Boiler Economizer: What is it? (Function & Construction)
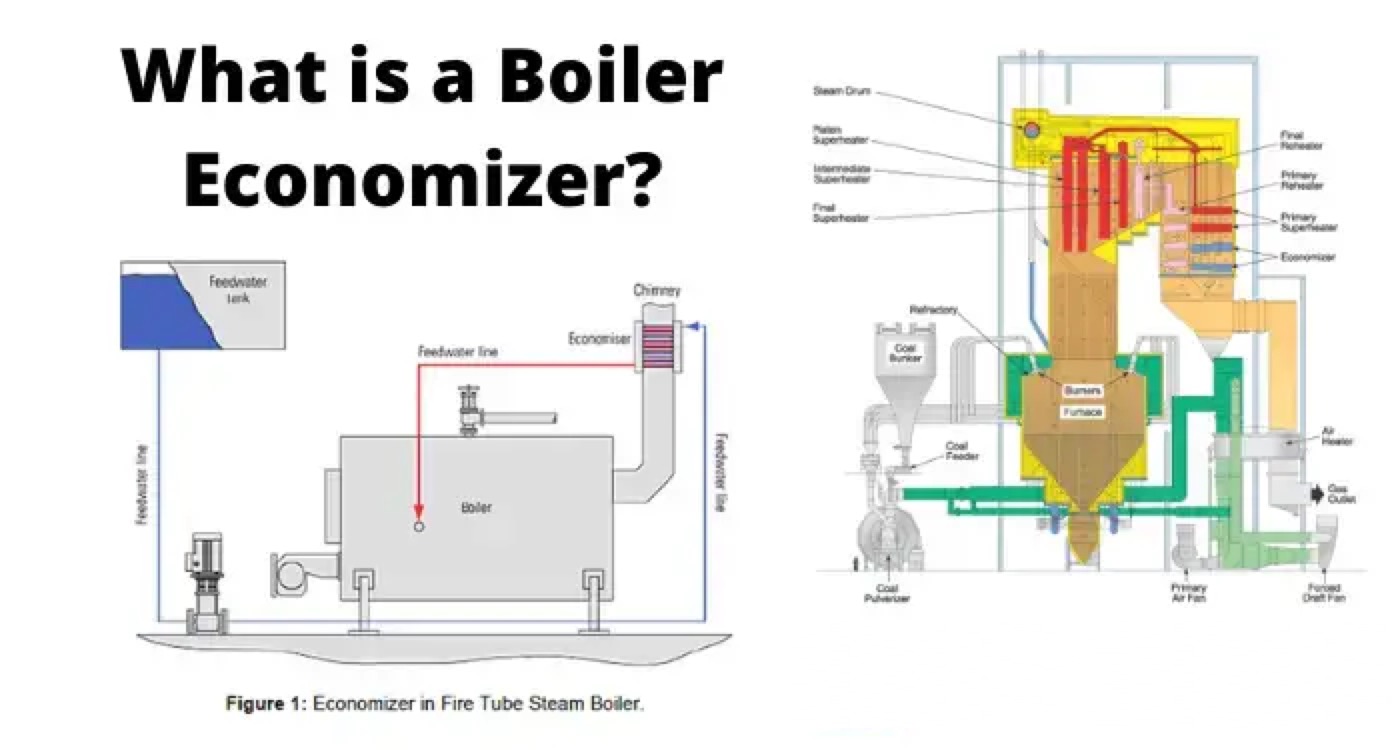
What Does an Economizer Do in a Boiler
A boiler economizer (also known as an economizer) are mechanical devices intended to reduce energy consumption or perform a useful function such as preheating a fluid. A boiler economizer is essentially a heat exchanger that makes a system more energy efficient by taking enthalpy in fluid streams that are hot, but not hot enough to be used in a boiler – hence recovering more useful enthalpy and improving the steam boiler’s efficiency.
After producing steam, flue gas comes out from the system (flue gas is the gas exiting to the atmosphere via a flue). Some heat energy remains in the flue gas when it goes out. If we cannot utilize this heat energy, it gets lost. Boiler economizer is a device that uses a portion this remained energy of the flue gas to heat up inlet water (feed water) to the boiler. Since the heat energy is given to the water before it gets fed to the boiler, the requirement of fuel for producing steam is optimized. Because of that, we call this device as an economizer.
Construction and Working Principle of Boiler Economizer
The construction and working principle of the boiler economizer is simple. At the bottom part, it has a horizontal inlet pipe through which we feed water with normal temperature to the economizer. There is another horizontal pipe fitted at the top of the economizer.
These two horizontal pipes, which are bottom and top pipes connected through a group of vertical pipes. There is an outlet valve fitted on the top horizontal pipe to supply hot water to the boiler. The flue gases from the boiler furnace flow through the vertical pipes of the economizer.

Here, the flue gases transfer remain heat to the water through the surface of the vertical pipe when the water goes up through the vertical pipes to top horizontal pipe. In this way heat of the flue gases gets utilized through the economizer for heating up the water before entering into the boiler for producing steam.
The flue gas will have ash particles mixed with it which will get deposited on vertical pipe surfaces. If special care is not taken there will be a thick layer of soot on the surfaces which insulate the heat to enter the water.
To remove this soot, the scraper is attached to each vertical pipe which continuously moves up and down by means of a chain pulley system. By scraping the soot fall down to the soot chamber placed at the bottom of the economizer. Then we collect the soot from the soot chamber. This is how a boiler economizer works. This is a very simple form of boiler economizer.
Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
Electrical4U is dedicated to the teaching and sharing of all things related to electrical and electronics engineering.













