What is a Transformer Core?
What is a Transformer Core?
Transformer Core Definition
A vital component of the transformer, it is responsible for providing the magnetic circuit to direct the magnetic field and convert the electromagnetic energy from the primary side to the secondary side. The design and quality of the core directly affect the efficiency, performance and life of the transformer.
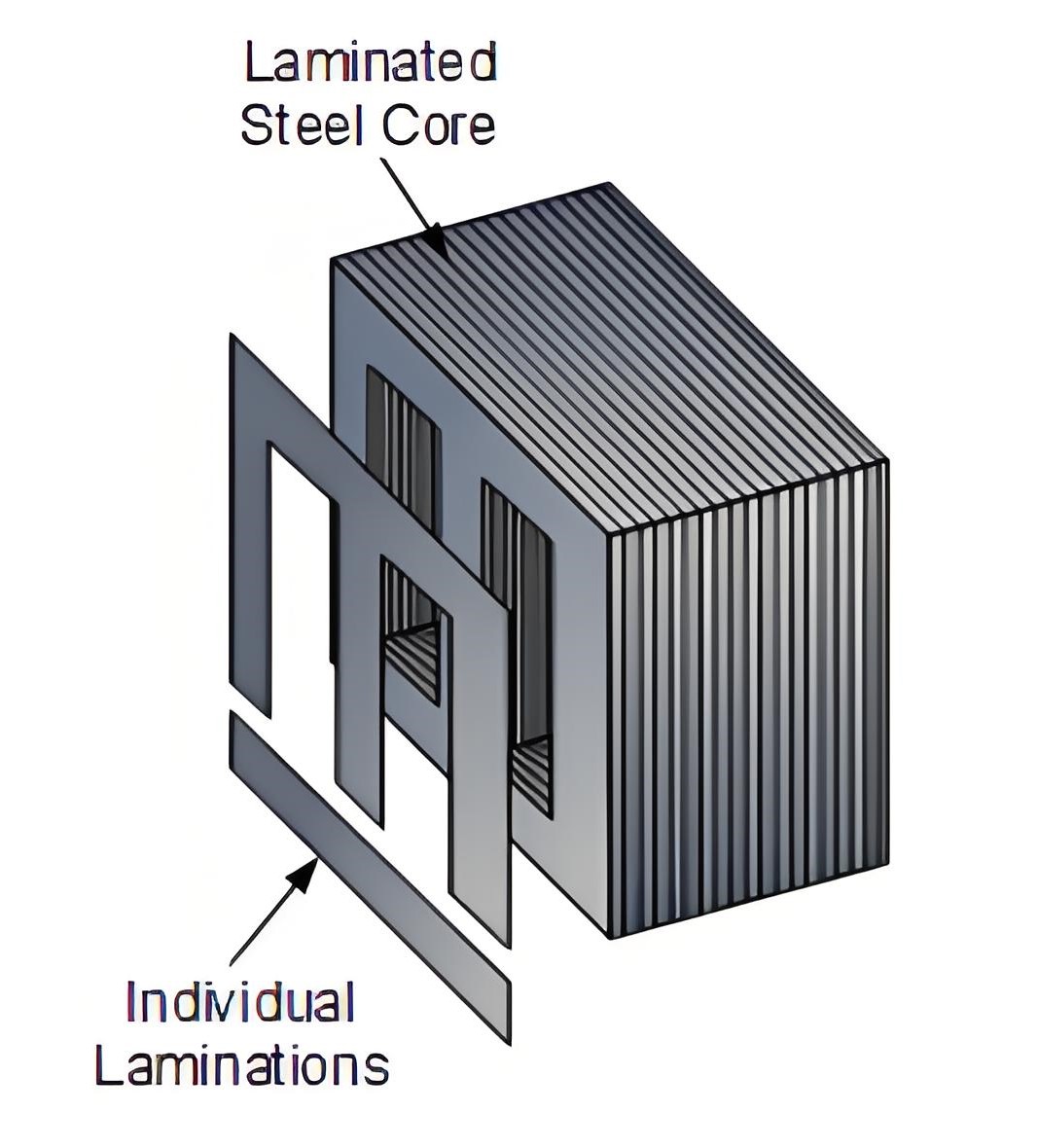
The role of the iron core
Providing magnetic circuit: The iron core provides a low reluctance path for the magnetic field in the transformer, allowing the magnetic field to move efficiently through the winding.
Energy conversion: Through the principle of electromagnetic induction, the core converts the electromagnetic energy of the primary side to the secondary side to achieve voltage conversion.
The material of the iron core
Silicon Steel (Electrical Steel)
It is the most common core material, with high permeability and low hysteresis loss characteristics.
Silicon steel sheets are usually specially treated to reduce eddy current losses and improve efficiency.
Amorphous Alloy
Lower hysteresis loss and eddy current loss for higher frequency applications.
The price is higher, but it can improve efficiency in some specific applications.
Ferrite
Suitable for high frequency transformer, with good temperature stability.
Usually used for small transformers in electronic devices.
Type of core
E-I core
It is composed of multiple E-shaped and I-shaped silicon steel sheets stacked, and is the most common iron core structure. Suitable for all types of transformers。
Toroidal Core
The shape is annular and is usually used in audio transformers and certain small power transformers.
It has higher permeability and lower magnetic leakage, but the processing cost is higher.
C-core
Composed of two semi-circular silicon steel sheets, it is commonly used in power adapters and transformers in switching power supplies.
Laminated Core
It is composed of multiple silicon steel sheets stacked by insulating coating to reduce eddy current loss.Suitable for all types of transformers.
Core design considerations
Magnetic saturation: The design needs to consider the maximum magnetic flux density of the iron core to avoid magnetic saturation under normal working conditions.
Eddy current losses: Eddy current losses are reduced through the use of sheet materials and insulating coatings.
Hysteresis loss: Select materials with low hysteresis loss to reduce energy loss.
Thermal stability: ensures that the core maintains stable performance at different temperatures.
Manufacturing process of iron core
Stamping: The silicon steel sheet is stamped into a specific shape by a die.
Stacking: The stamped silicon steel sheet is stacked to form an iron core.
Bonding: Sometimes special adhesives are used to bond the silicon steel sheets together to reduce vibration and noise.
Core maintenance
Cleaning: Clean the surface of the iron core regularly to avoid dust and dirt affecting heat dissipation.
Check: Check the physical state of the core regularly to ensure that there are no cracks or deformation.
Insulation: Ensure that the insulating material between the core and the winding is intact.
Matters needing attention
Safety operation: When performing maintenance or inspection, follow the safety operation rules to ensure the safety of personnel.
Environmental adaptability: Select core materials and structures suitable for local environmental conditions.
Conclusion
Through reasonable design and manufacture, the transformer core can ensure the efficient and stable operation of the transformer.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













