What is Transformer Cooling System?
What is Transformer Cooling System?
Transformer Cooling System Definition
A transformer cooling system is defined as methods used to dissipate heat generated in transformers to prevent damage and ensure efficiency.
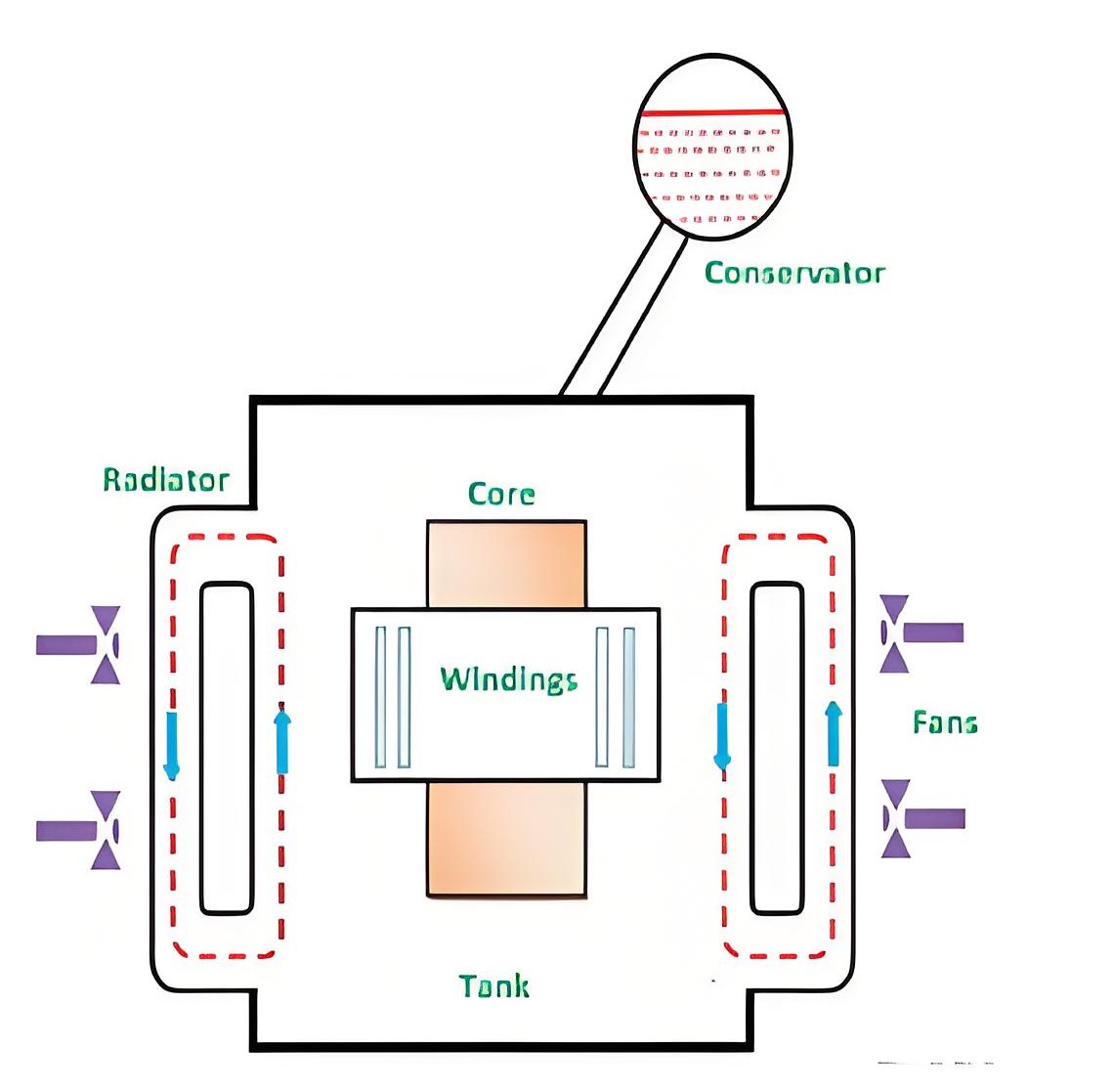
Components of the cooling system
Radiators or Coolers
Provides a large area of heat exchange surface, so that the heat in the oil can be transferred to the surrounding air or water.
Fans
Accelerate air flow and improve heat dissipation efficiency.
Oil Pumps
In a forced oil circulation system, it is used to push the oil to circulate inside and outside the transformer.
Coolers
In water-cooling systems, it is used to transfer heat from oil to water.
Control device
Including temperature controller, flow controller, etc., for monitoring and regulating the operation of the cooling system.
Type of cooling system
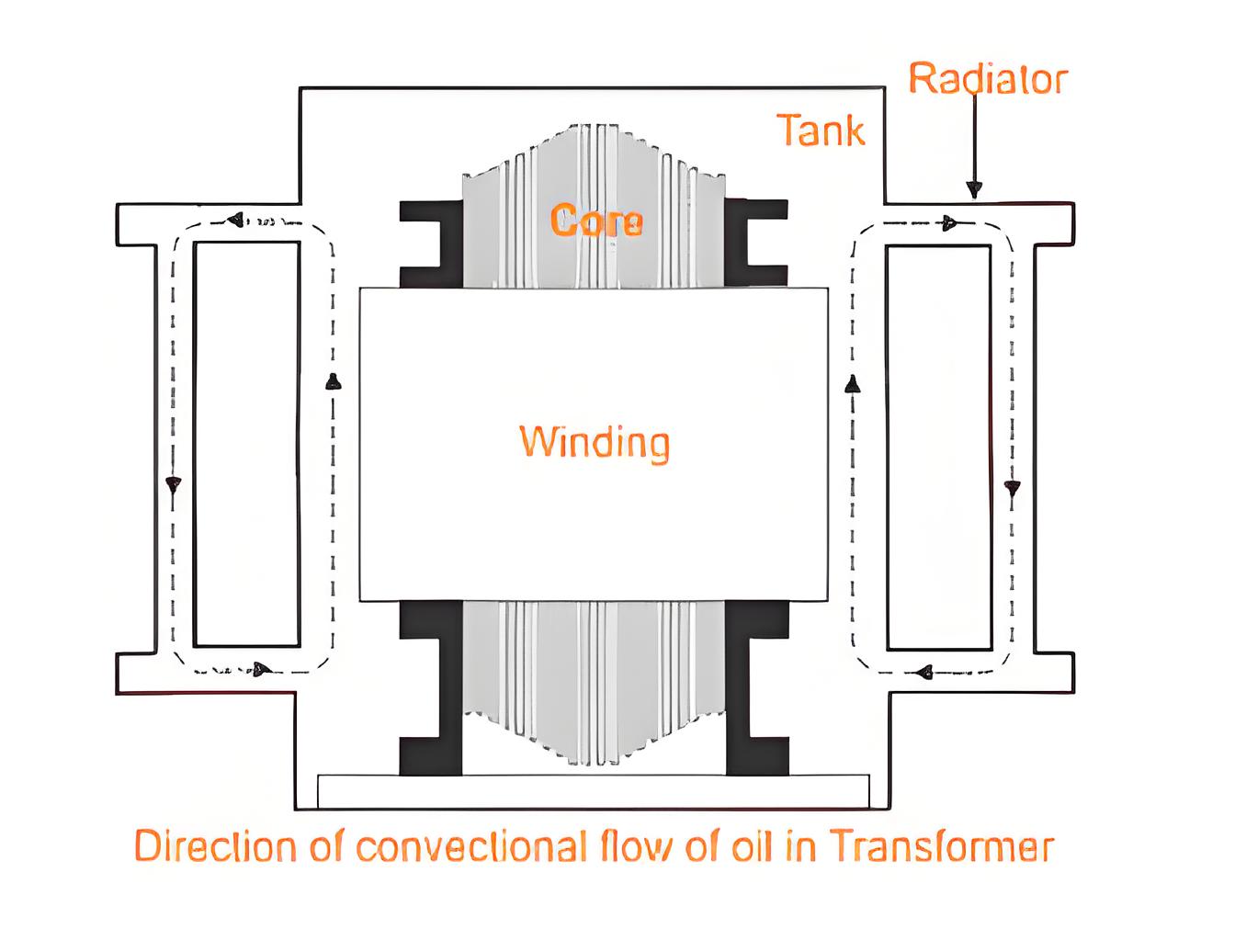
ONAN Cooling
ONAN cooling uses natural oil and air circulation to cool the transformer, relying on convection for heat dissipation.
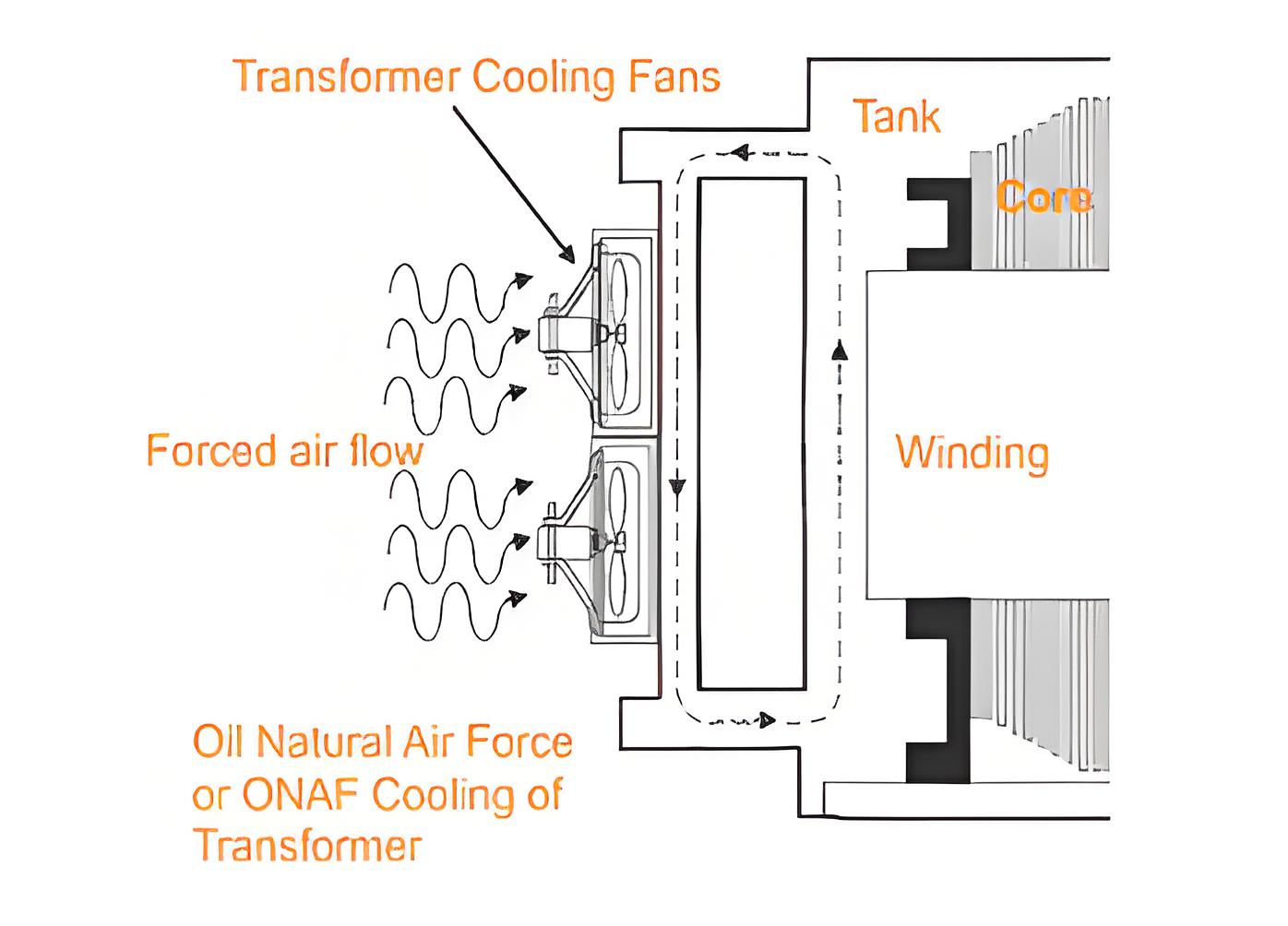
ONAF Cooling
ONAF cooling employs fans to blow air over the transformer, enhancing heat dissipation by forced air circulation.
ODAF Transformer
The ODAF (Oil Directed Air Forced) transformer uses directed oil flow and forced air to cool high-rating transformers efficiently.
ODAF Transformer
The ODAF (Oil Directed Air Forced) transformer uses directed oil flow and forced air to cool high-rating transformers efficiently.
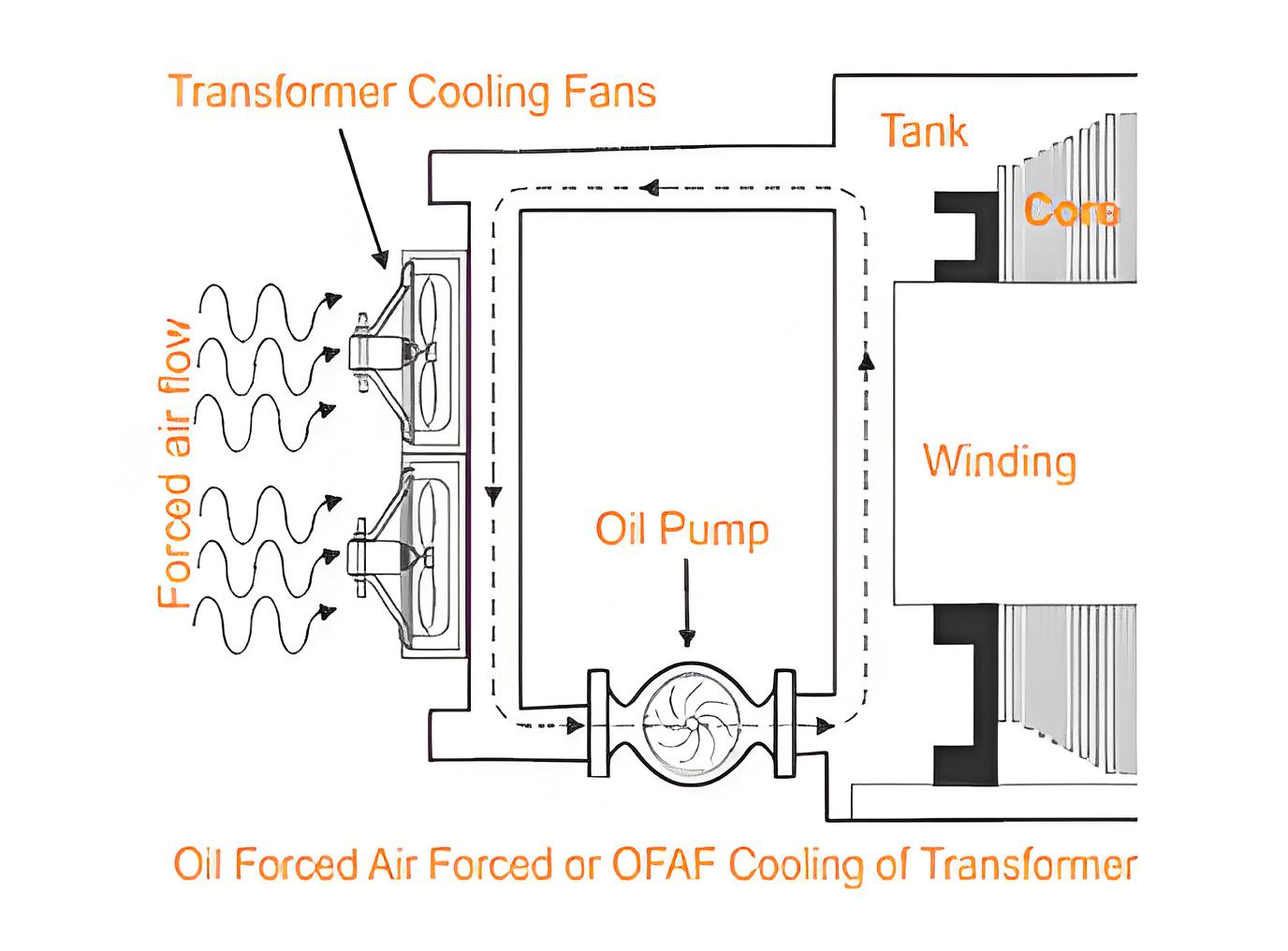
OFAF Cooling
OFAF cooling combines oil pumps and air fans to circulate oil and cool the transformer quickly and efficiently.
Conclusion
Through reasonable design and maintenance, the transformer cooling system can ensure the safe and stable operation of the transformer
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













