Explain Biot Savart Law
What exactly is Biot Savart Law?
The Biot Savart Law is a mathematical equation that describes the magnetic field produced by a constant electric current. It connects the magnetic field to the electric current’s size, direction, length, and proximity.
Ampere’s circuital law and
Gauss’ theorem
are both consistent with the Biot-Savart law.
The Biot-Savart law is essential to magnetostatics, having a similar function to Coulomb’s law in electrostatics.
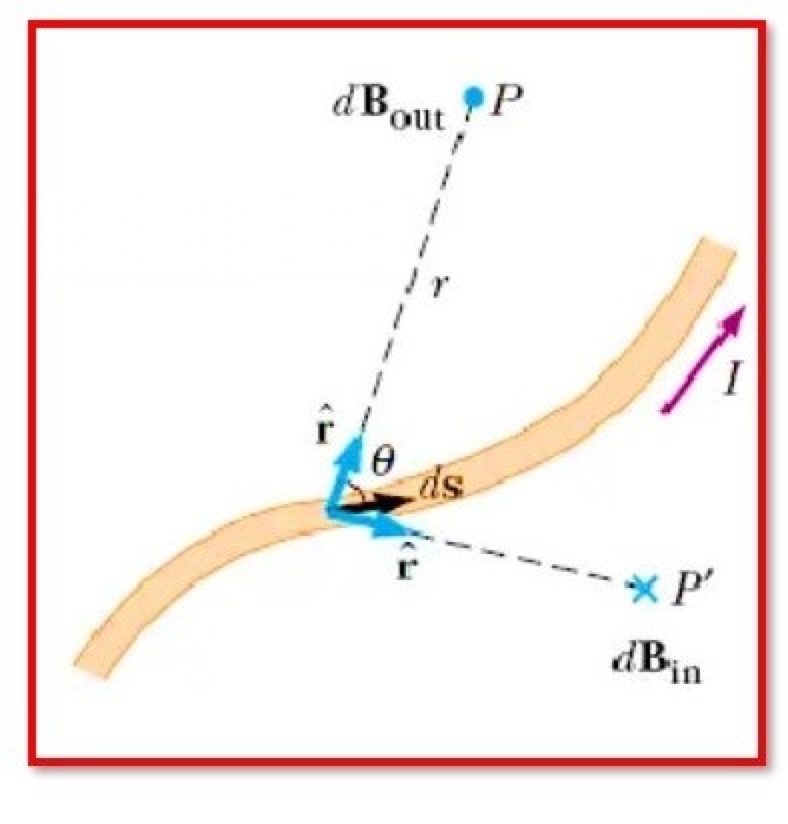
Biot Savart Law Statement:
According to the Biot-Savart law, the magnetic flux density produced at any point by a small current element is:
Directly proportional to the length of the current element, the magnitude of the current, and the sine of the angle between the direction of the current and the line connecting the current element to the point of the magnetic field, and
Inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the current element and the centre of the magnetic field,
Where the direction of the magnetic field at that place is the same as the direction.
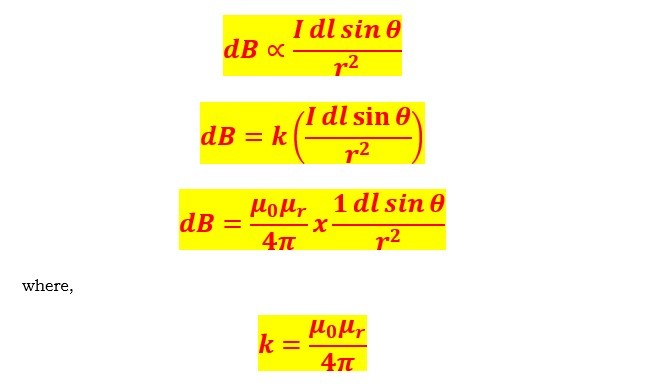
l = Length,
K = Constant
Importance of the Biot-Savart Law:
In electrostatics, the Biot-Savart law is analogous to Coulomb’s law.
The law also applies to very small conductors that carry current.
The law is true for symmetrical current distribution.
Biot Savart Law Applications:
Biot-Savart law can be used to compute magnetic responses at the atomic or molecule level.
It is also used to compute the velocity caused by vortex lines in aerodynamic theory.
Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
As an electrical engineer with 5 years of experience, I focus on transformer and circuit breaker reliability in 110/33-11kV and 33/11kV substations. I am a professional electrical engineer with experience in transformer service and maintenance.