What is a Instrument Transformer?
What is a Instrument Transformer?
Instrument Transformer Definition
An instrument transformer is a device that steps down high voltage and current from power systems to manageable levels for measurement and safety.

Advantages
Large voltages and currents in AC power systems can be accurately measured using instruments with small ratings, such as 5 A and 110–120 V.
Lower the cost
Which reduces the electrical insulation requirement for measuring instruments and protective circuits and also assures the safety of operators.
Several measuring instruments can be connected through a single transformer to power system.
Due to low voltage and current level in measuring and protective circuit, there is low power consumption in measuring and protective circuits
Types of Instrument Transformers
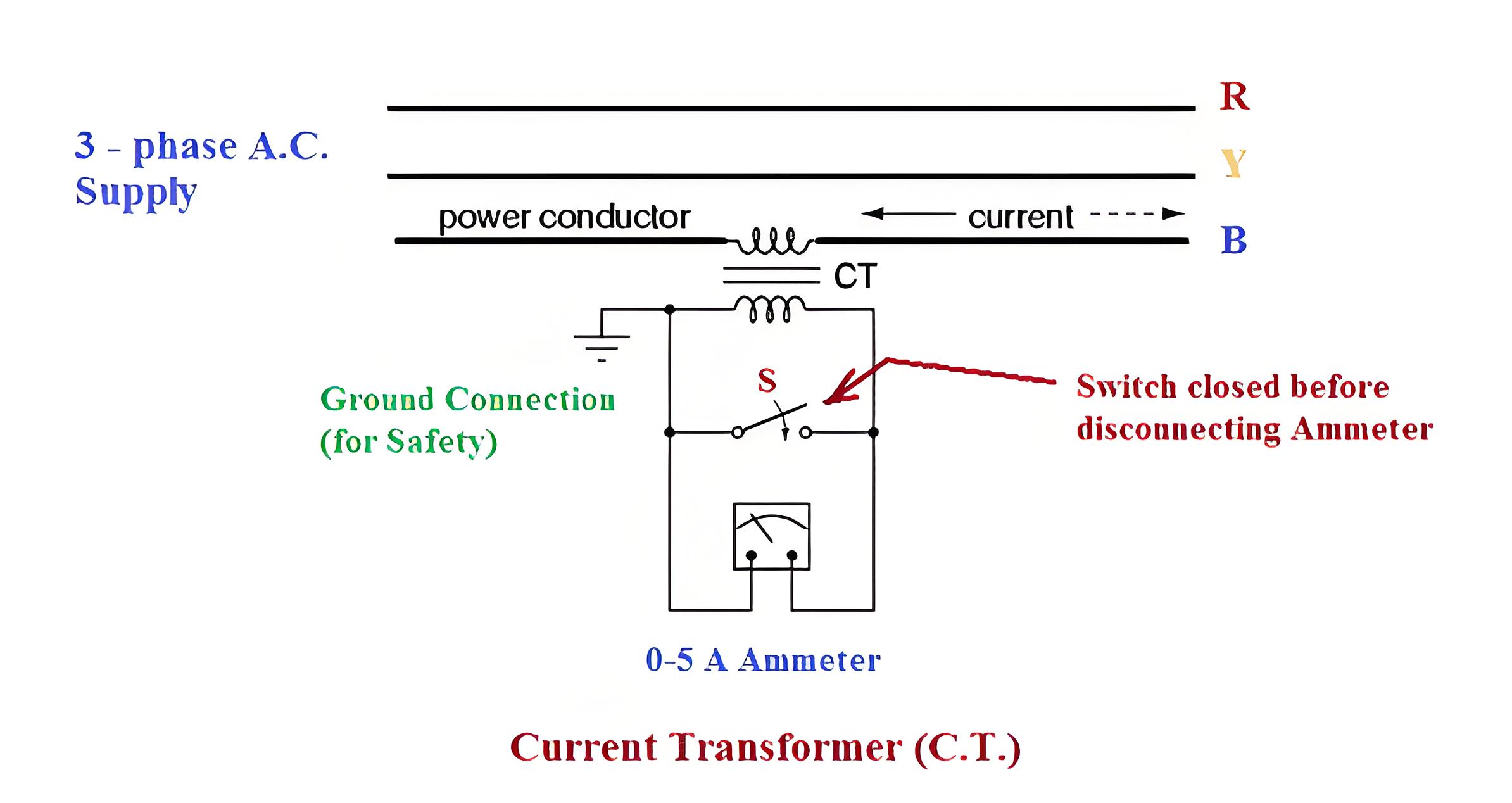
Current Transformers (C.T.)
Current transformer is used to step down the current of power system to a lower level to make it feasible to be measured by small rating Ammeter (i.e. 5A ammeter). A typical connection diagram of a current transformer is shown in figure below.
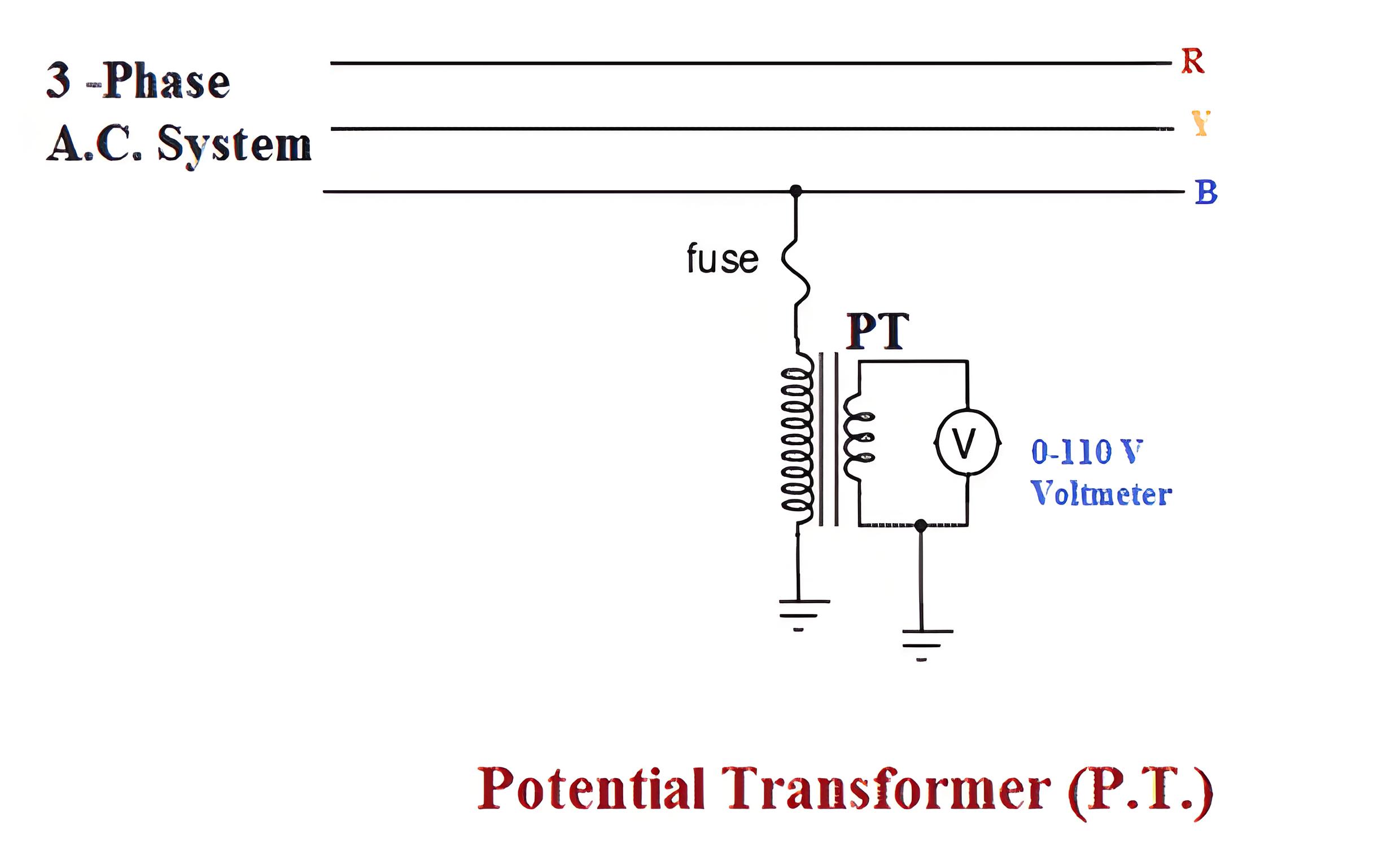
Potential Transformers (P.T.)
Potential transformer is used to step down the voltage of power system to a lower level to make is feasible to be measured by small rating voltmeter i.e. 110 – 120 V voltmeter. A typical connection diagram of a potential transformer is showing figure below.
Safety and Functionality
These transformers include safety features such as grounding and operation under specific circuit conditions (short-circuited for C.T.s, open-circuited for P.T.s) to ensure accuracy and prevent accidents.
Educational Resources
Books by authors like Bakshi and Morris provide additional information and technical insights into the use and application of instrument transformers.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.