Electrostatic Precipitator: What is it And How Does it Work?
The flue gases produced due to the combustion of solid pulverized fuel in the furnace contain plenty of dust particles.
When a chimney releases these flue gases in the atmosphere without filtering these dust particles, the atmosphere may get polluted.
Hence, these dust particles need to be removed from the flue gases as much as possible before these flue gases get discharged into the atmosphere. By removing the dust particles from flue gases, we can control air pollution.
An electrostatic precipitator does this work for a furnace system. We install this device in the way of flue gases from the furnace to the chimney so that the device can filter the flue gases before they enter the chimney.
Working Principle of Electrostatic Precipitator
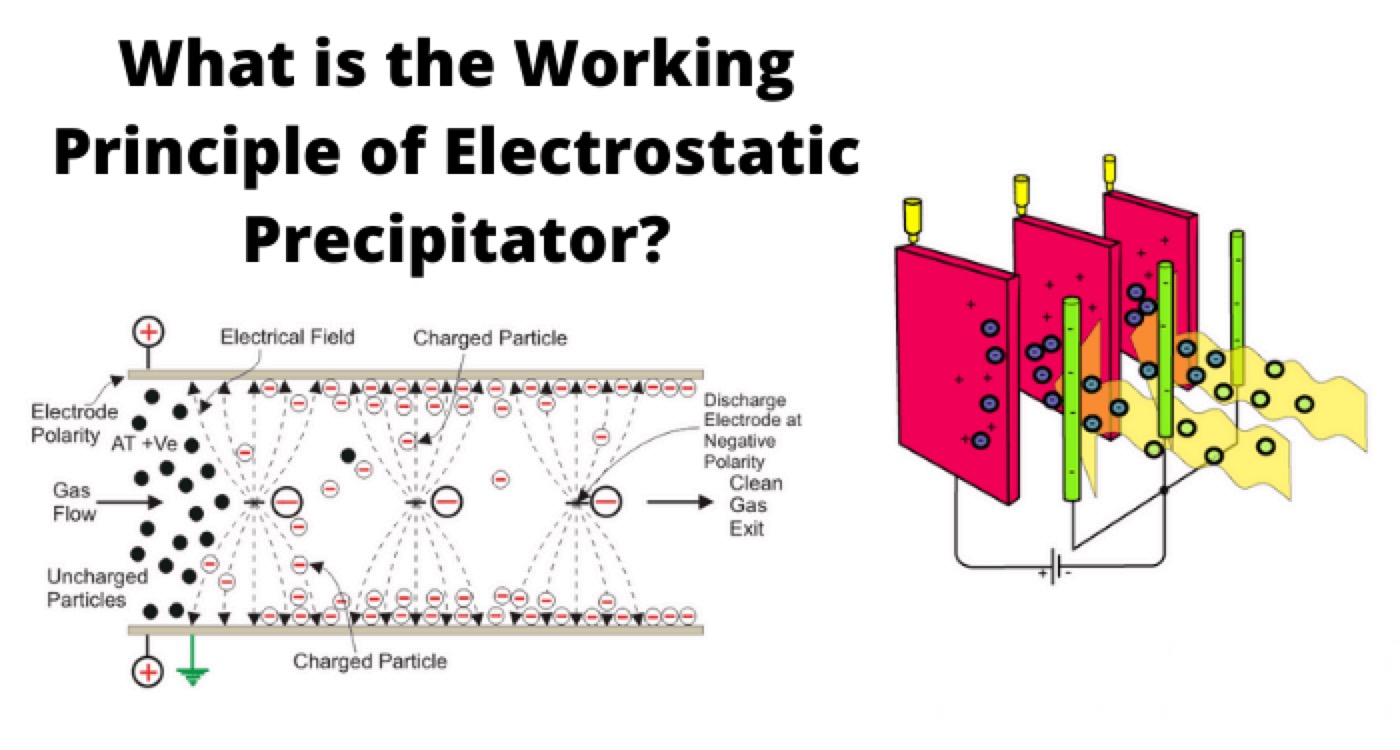
The working principle of the electrostatic precipitator is quite simple. It has two sets of electrodes one is positive, and another is negative.
The negative electrodes are in the form of a rod or wire mesh. Positive electrodes are in the form of plates.
The positive plates and negative electrodes are placed vertically in the electrostatic precipitator alternatively one after another.
The negative electrodes are connected to a negative terminal of a high voltage DC source, and positive plates are connected to the positive terminal of the DC source.
The positive terminal of the DC source may be grounded to get stronger negativity in the negative electrodes.
The distance between each negative electrode and positive plate and the DC voltage applied across them are so adjusted that the voltage gradient between each negative electrode and adjacent positive plate becomes quite high to ionize the medium between these.
The medium between the electrodes is air, and due to the high negativity of negative electrodes, there may be a corona discharge surround the negative electrode rods or wire mesh.
The air molecules in the field between the electrodes become ionized, and hence there will be plenty of free electrons and ions in the space. The entire system is enclosed by a metallic container on which one side is provided with an inlet of the flue gases, and the opposite side is provided with the outlet of the filtered gases.
As soon as the flue gases enter into the electrostatic precipitator, dust particles in the gases collide with the free electrons available in the medium between the electrodes and the free electrons will be attached to the dust particles.
As a result, the dust particles become negatively charged. Then these negatively charged particles will be attracted due to the electrostatic force of the positive plates.
Consequently, the charged dust particles move towards the positive plates and deposit on positive plates.
Here, the extra electron from the dust particles will be removed on positive plates, and the particles then fall due to gravitational force. We call the positive plates collecting plates.
The flue gases after traveling through the electrostatic precipitator become almost free from ash particles and ultimately get discharged to the atmosphere through the chimney.
An electrostatic precipitator does not contribute directly to the production of electricity in the thermal power plant, but it helps to keep the atmosphere clean which is quite important for living beings.
Hoppers are fitted below the electrostatic precipitator chamber for collecting dust particles. Water pray may be used on the top to accelerate the removal of the dust from the collecting plates.

Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
Electrical4U is dedicated to the teaching and sharing of all things related to electrical and electronics engineering.













