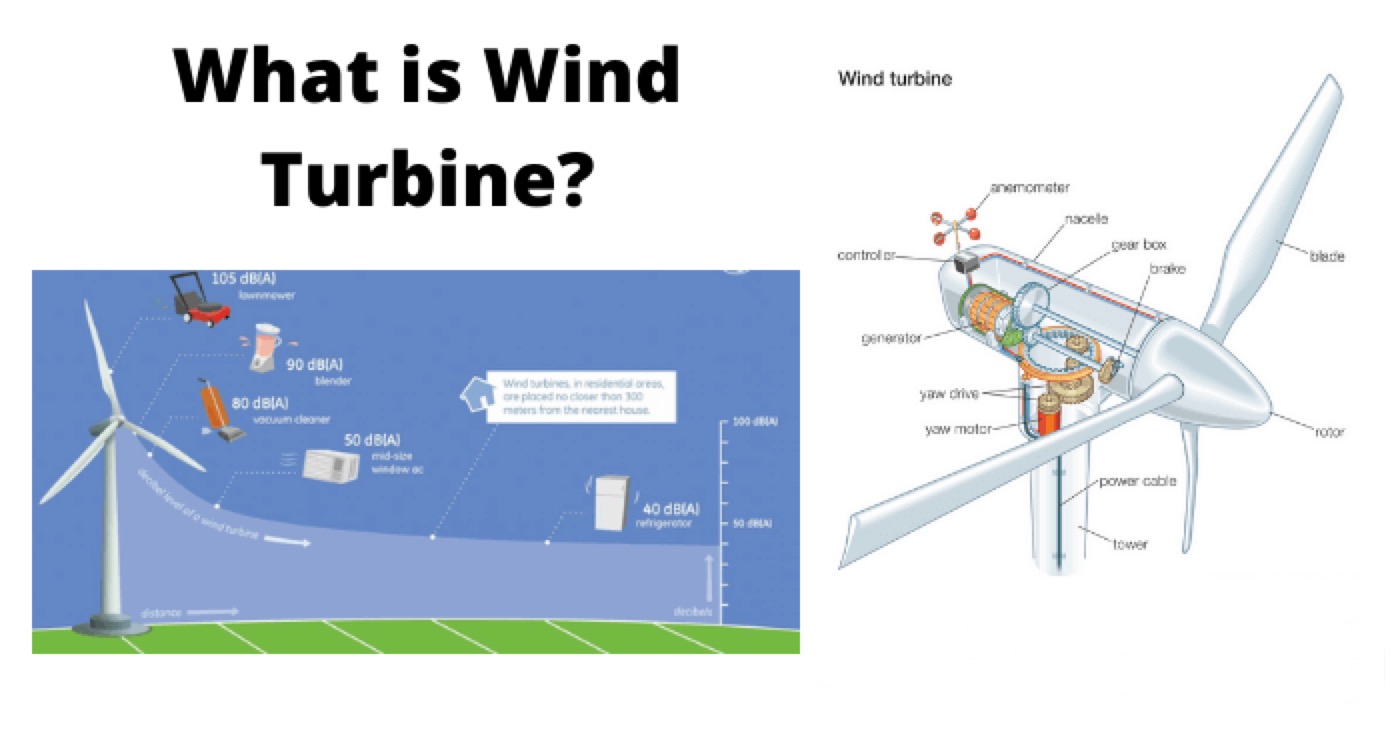
A horizontal axis wind turbine (HAWT) is defined as a wind turbine that has a horizontal or parallel axis of rotation with respect to the ground. HAWTs are the most common type of wind turbines used for large-scale electricity generation. They typically have three blades that resemble airplane propellers, although some may have two or one blades.
The main components of a HAWT are:
The rotor, which consists of the blades and the hub that connects them to the shaft.
The nacelle houses the generator, gearbox, brake, yaw system, and other mechanical and electrical components.
The tower supports the nacelle and the rotor and elevates them above the ground to capture more wind.
The foundation anchors the tower to the ground and transfers the loads from the wind turbine.

The working principle of a HAWT is based on a lift, which is the force that pushes an object upward when air flows over its surface. The blades of a HAWT are shaped like airfoils, which create a pressure difference between their upper and lower surfaces when the wind blows. This pressure difference causes the blades to rotate around the horizontal axis, which in turn drives the shaft and the generator to produce electricity.
The rotor plane of a HAWT must be aligned with the wind direction to maximize its efficiency. Therefore, a HAWT has a wind sensor and a yaw system that adjust the orientation of the nacelle according to the wind direction. A HAWT also has a pitch system that changes the angle of attack of the blades to control their rotational speed and power output.

The advantages of HAWTs are:
They have higher efficiency than vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) because they can capture more wind energy with less drag.
They have lower torque ripple and mechanical stress than VAWTs because they have fewer changes in aerodynamic forces during each rotation.
They can be installed offshore on floating platforms or fixed foundations, where the wind speed is higher and more consistent.
The disadvantages of HAWTs are:
They require a tall tower and a large land area to avoid turbulence and interference from nearby structures or terrain.
They are more expensive and complex to install and maintain than VAWTs because they have more moving parts and electrical components.
They are more susceptible to fatigue and damage from high winds, storms, lightning, birds, or ice.
What is a Vertical Axis Wind Turbine?
A vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT) is defined as a wind turbine that has a vertical or perpendicular axis of rotation with respect to the ground. VAWTs are less common than HAWTs, but they have some advantages for small-scale and urban applications. They usually have two or three blades that are either straight or curved.
The main components of a VAWT are:
The rotor, which consists of the blades and the vertical shaft that connects them to the generator.
The generator, which converts the mechanical energy of the rotor into electrical energy.
The base, which supports the rotor and the generator and connects them to the ground.

The working principle of a VAWT is based on drag, which is the force that opposes the motion of an object when air flows over its surface. The blades of a VAWT are symmetrical or asymmetrical, which create different amounts of drag when they face or oppose the wind direction. This drag difference causes the blades to rotate around the vertical axis, which in turn drives the generator to produce electricity.
The rotor plane of a VAWT does not need to be aligned with the wind direction because it can capture wind from any direction. Therefore, a VAWT does not have a yaw system or a wind sensor. However, a VAWT may have a pitch system that changes the angle of attack of the blades to control their rotational speed and power output.

The advantages of VAWTs are:
They have lower installation and maintenance costs than HAWTs because they have fewer moving parts and electrical components.
They have lower noise levels than HAWTs because they rotate at slower speeds.
They can be installed on rooftops or near buildings because they have lower heights and smaller footprints than HAWTs.
The disadvantages of VAWTs are:
They have lower efficiency than HAWTs because they have more drag and less lift.
They have higher torque ripple and mechanical stress than HAWTs because they have more changes in aerodynamic forces during each rotation.
They cannot be installed offshore because they are less stable and durable than HAWTs.
Types of Vertical Axis Wind Turbines
There are two main types of VAWTs based on their blade design: Darrieus and Savonius.
Darrieus Turbines
Darrieus turbines are VAWTs that have curved blades that resemble an eggbeater or a trochoid. They were invented by French engineer Georges Darrieus in 1931. Darrieus turbines use lift as well as drag to rotate their blades. They can achieve high rotational speeds, but they require an external start-up mechanism, such as an electric motor or another turbine, because they cannot self-start.
The advantages of Darrieus turbines are:
They have a higher power coefficient than Savonius turbines because they use lift as well as drag.
They have a lower solidity ratio than Savonius turbines because they have fewer blades with larger gaps between them.
The disadvantages of Darrieus turbines are:
They require an external start-up mechanism because they cannot self-start.
They have higher centrifugal forces than Savonius turbines because they rotate at faster speeds.
Savonius Turbines
Savonius turbines are VAWTs that have straight blades that resemble an S-shape or a half-barrel. They were invented by Finnish engineer Sigurd Savonius in 1922. Savonius turbines use only drag to rotate their blades. They can self-start, but they have low rotational speeds and low power coefficients.
The advantages of Savonius turbines are:
They can self-start because they use only drag.
They have lower centrifugal forces than Darrieus turbines because they rotate at slower speeds.
The disadvantages of Savonius turbines are:
They have a lower power coefficient than Darrieus turbines because they use only drag.
They have a higher solidity ratio than Darrieus turbines because they have more blades with smaller gaps between them.
Comparison Between Horizontal and Vertical Axis Wind Turbines
The following table summarizes some of the main differences between horizontal and vertical-axis wind turbines:
Aspect |
Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine |
Vertical Axis Wind Turbine |
Axis orientation |
Parallel to the ground |
Perpendicular to the ground |
Wind direction |
Must be aligned with it |
Can capture it from any direction |
Yaw system |
Required |
Not required |
Pitch system |
Required |
Optional |
Start-up mechanism |
Not required |
Required for some types |
Efficiency |
High |
Low |
Torque ripple |
Low |
High |
Mechanical stress |
Low |
High |
Installation cost |
High |
Low |
Maintenance cost |
High |
Low |
Noise level |
High |
Low |
Height |
High |
Low |
Land area |
Large |
Small |
Offshore suitability |
High |
Low |
Conclusion
Horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWTs) and vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) are two types of wind turbines that differ in their axis orientation, blade design, working principle, efficiency, performance, cost, noise level, installation location, and environmental impact. HAWTs are more suitable for large-scale electricity generation in open areas with consistent wind direction, while VAWTs are more suitable for small-scale electricity generation in urban areas with variable wind direction.
Both types of wind turbines have their advantages and disadvantages depending on their specific applications. Therefore, it is important to consider various factors such as wind speed, site conditions, power demand, budget, aesthetics, safety, reliability, durability, etc., before choosing between horizontal and vertical axis wind turbines.
Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
Electrical4U is dedicated to the teaching and sharing of all things related to electrical and electronics engineering.













