What is an Electrical Fuse?
What is an Electrical Fuse?
Electrical Fuse Definition
An electrical fuse is a protective device that breaks the circuit when the current exceeds a predetermined value to prevent damage.
Fuse Wire Function
The fuse wire carries normal current without excessive heating but melts and breaks the circuit when excess current flows through.
Major Parameter
Minimum Fusing Current
Current Rating of Fuse
Fusing Factor
Prospective Current in Fuse
Melting Time of Fuse
Operating Time of Fuse
Fuse Law
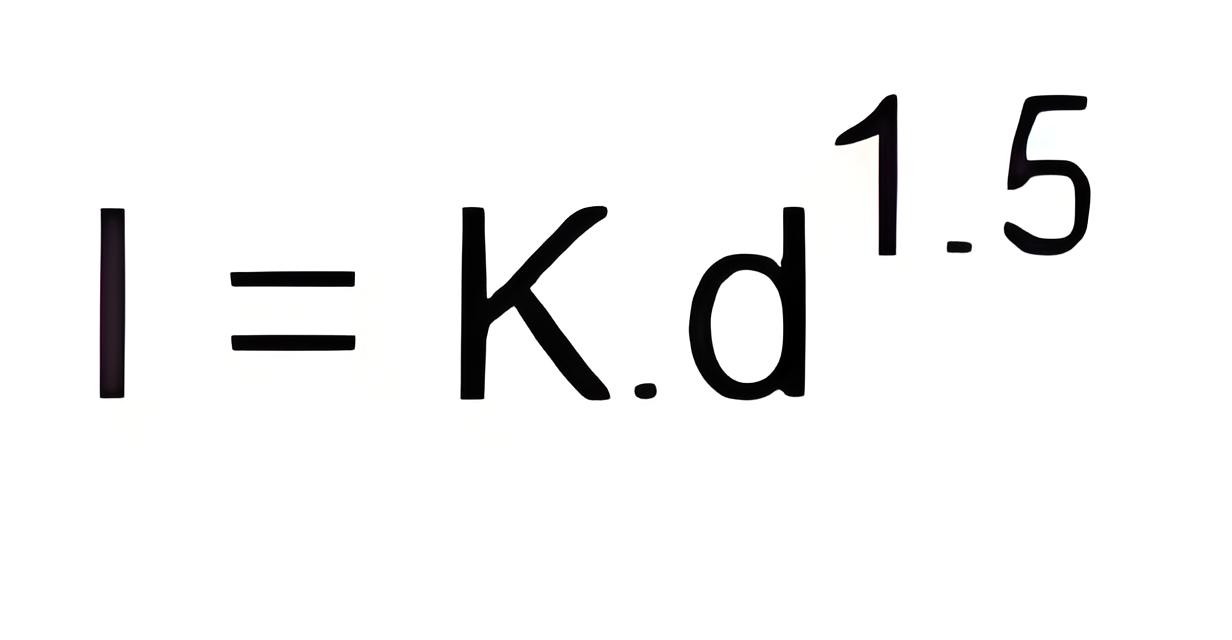
Materials for Fuse Wires
Common fuse wire materials include tin, lead, zinc, silver, antimony, copper, and aluminum, each with specific melting points and resistances.
HRC Fuse
An HRC fuse, or High Rupturing Capacity fuse, can handle heavy short-circuit currents for a set period before blowing, providing reliable circuit protection.
Operating Time of Fuse
The operating time of a fuse is the sum of its melting time and arcing time, defining how long it takes to interrupt the current flow during a fault.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













