Statement, Formula, Uses, and Limits of Coulomb’s Law
Coulomb’s Law:
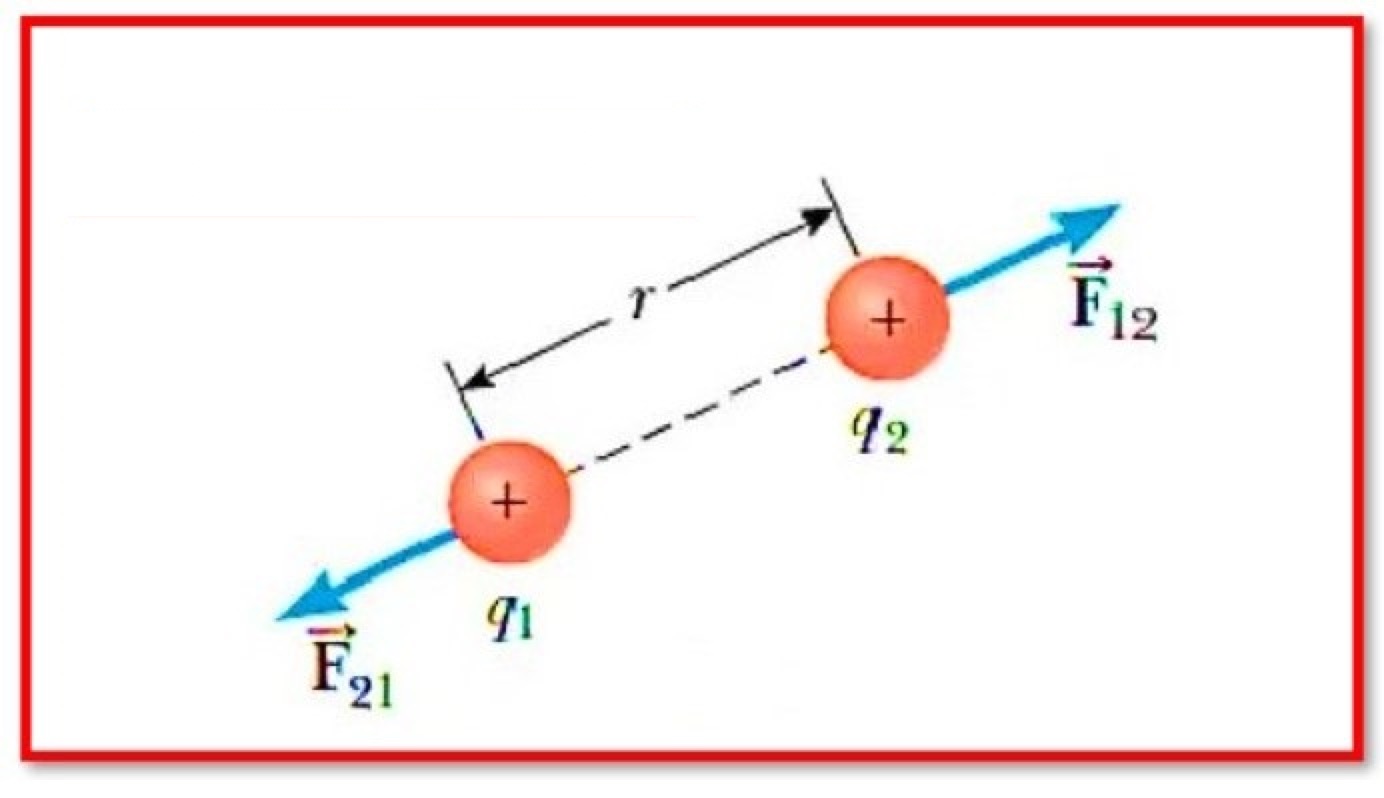
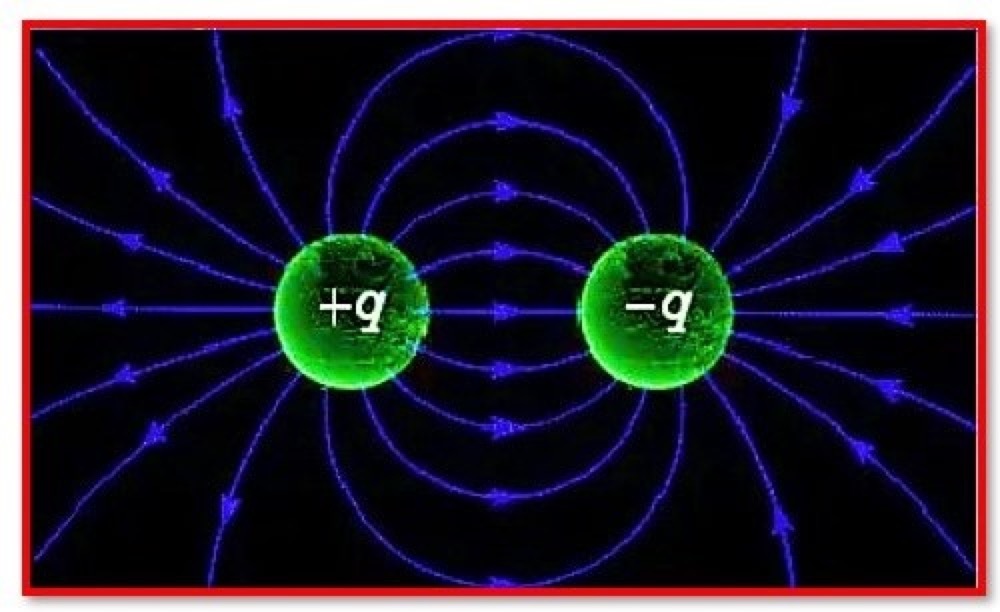
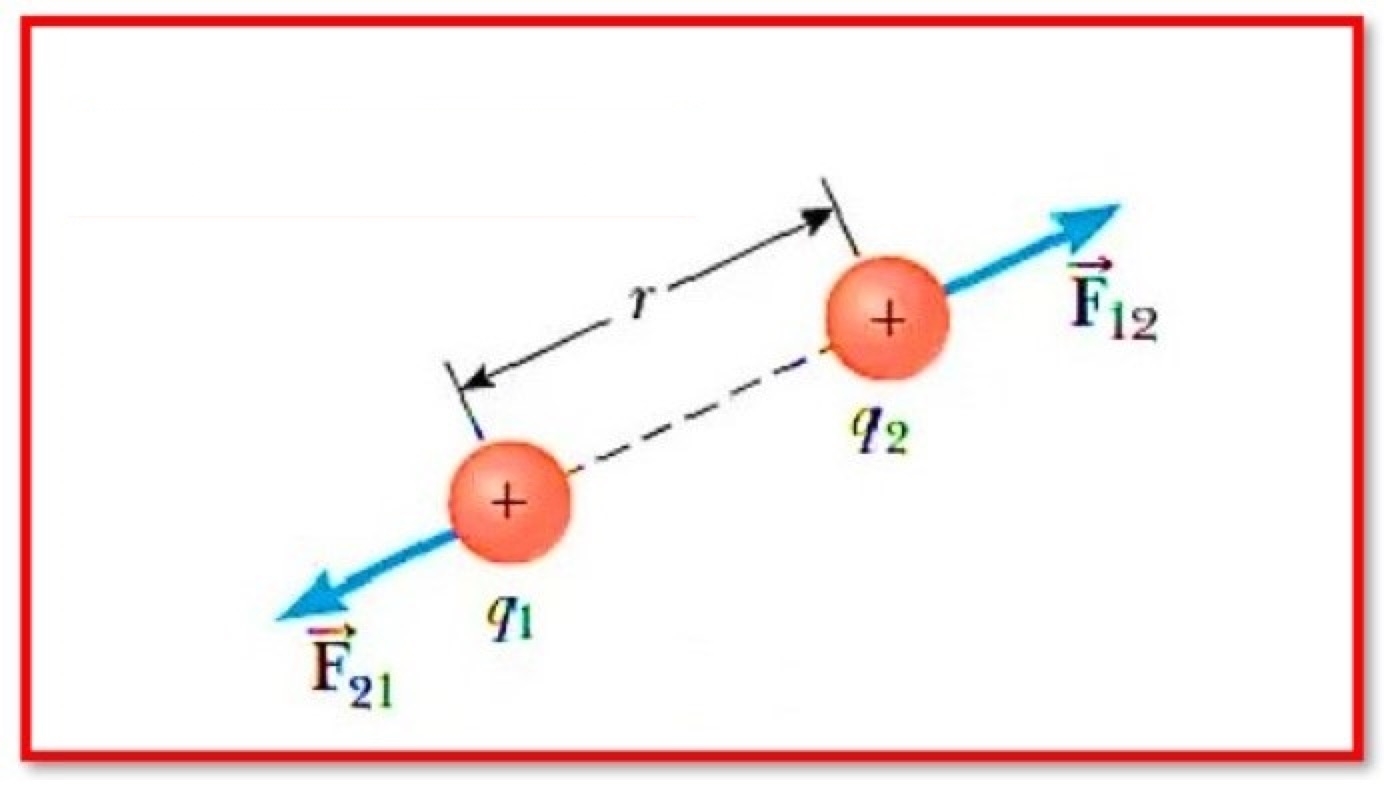
Coulomb’s law states that the force of attraction or repulsion between two charges is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of their distance from one another. It functions on the section that connects the two charges that are regarded of as point charges.
Coulomb’s Law Formula:
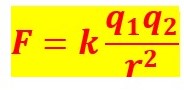
Where,
F= Electric Force,
K= Coulomb’s Constant,
q1, q2 = charges
r= between distance
What Is one Coulomb of Charge?
It is known as a coulomb when two charges are placed one metre apart in a vacuum and repel one another with a force of 9 X 109 N.
What is Coulomb Force?
Coulomb force, commonly referred to as electrostatic force or Coulomb interaction, is the attraction or repulsion of charged particles or substances. The Coulomb force is a neutral, internal, reciprocal force.
Application of Coulomb’s Law:
The most fundamental law of electrostatic physics, known as Coulomb’s law, is employed in the calculations for the following key applications:
1. The electrostatic force that exists between the point charges is calculated by Coulomb’s law.
2. Additionally, the distance between two point charged bodies is determined by Coulomb’s law.
3. The electrostatic force caused by several charges acting on a point charge can also be calculated using Coulomb’s law.
Limitations of Coulomb’s Law:
Coulomb’s law only applies when the point charges are balanced.
Coulomb’s law may not be applicable when charged bodies have arbitrary shapes. It is because we are unable to determine the separation between the centres of bodies for arbitrary shaped bodies.
Coulomb’s law cannot be used to calculate the force between charges on the large planets.
Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
As an electrical engineer with 5 years of experience, I focus on transformer and circuit breaker reliability in 110/33-11kV and 33/11kV substations. I am a professional electrical engineer with experience in transformer service and maintenance.