What are Voltage and Turn Ratio Test of Transformer?
What are Voltage and Turn Ratio Test of Transformer?
Transformer Turn Ratio Definition
The transformer turn ratio is defined as the ratio of the number of turns in the HV winding to the number of turns in the LV winding.
Voltage Ratio Test of Transformer
This test checks if the voltage ratio matches the expected turn ratio by applying voltage to the HV winding and measuring the induced voltage in the LV winding.
Testing Procedure
First, the tap changer of transformer is kept in the lowest position and LV terminals are kept open.
Then apply 3-phase 415 V supply on HV terminals. Measure the voltages applied on each phase (Phase-phase) on HV and induced voltages at LV terminals simultaneously.
After measuring the voltages at HV and LV terminals, the tap changer of transformer should be raised by one position and repeat test.
Repeat the same for each of the tap position separately.
Use of TTR Meter
The theoretical turn ratio is adjusted on the TTR meter by changing the settings on the adjustable transformer until the percentage error indicator shows a balance.
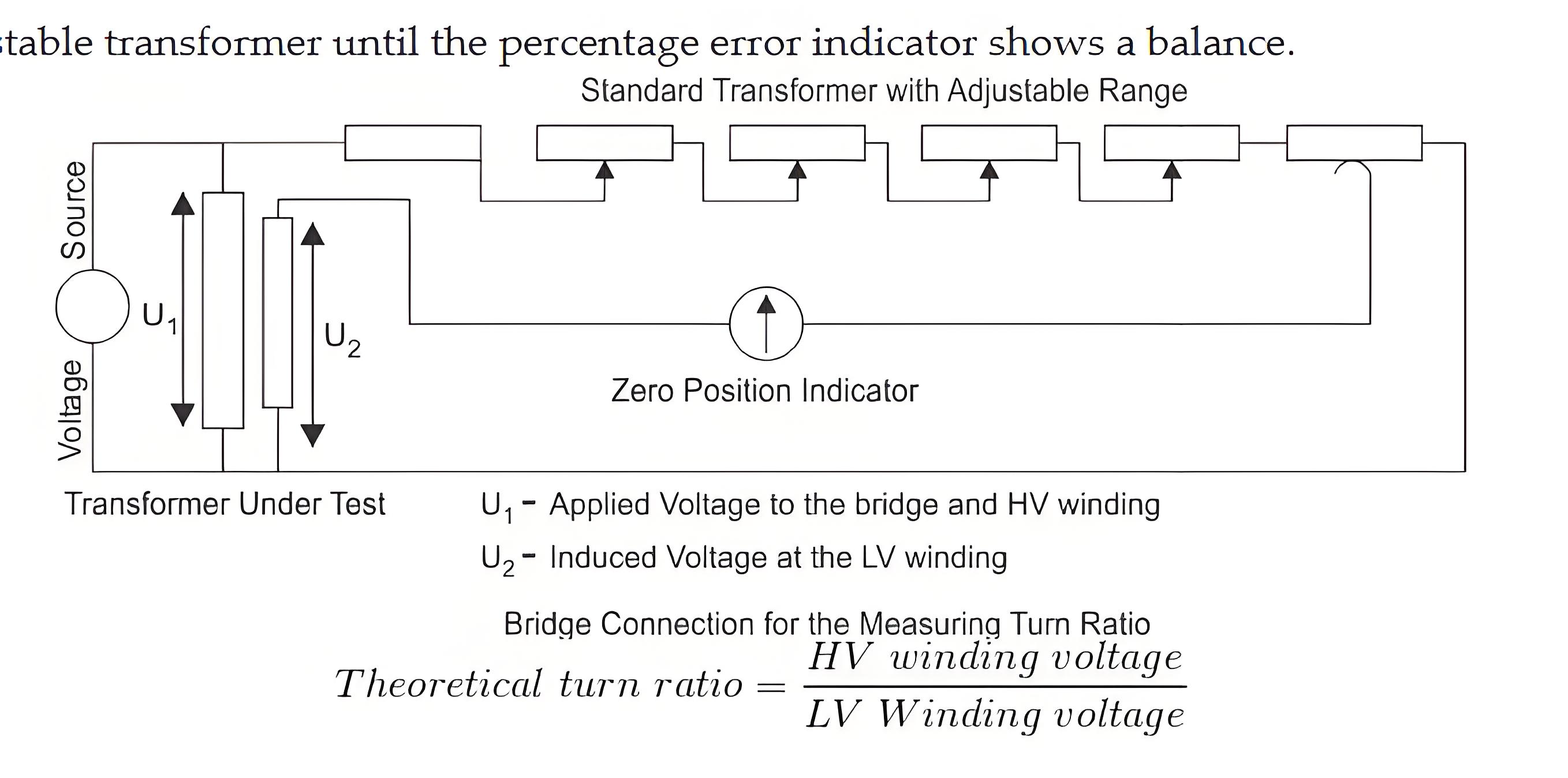
The reading on this indicator implies the deviaton of measured turn ratio from expected turn ratio in percentage.
Detecting Faults
Out-of-tolerance, ratio test of transformer can be due to shorted turns, especially if there is an associated high excitation current. Open turns in HV winding will indicate very low exciting current and no output voltage since open turns in HV winding causes no excitation current in the winding means no flux hence no induced voltage.

The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.