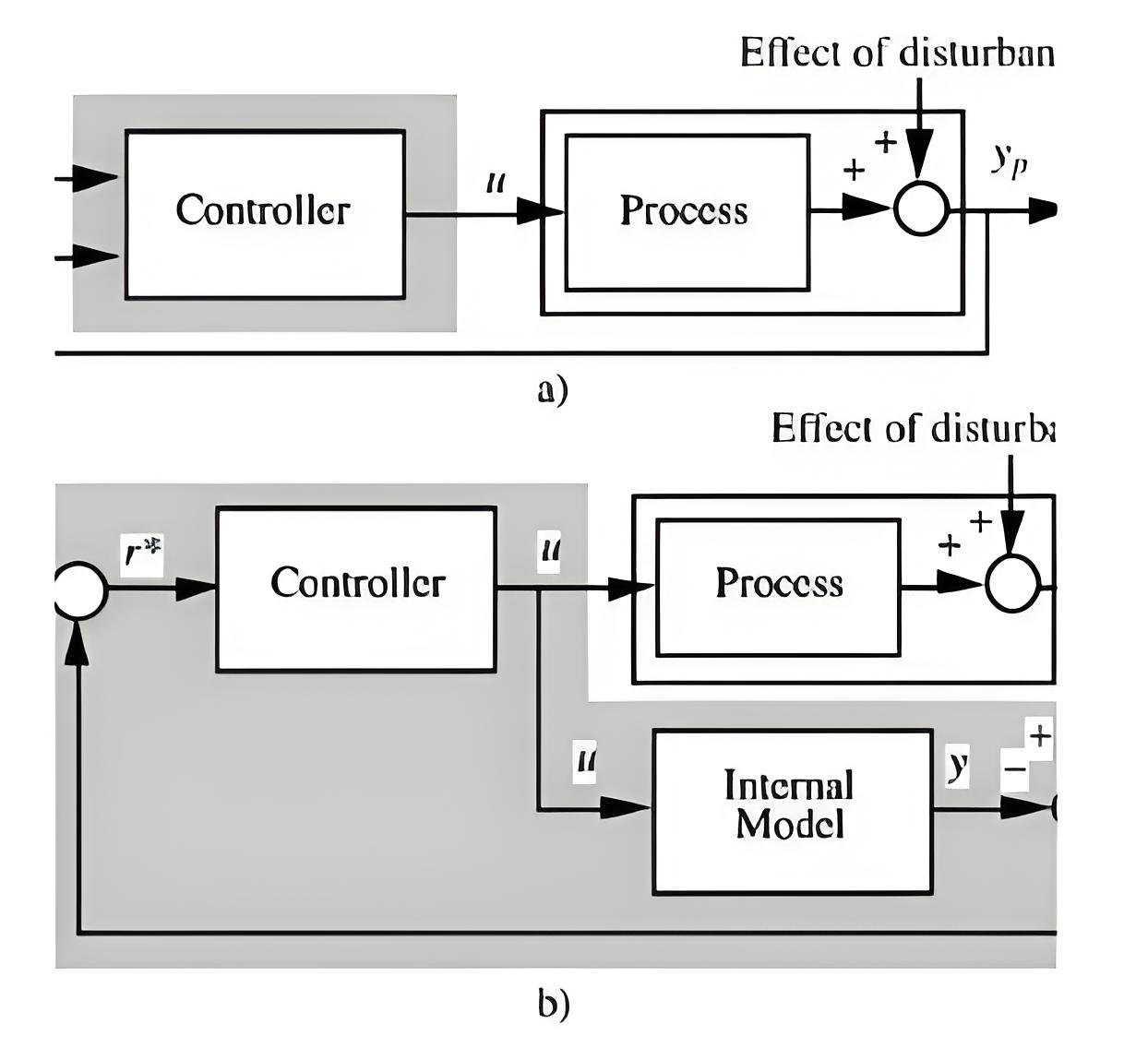
Type of control system
Control Systems Overview
A control system is a device or set of devices that manage and regulate the behavior of other devices to achieve desired results.
Linear Systems
Linear control systems adhere to principles of homogeneity and additivity, ensuring consistent and proportional responses.
Non-Linear Systems
Non-linear control systems do not follow linear rules, often resulting in behavior that varies significantly with different inputs.
Digital vs Analog
Digital systems provide improved accuracy, reliability, and efficiency over analog systems, especially in handling non-linear control systems.
Single Input Single Output Systems
These are also known as SISO type of system. In this, the system has single input for a single output. Various example of this kind of system may include temperature control, position control system, etc.
Multiple Input Multiple Output Systems
Known as MIMO systems, these have multiple outputs for multiple inputs. Examples include Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) among others.
Lumped Parameter System
In these types of control systems, the various active and passive components are assumed to be concentrated at a point and that’s why these are called lumped parameter type of system. Analysis of such type of system is very easy which includes differential equations.
Distributed Parameter System
In these types of control systems, the various active (like inductors and capacitors) and passive parameters (resistor) are assumed to be distributed uniformly along the length and that’s why these are called distributed parameter type of system. Analysis of such type of system is slightly difficult which includes partial differential equations.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













