What is Cogeneration ?
What is Cogeneration ?
Cogeneration Definition
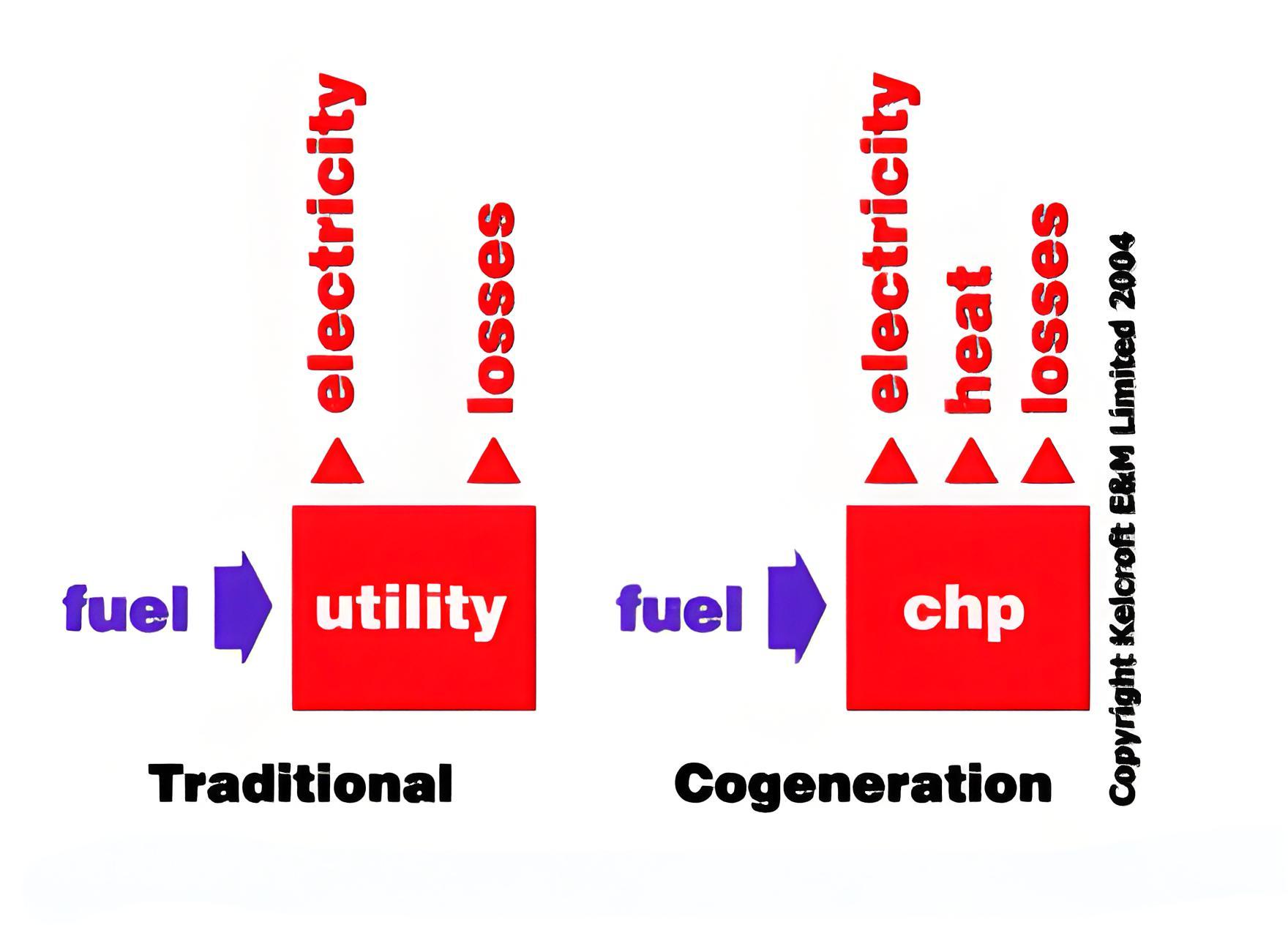
Cogeneration, or combined heat and power (CHP), is defined as a system that produces both electricity and heat from a single fuel source.
High Efficiency
Cogeneration plants are highly efficient, with efficiency rates of 80-90%, compared to the 35% efficiency of conventional power plants.
Environmental Benefits
Cogeneration reduces emissions of pollutants and greenhouse gases, helping to combat climate change.
Economic Advantages
Cogeneration helps to improve the efficiency of the plant.
Cogeneration reduce air emissions of particulate matter, nitrous oxides, sulphur dioxide, mercury and carbon dioxide which would otherwise leads to greenhouse effect.
It reduces cost of production and improve productivity.
Cogeneration system helps to save water consumption and water costs.
Cogeneration system is more economical as compared to conventional power plant.
Configuration of Cogeneration Plant
Gas turbine Combine heat power plants which uses the waste heat in the flue gas emerging out of gas turbines.
Steam turbine Combine heat power plants that use the heating system as the jet steam condenser for the steam turbine.
Molten-carbonate fuel cells have a hot exhaust, very suitable for heating.
Combined cycle power plants adapted for Combine Heat and Power.
Types of Cogeneration Plants
Topping cycle power plant
Bottoming cycle power plant
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













