Power Plant: What Are They? (& the Types of Power Plants)
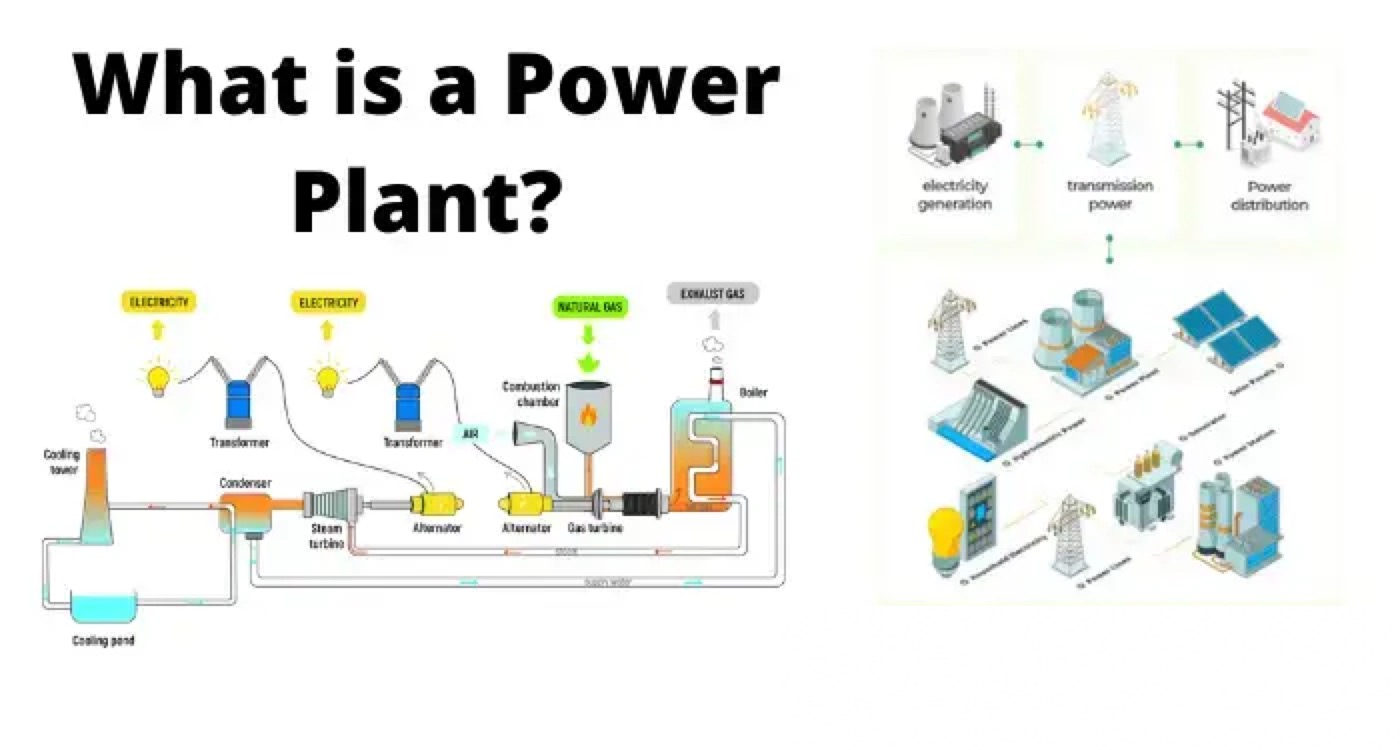
What is a Power Plant?
A power plant (also known as a power station or power generating station), is an industrial location that is utilized for the generation and distribution of electric power on a mass scale. Many power stations contain one or more generators, a rotating machine that converts mechanical power into three-phase electric power (these are also known as an alternator). The relative motion between a magnetic field and an electrical conductor creates an electric current.
These are generally located in the sub-urban regions or several kilometers away from the cities or the load centers, because of its requisites like huge land and water demand, along with several operating constraints like waste disposal, etc.
For this reason, a power generating station has to not only concern itself with the efficient generation of power, but also in the transmission of this power. This is why power plants are often closely accompanied by transformer switchyards. These switchyards increase the transmission voltage of the power, which allows it to be more efficiently transmitted over long distances.
The energy source harnessed to turn the generator shaft varies widely and is chiefly dependent on the type of fuel used. The fuel choice dictates what we call the power plant, and this is how the various types of power plants are classified.

Types of Power Plants
The different types of power plants are classified depending on the type of fuel used. For the purpose of bulk power generation, thermal, nuclear, and hydropower are the most efficient. A power generating station can be broadly classified into the three above-mentioned types. Let us have a look at these types of power stations in detail.
Thermal Power Station
A thermal power station or a coal fired thermal power plant is by far, the most conventional method of generating electric power with reasonably high efficiency. It uses coal as the primary fuel to boil the water available to superheated steam for driving the steam turbine.
The steam turbine is then mechanically coupled to an alternator rotor, the rotation of which results in the generation of electric power. Generally in India, bituminous coal or brown coal are used as fuel of boiler which has volatile content ranging from 8 to 33% and ash content 5 to 16 %. To enhance the thermal efficiency of the plant, the coal is used in the boiler in its pulverized form.
In coal fired thermal power plant, steam is obtained in very high pressure inside the steam boiler by burning the pulverized coal. This steam is then super heated in the super heater to extreme high temperature. This super heated steam is then allowed to enter into the turbine, as the turbine blades are rotated by the pressure of the steam.
The turbine is mechanically coupled with alternator in a way that its rotor will rotate with the rotation of turbine blades. After entering into the turbine, the steam pressure suddenly falls leading to corresponding increase in the steam volume.
After having imparted energy into the turbine rotors, the steam is made to pass out of the turbine blades into the steam condenser of the turbine. In the condenser, cold water at ambient temperature is circulated with the help of a pump which leads to the condensation of the low-pressure wet steam.
Then this condensed water is further supplied to low pressure water heater where the low pressure steam increases the temperature of this feed water, it is again heated in high pressure. This outlines the basic working methodology of a thermal power plant.
Advantages of Thermal Power Plants
Fuel used i.e coal is quite cheaper.
Initial cost is less as compared to other generating stations.
It requires less space as compared to hydro-electric power stations.
Disadvantages of Thermal Power Plants
It pollutes atmosphere due to production of smoke and fumes.
Running cost of the power plant is more than hydro electric plant.
Nuclear Power Station
Nuclear power plants are similar to thermal stations in more ways than one. However, the exception here is that radioactive elements like uranium and thorium are used as the primary fuel in place of coal. Also in a Nuclear station, the furnace and the boiler are replaced by the nuclear reactor and the heat exchanger tubes.
For the process of nuclear power generation, the radioactive fuels are made to undergo fission reaction within the nuclear reactors. The fission reaction, propagates like a controlled chain reaction and is accompanied by unprecedented amount of energy produced, which is manifested in the form of heat.
This heat is then transferred to the water present in the heat exchanger tubes. As a result, super heated steam at very high temperature is produced. Once the process of steam formation is accomplished, the remaining process is exactly similar to a thermal power plant, as this steam will further drive the turbine blades to generate electricity.
Hydro-Electric Power Station
In Hydroelectric plants, the energy of the falling water is utilized to drive the turbine which in turn runs the generator to produce electricity. Rain falling upon the earth’s surface has potential energy relative to the oceans towards which it flows. This energy is converted to shaft work where the waterfalls through an appreciable vertical distance. The hydraulic power is, therefore, a naturally available renewable energy given by the equation:
P = gρ QH
Where, g = acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/sec 2
ρ = density of water = 1000 kg/m3
H = height of fall of water.
This power is utilized for rotating the alternator shaft, to convert it to equivalent electrical energy.
An important point to be noted is that the hydro-electric plants are of much lower capacity compared to their thermal or nuclear counterpart.
For this reason, hydro plants are generally used in scheduling with thermal stations, to serve the load during peak hours. They in a way assist the thermal or the nuclear plant to deliver power efficiently during periods of peak hours.
Advantages of Hydro Electric Power Station
It requires no fuel, water is used for generation of electrical energy.
It is neat and clean energy generation.
Construction is simple, less maintenance is required.
It helps in irrigation and flood control also.
Disadvantages Hydro Electric Power Station
It involves high capital cost due to dam construction.
Availability of water depends upon weather conditions.
It requires high transmission cost as the plant is located in hilly areas.
Types of Power Generation
As mentioned above, depending on the type of fuel used, the power generating stations as well as the types of power generation are classified. Therefore the 3 major classifications for power production in reasonably large scale are:
Thermal power generation
Nuclear power generation
Hydro-electric power generation
Apart from these major types of power generations, we can resort to small scale generation techniques as well, to serve the discrete demands. These are often referred to as the alternative methods or non conventional energy of power generation and can be classified as :-
Solar power generation. (making use of the available solar energy)
Geo-thermal power generation. (Energy available in the Earth’s crust)
Tidal power generation.
Wind power generation (energy available from the wind turbines)
These alternative sources of generation has been given due importance in the last few decades owing to the depleting amount of the natural fuels available to us. In the centuries to come, a stage might be reached when several countries across the globe would run out of their entire reserve for fossil fuels.
The only way forward would then lie in the mercy of these alternative sources of energy which might play an instrumental role in shaping the energy supplies of the future. For this reason, these might rightfully be referred to as the energy of the future.
Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
Blake is an electrical engineering leader with 20+ years of expertise in imaging technology innovation. Former CTO of a global scientific camera manufacturer, he now drives strategic R&D and CCD-to-CMOS transitions at Jingtu Optoelectronics. His career combines technical excellence in precision instrumentation with cross-disciplinary team leadership across global markets.













