What is a Deaerating Heater ?
What is a Deaerating Heater ?
Deaerating Heater Definition
A deaerating heater (deaerator) is defined as a device that removes dissolved gases from boiler feedwater to prevent corrosion and improve efficiency.
How It Works
Deaerating heaters use steam to heat the feedwater and strip dissolved gases, which are then vented away.
Efficiency Factors
Temperature
Pressure
Steam quality
Deaerator design
Benefits
Improve boiler efficiency
Reduce corrosion
lower chemical costs
Increase reliability
Types of Deaerating Heaters
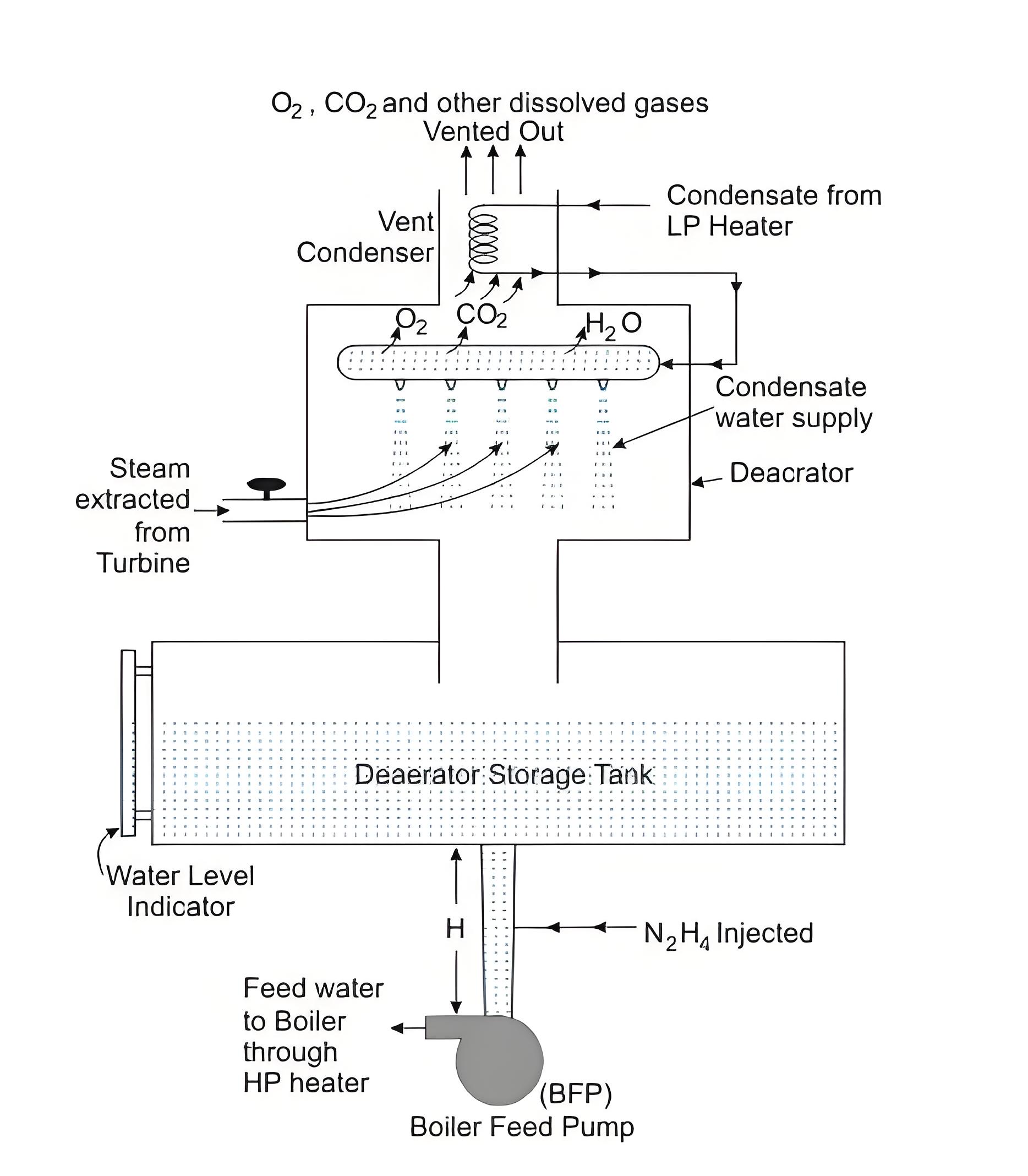
Tray type
Advantages
It can handle a wide range of feedwater flow rates and temperatures.
It can achieve very low levels of dissolved oxygen (less than 5 ppb) and carbon dioxide (less than 1 ppm).
It has a large storage capacity for feedwater, which helps to maintain constant pressure and temperature in the boiler.
Disadvantages
It requires a large amount of steam for deaeration, which reduces the thermal efficiency of the cycle.
It has a high capital cost and maintenance cost due to the complexity and size of the vessel and trays.
It is susceptible to scaling and fouling on the trays, which reduces heat transfer and deaeration efficiency.
Spray type
Advantages
It requires less steam for deaeration than a tray-type deaerating heater, which improves the thermal efficiency of the cycle.
It has a lower capital cost and maintenance cost than a tray-type deaerating heater due to the simplicity and compactness of the vessel and nozzle.
It is less prone to scaling and fouling than a tray-type deaerating heater due to the high velocity and turbulence of the water and steam.
Disadvantages
It cannot handle very high or very low feedwater flow rates and temperatures without affecting the deaeration efficiency.
It cannot achieve as low levels of dissolved oxygen (about 10 ppb) and carbon dioxide (about 5 ppm) as a tray-type deaerating heater.
It has a smaller storage capacity for feedwater than a tray-type deaerating heater, which makes it more sensitive to pressure and temperature fluctuations in the boiler.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













