What is Transformer Water Content Test?
What is Transformer Water Content Test?
Water Content Test Definition
The water content test in insulating oil is defined as a process using Karl Fischer Titration to measure water levels.
Karl Fischer Principle
To measure water content in insulating oil, we use Karl Fischer Titration. In this method, water (H2O) reacts chemically with iodine (I2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), an organic base (C5H5C), and alcohol (CH3OH) in an organic solvent.
The sample is mixed with sulfur dioxide, iodide ions, and an organic base/alcohol. Iodide ions are produced by electrolysis and participate in the reactions. As long as the reaction continues, no free iodide ions remain in the solution.
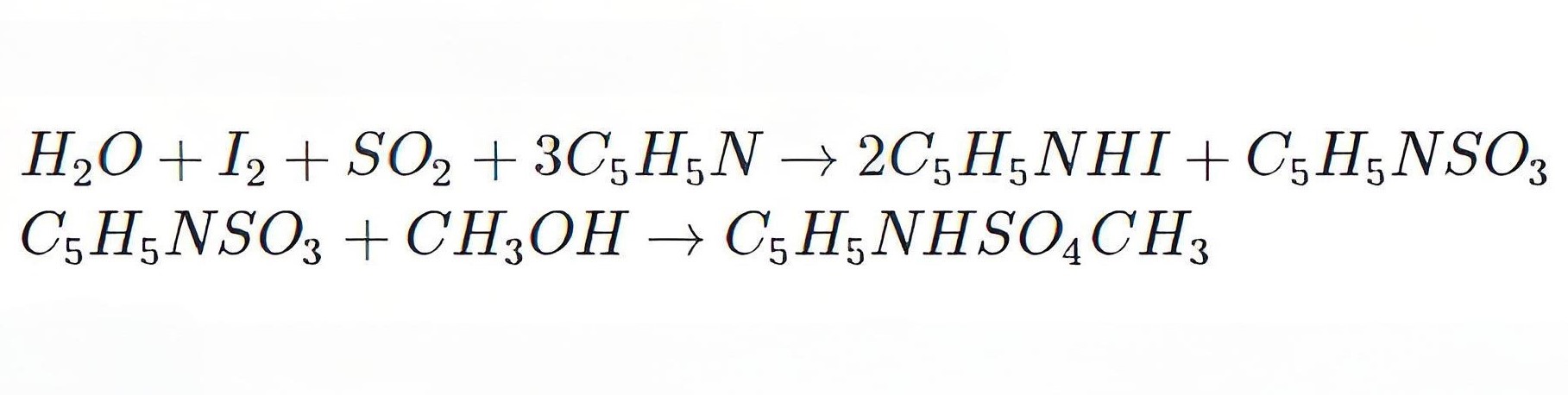
The iodide ions produced by electrolysis are consumed as long as water molecules are present. When there is no more water to react, the Karl Fischer reactions stop. Two platinum electrodes in the solution detect this endpoint. The presence of iodide ions after the reaction changes the voltage-current ratio, indicating the reaction’s end.
According to Faraday law of electrolysis, the amount of iodine reacting is proportional to the electricity consumed for electrolysis during the Karl Fischer reactions. By measuring the electricity consumed until the reaction ends, we can calculate the actual mass of iodine involved. From the reaction equation, we know that one mole of iodine reacts with one mole of water. Therefore, 127 grams of iodine will react with 18 grams of water. This allows us to determine the exact amount of water in the insulating oil sample.
Electrolysis Role
Electrolysis produces iodide ions, which react with water in the solution.
Detection of Reaction Endpoint
Platinum electrodes detect the endpoint of the Karl Fischer reaction when no more water is present.
Calculation of Water Content
Using the electricity consumed during the reaction, the exact quantity of water in the insulating oil is calculated.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













