Medium Velocity Water Spray (MVWS) System
An MVWS system (short for a Medium Velocity Water Spray System) is a water-based fire protection system. MVWS systems are used to provide cooling and/or control the burning in many large scale industrial applications, such as in thermal power plants.
As their name suggests, medium velocity water spray nozzles are designed to spray water at a medium velocity (i.e. the strength of the spray is weaker than HVWS systems). MVWS systems are best suited for protecting hazards involving light oils – where emulsification from high-velocity water sprayers (HVWS) is not possible.
When a fire occurs in another area of the plant, medium velocity sprayers are an effective method of protecting nearby structures from heat during a fire by providing a continuous cooling spray over the exposed surfaces.

MVWS System Applications
Medium velocity water spray systems are commonly used to protect a lot of equipment within a plant, including:
Cable gallery and cable spreader room in the main plant area
ESP control room
Switchyard room
Ash handling plant area
Coal handling plant area
Water treatment plant area
Circulating water pump area
Seawater intake area
Fuel oil pump house
All coal conveyor gallery in tunnels/underground and above ground
Coal transfer points and junction towers
Crusher house
Emergency DG Building
Fuel oil pump house (loading and unloading areas)
Fuel oil storage tanks
Difference Between High Velocity and Medium Velocity Water Spray System
A High Velocity Water Spray (HVWS) system is a water-based fire protection system that sprays water a high velocity – i.e. at a higher strength than a MVWS system.
You would be forgiven for thinking that a HVWS system is strictly better than a MVWS system since the water pressure is higher. But, this isn’t always the case.
HVWS systems are often used to protect equipment that incorporates heavy or medium oils. Equipment such as oil type circuit breakers and transformers, diesel engines and fuel oil storage tanks, turboalternator lube oil systems, and oil-fired boilers.
The high-velocity discharge water jet forms a cone of coarse spray of uniform density. This coarse spray is able to penetrate the flame zone and reach the surface of the burning oil. The turbulence created by the high velocity spray forms an oil-in-water emulsion on the surface of the oil that will not burn. This “emulsification” is the main way the fire is extinguished – along with the cooling and smothering effect.
So now the we understand what HVWS systems do, let’s summarise the main differences between MVWS vs HVWS systems:
Medium-velocity water spray systems are designed to control fires involving lighter oils, liquefied petroleum gases, and other flammable liquids with flash points typically below 650 C.
High-velocity water spray systems are installed to extinguish fires involving heavy or medium oils, and other flammable liquids with flash points typically above 650 C (1500 F).
MVWS System Design Requirements
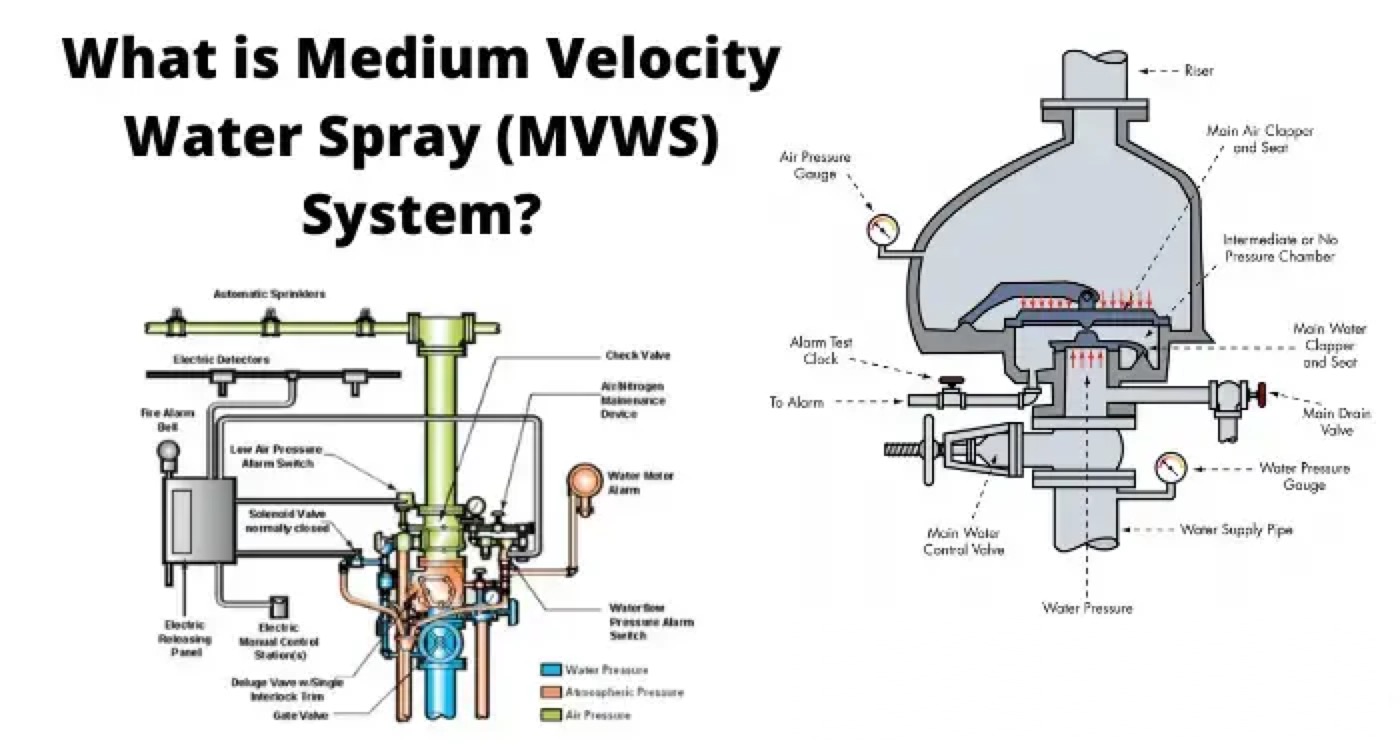
Medium velocity water spray system design requirements are designed as per TAC regulations. The MVWS system shall consists of a network of open spray nozzles fitted with a special deflector to give required angle of discharge for the water around the area mentioned above.
The sprayers shall discharge a cone of water spray consisting of medium size droplets of water. The water supply to the MVWS system shall consist of a network of open spray nozzles fitted with a special deflector to give the required angle of discharge for the water around the area to be protected. The water supply to the MVWS system shall be controlled by a deluge valve which shall operate electrically actuated solenoid valve on the release of water pressure.

In order to avoid total flooding of the entire area of cable gallery/ coal conveyor system, the area to be protected by shall be divided into a number of zones. Each zone shall have a separate water supply network controlled by a deluge valve.
A fire detection system provided for the MVWS protected area shall sense fire and shall actuate the deluge valve. In the event of fire in one zone, the deluge valve of the corresponding zone and those of adjacent zones on either side shall be opened.
MVWS System for Cable Galleries
The cable galleries shall have number of rows of cable trays and each row will have number of tiers of cable trays. Each of the cable rows shall be provided with a network of water distribution piping and nozzles.
The distribution network shall consist of distribution header for each row of cable tray and on these headers drop pipes shall be provided so as to cover all the tires. In case of fire in the cable gallery, addressable multi-sensor detector supplemented with linear heat sensing cable of digital type shall be used for detection of fire.
Upon detection of fire MVW spray system shall be brought into operation by automatically opening of deluge valve, which shall allow the projectors located in that area to direct water in the form of spray, which which will cut of oxygen supply and extinguish the fire.
As per TAC regulations the density of spray water system in cable galleries shall be 12.2 lpm/m2 of the surface area for spray system. The pressure at the hydraulically most remote projector in the network shall not be less than 2.8 bar.
MVWS System in Mining
MVWS for coal conveyors shall be provided for both top and return conveyors. Junction towers, transfer towers, crusher house and all other areas shall also be covered. Fire in the coal conveyor will be detected by the linear heat sensing cables and infrared ember detectors which shall provide signal for electrical actuation for deluge valve.
MVWS system spray nozzles shall be provided in the centre of the conveyor belt for top conveyors, and on either side of the conveyor at 4 meters intervals. Staggering of sprayers are recommended for bottom conveyors. Conveyor walkways shall not be affected by MVWS system pipe routing.
As per TAC regulations, the density of spray water system in coal conveyors shall be 10.2 lpm/m2 of the surface area for spray system. Hydraulically remotest sprayer shall have the minimum-pressure 1.4 bars. However the pressure at the hydraulically favorable sprayer shall not exceed 3.5 bars.
MVWS System for Fuel Oil Pump House and EDG Buildings
MVWS system for fuel oil pump house and Emergency DG (EDG) building shall be designed considering the pump house as a single zone. A network of pipes with spray nozzles shall be located near the roof of the pump house which shall be connected to a deluge valve.
The fire in fuel oil pump house and Emergency DG (EDG) building shall be detected by a detection-system comprising of quartzoid bulb detector which shall actuate the delude valve. Probe type heat detector shall be used for detection of fire on the fuel oil storage tanks.
As per TAC regulations the density of spray water system in Fuel oil pump house and Emergency DG set building shall be 10.2 lpm/m2 of the surface area for spray system. The pressure at the hydraulically most remote projector in the network shall not be less than 1.4 bar and 2.8 bar.
As per TAC the density of spray water for fuel oil storage tank shall be 3 lpm/m2 of surface area.
Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
Electrical4U is dedicated to the teaching and sharing of all things related to electrical and electronics engineering.













