Stirling Boiler
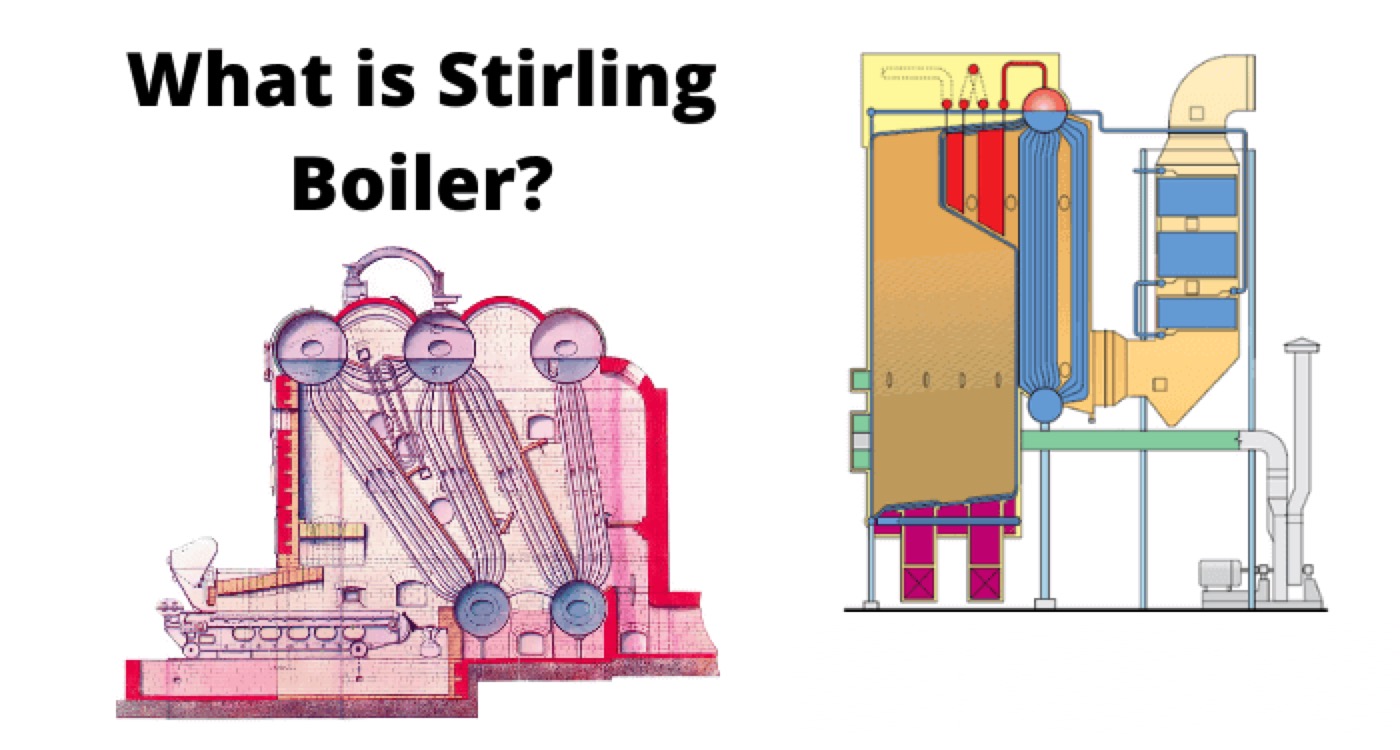
Stirling Boiler is one of the most basic variety of bent tube boiler. In most of the modern thermal power generating plants we use bent tube boiler. Stirling Boiler is one of the largest capacity boiler. A Stirling Boiler can generate as high as 50,000 kg steam per hour and can produce pressure as high as 60 kgf per cm2. This boiler was first designed in the year of 1888 by Alan Stirling so we refer the boiler as Stirling Boiler. Because of the huge capacity we can use this boiler in central power stations.
In Stirling Boiler there are three steam drums and two mud drums. Three steam drums are placed on the top portion of the boiler system structure and two mud drums are placed on bottom of the structure. The top steam drums are connected to the bottom mud drums with banks of bent tubes. Since the tubes are bent, the mechanical stresses due to expansion of the pipes during heating can not effect the system much. The steam drums, mud drums and bent tubes are made of steel. Also still structure is used to support the entire system.
The entire system is enclosed by a brickwork. Here the brick enclosure is used to prevent the heat dissipation to the surroundings. The fire door is constructed at the bottom side of the brick enclosure wall. The damper is provided on the other side of the brick enclosure wall to take out the combustion gas as when required.
The fire brick arch is provided above the furnace. Three baffles are provided in the boiler system to allow the combustion gas to flow in zigzag way. There is one water circulating tubes connecting the mud drums. Also there are steam circulating tubes connecting middle steam drums to outer steam drums. There is also a group of hot water circulating tube from front steam drum to middle steam drum.
A safety value is provided on the back steam drum. Finally the steam is collected from middle steam drum. The steam compartment is constructed inside the middle steam drum. The super heater is connected to steam compartment through a steel pipe.
Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
Electrical4U is dedicated to the teaching and sharing of all things related to electrical and electronics engineering.













