Methods of Firing Steam Boiler
For obtaining maximum fuel combustion efficiency it is required to complete combustion of fuel inside the boiler furnace. For that, the sufficient supply of air and proper mixing of air with fuel are primary requirements. Adequate supply of fuel particles for proper burning also to be maintained.
The combustion should produce designated temperature of the steam boiler and maintains it consistently.
In addition to these, the methods of firing steam boiler are such that, the system may easily be handled and also, operation and maintenance should be minimum. There are mainly two methods of firing steam boiler with coal as fuel. One is solid fuel firing other is pulverized fuel firing.
Let us discuss one by one.
There are mainly two types of solid fuel firing system
Hand Firing
Mechanical Stroke Firing
Smaller size boiler can be operated by hand firing system. This system was commonly used to drive coal engine locomotive in past. Here, coal chips are put into the furnace frequently by shovels.
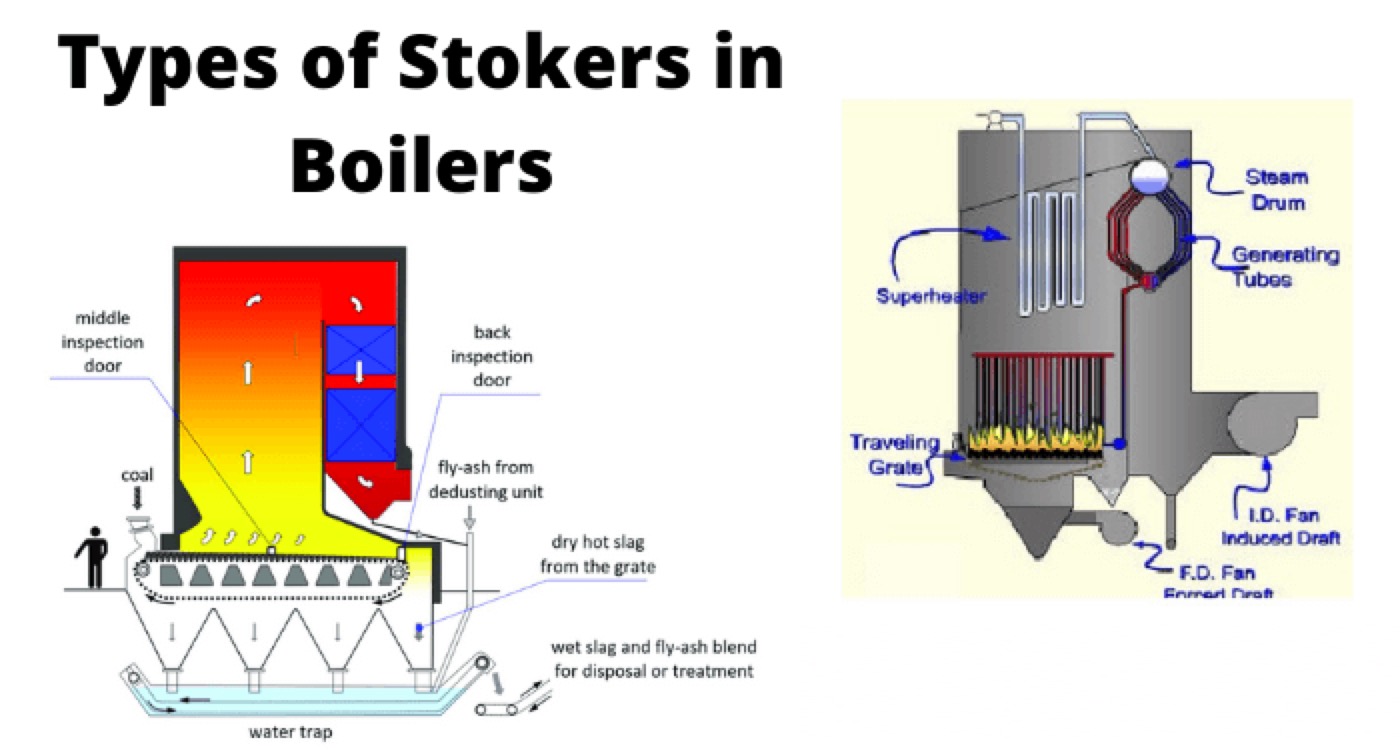
Mechanical Stoker Firing
When fuel i.e. coal is put into the steam boiler furnace by means of a mechanical stoker, the firing of boiler method is referred as mechanical stoker firing. There are mainly two types of mechanical stoker firing systems.
Under Feed Mechanical Stoker Firing
Here, combustion takes place on the grate. The primary air is fed below the grate. The secondary air is allowed at the top of the grate. When the coal is burnt, it is pushed down by fresh coal. The fresh coal is pushed on the grate using rams as shown.
The ignition occurs downwards against the primary air flow. The volatile matter filters through the bed and is completely burnt. The combustion rate is high. The light ash contents and combustion gases fly away to the atmosphere along with primary air. Heavier ash contents come down over the grate and ultimately fall into the ash pit.
Travel Grate Stoker Solid Coal Firing
Here, the coal is burnt on a chain grate which continuously travels forwards slowly, and combustion takes place during the journey of coal from the first end to the last end of the furnace. At the end of the combustion, heavier ash contents fall into ash pit by gravitational force as the grate chain moves like a conveyor belt. The lighter ash particles and combustion gases fly away with primary air.
Pulverized Fuel Firing
For obtaining the most calorific value of coal, the coal is pulverised in fine powder and then mixed with sufficient air. The mixture of coal powder and the air is fired in the steam boiler furnace to achieve most efficient combustion process. Pulverized fuel firing is most modern and efficient method of boiler firing.
Due to pulverization, the surface area of coal becomes much larger, and in this method air required for combustion is much less. As the quantity of required air and fuel both are less, loss of heat in this method of boiler firing is much less. Hence temperature can easily be reached to the designated level. As the combustion is most efficient pulverized coal firing increases the overall efficiency of a steam boiler. As handling of lighter coal dust is much easier than the handling of heavier coal chips, it is quite easy to control the output of the boiler by controlling the supply of fuel to the furnace. Hence fluctuation of system load can smoothly be met.
In addition these advantages, pulverized coal firing system has many disadvantages. Such as
The initial cost of installing this plant is very high.
Not only initial cost, running cost of this plant is quite high as separate pulverisation plant is to install and run additionally.
High temperature causes high thermal loss through flue gas.
This type of method of boiler firing has always a risk of explosion.
This is also difficult and expensive to filter fine ash particles from exhaust gases. Moreover, the quantity of ash particles in the exhaust gases is more in pulverized system.
Pulverization Process
The process of pulverization is discussed here in brief.
First the coal is crushed by preliminary crasher. The coal is crushed to 2.5 cm. or less.
Then this crushed coal is passed through a magnetic separator to separate any iron content from the coal. Iron must be removed, otherwise during pulverizing iron particles will cause spark which results in unwanted fire hazard.
After that, crushed coal is dried properly before pulverization. The moisture content must be less than 2% after drying operation.
Then the coal is crushed again in fine particles in a ball mill. This process is referred as pulverization.
This pulverized coal is then puffed with air and put into furnace as fluid.
Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
Electrical4U is dedicated to the teaching and sharing of all things related to electrical and electronics engineering.













