Steam Thermal Power Plant
Thermal Power Plant Definition
A thermal power plant uses coal, air, and water to generate electricity based on the Rankine Cycle.
A thermal power generating plant works using the Rankine Cycle. It needs three main inputs to produce electricity: coal, air, and water.
Coal is used as fuel here because we are going to draw the flow diagram of a coal thermal power generating plant. Coal creates required heat energy by combustion in the furnace.
Air is supplied to the furnace to accelerate the combustion rate of the coal and to continue the flow of flue gases inside the heating system. Water is required in a thermal power plant inside a boiler to produce steam. This steam drives the turbine.
The turbine is connected to a generator, which produces electrical power. There are three main flow circuits in a thermal power plant based on the primary inputs.
Coal Circuit
Coal is transported from suppliers to the plant’s coal storage yard. It is then delivered to pulverizing plants using a conveyor.
After removing unwanted substances from the coal, it is pulverized in coal dust. Pulverisation makes the coal more efficient for burning. After the combustion of the coal, the ash is collected to the ash handling plant. Then the ash is finally collected to the ash storage yard.
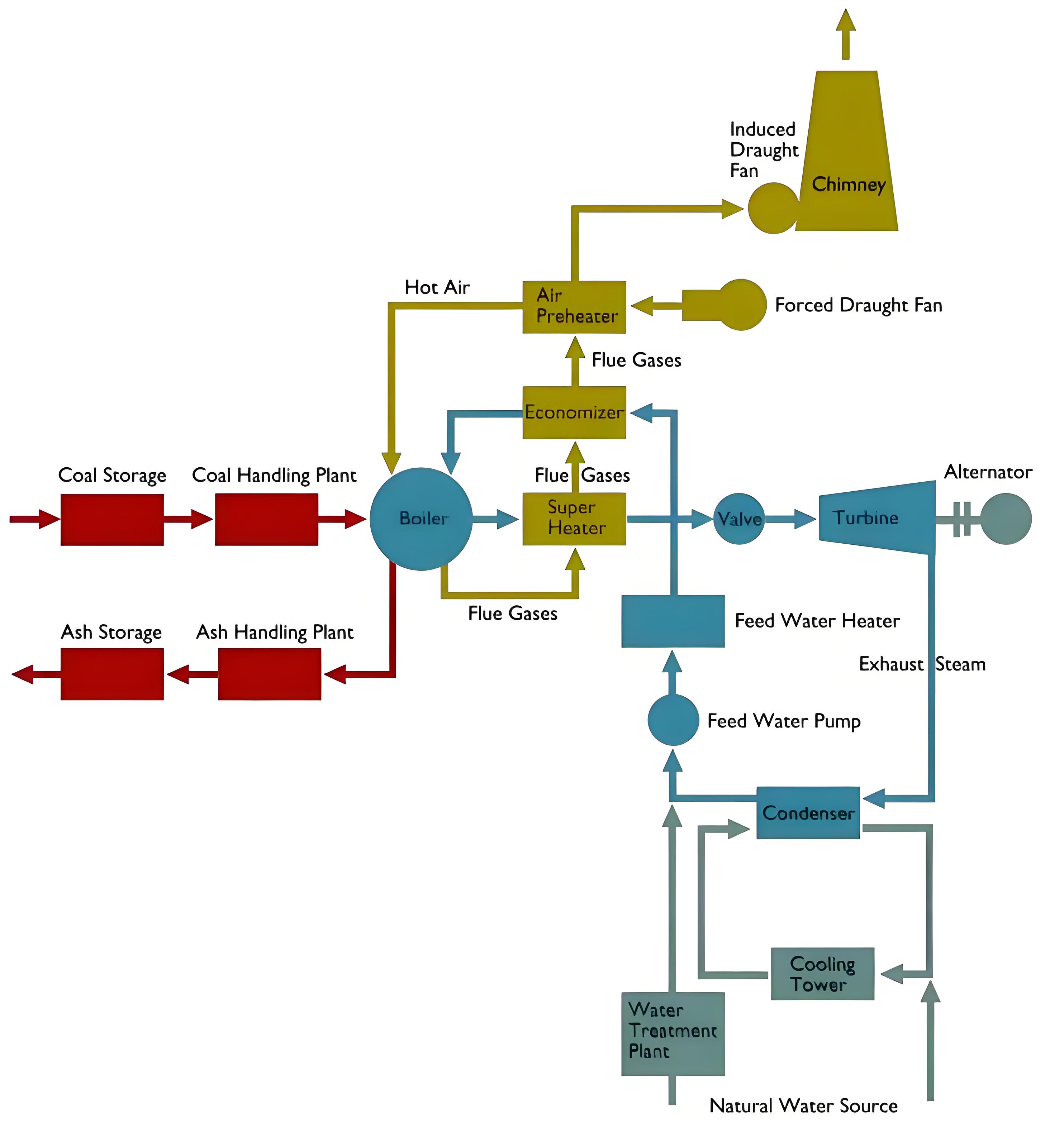
Air Circuit
Air is supplied to the furnace with forced draught fans. But it is not directly charged to the boiler furnace before it is charged to the boiler furnace it is passed through an air preheater.
In the air preheater, the heat of the exhaust flue gases is transferred to the inlet air before it enters the furnace.
In the furnace, this air supplies required oxygen for combustion. Then this air carries the generated heat and flue gases due to the combustion through the boiler tube surfaces.
Here significant part of the heat is transferred to the boiler. The flue gases then pass through the superheater where the steam coming from the boiler gets further heated up to the spearheading temperatures.
Then the flue gases come to the economizer where some of the remaining portions of the heat of flue gases are utilized for increasing the temperature of the water before it enters the boiler.
The flue gases then pass through the air preheater where a portion remaining heat is transferred to the inlet air before it enters the boiler furnace.
After passing through the air preheater, the gases ultimately go to the chimney by induced draught fans.
Normally in thermal power plants, forced draught is used at the entry of air from the atmosphere, and induced draught is used at the exit of flue gases from the system through the chimney.
Water-Steam Circuit
The water-steam circuit of a thermal power generating plant is a semi-closed circuit. Here comparatively not much water is required to supply to the boiler from external sources since the same water is reused again and again by condensing the steam after its mechanical work of rotating turbine.
Water is first sourced from a river or another suitable natural source.
This water then is taken to the water treatment plant for removing unwanted particles and substances from the water. This water is then fed to the boiler through an economizer.
In the boiler, the water is converted into steam. This steam then goes to the super-heater, where the steam is heated up to the superheating temperature. The superheated steam then goes to the turbine through a series of nozzles.
At the outlet of these nozzles, the high pressure and high-temperature steam suddenly expands and hence gets kinetic energy. Because of this kinetic energy, the steam rotates the turbine.
The turbine is coupled with a generator and the generator produces alternating electricity to the grid.
Suddenly expanded steam exhaust from the turbine to the condenser. Where the steam is condensed back to the water with the help of a water circulating cooling system associated with cooling towers.
This condensed water is then fed back to the boiler through the economizer. The water supply from an external source of water is limited here because of using condensed steam in the boiler system of the thermal power generating plant.
Thermal Power Plant Process Flow Diagram
The flow diagram of a steam thermal power plant shows how coal, air, and water are processed to generate electricity.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













