What is are High Voltage Transformer?
What is are High Voltage Transformer?
High Voltage Transformer Definition
A high voltage transformer is defined as a device that changes high-voltage AC power to low-voltage AC power or vice versa, functioning above 35 kV.
Core Applications
High voltage transformers are crucial for testing electrical components, efficient power distribution, and enhancing voltage stability through FACTS systems.
Essential Features
These transformers are characterized by their ability to handle high voltages and currents, requiring robust insulation and cooling systems.
Testing Standards
High voltage transformers undergo rigorous testing to meet IEEE standards, ensuring their reliability and safety in various electrical applications.
Transformer Types
Testing Transformers
Testing transformers are used to generate high voltages for testing the insulation strength and performance of electrical equipment and components, such as cables, insulators, switchgear, motors, etc.
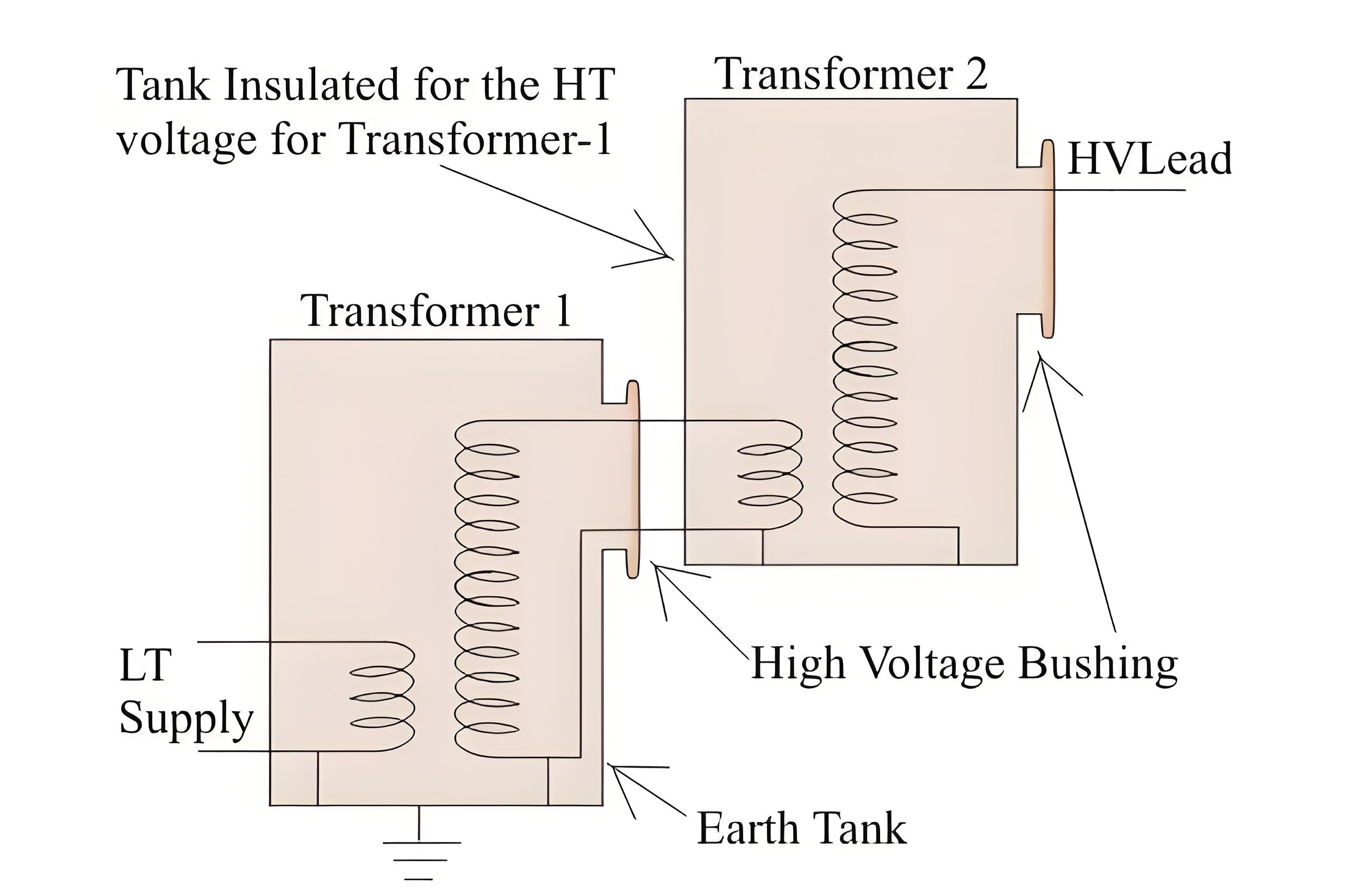
Cascaded Testing Transformers Advantages
The higher output voltage can be achieved with smaller and cheaper units
Lower insulation stress on each unit due to lower individual voltages
Higher efficiency and lower losses due to lower currents
Cascaded Testing Transformers Disadvantages
More complex wiring and synchronization of the primary sources
Higher risk of partial discharge and corona due to higher total voltage
Higher capacitance and inductance of the secondary circuit due to longer wires
Power Transformers
Power transformers are used to step up or step down the voltage level for power transmission and distribution.
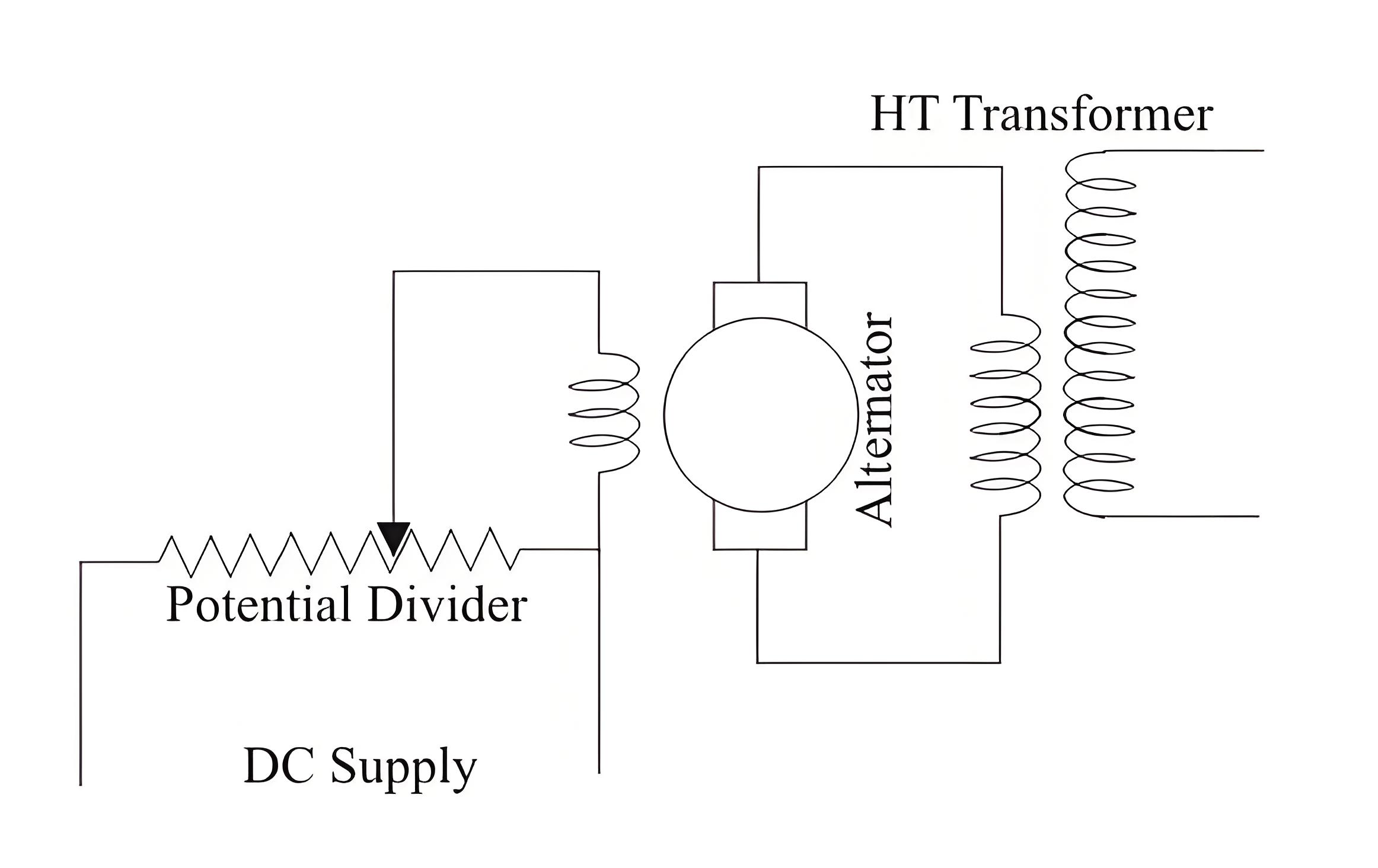
Power Transformers Advantages
They reduce power losses, improve voltage regulation, and increase system stability and reliability.
HVDC Transformers
HVDC transformers convert AC power to DC power for use in high-voltage direct current systems, essential for long-distance power transmission and connecting different power grids.
HVDC Transformers Advantages
They can withstand high DC voltages and currents, harmonics, polarity reversals and transient overvoltages.
FACTS Transformers
FACTS transformers manage reactive power and maintain voltage stability in AC power systems, enhancing performance with advanced power electronics.
FACTS Transformers Advantages
They must also provide precise voltage regulation and fast response.
Special Transformers Advantages
Special transformers cater to unique applications that demand specific features
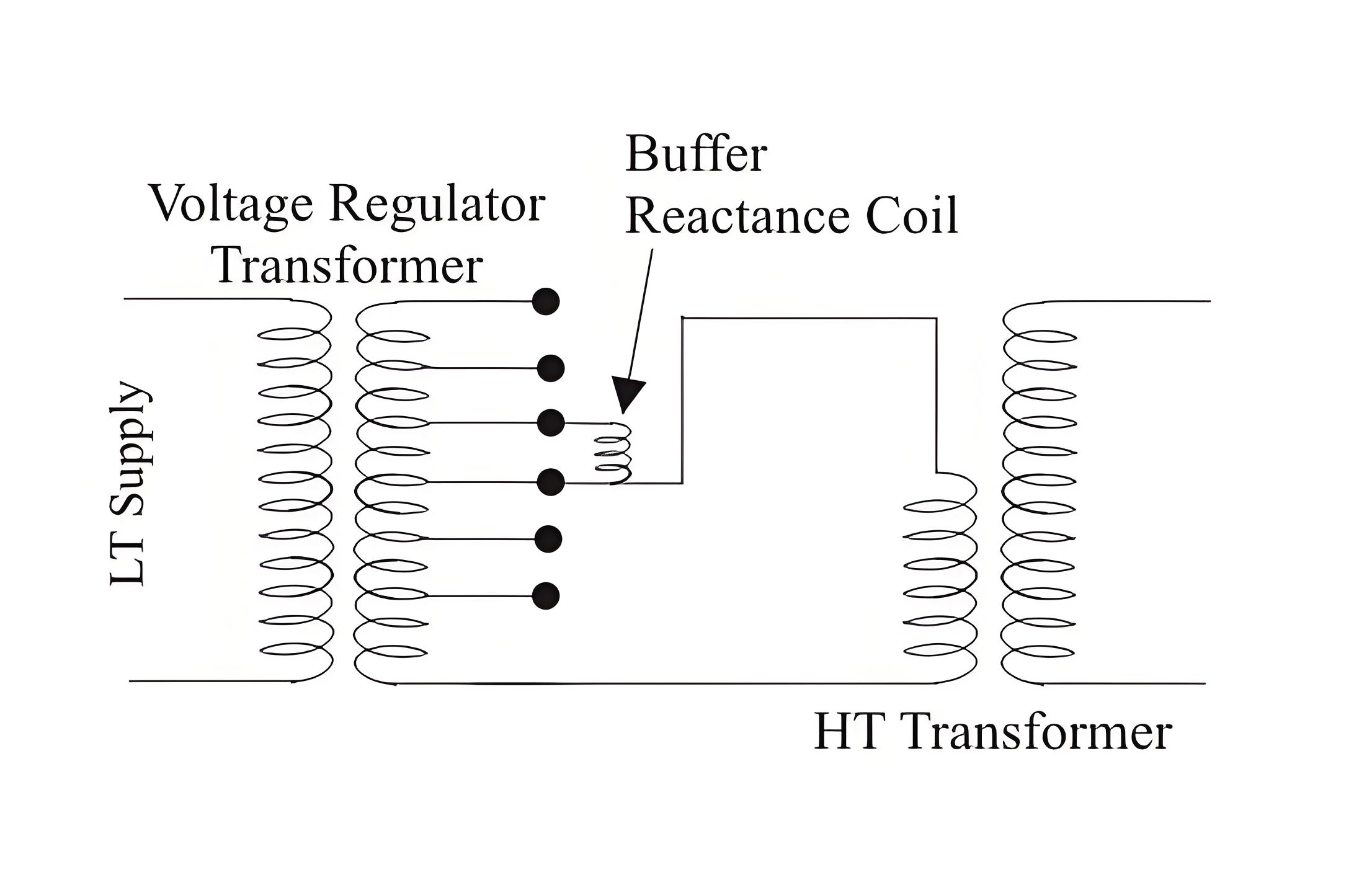
Special Transformers Type
Impulse transformers
High-frequency transformers
Instrument transformers
Isolation transformers
Auto-transformers
Arc-furnace transformers
Traction transformers
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.