What is a Shunt Reactor?
What is a Shunt Reactor?
Shunt Reactor Definition
A shunt reactor is defined as an electrical device used in high voltage power systems to stabilize voltage during load changes.
Voltage Stabilization
It controls dynamic overvoltage and provides capacitive reactive power compensation in systems above 400kV.
Impedance Types
Shunt reactors come in gapped core or magnetically shielded air core types to maintain constant impedance and avoid harmonic currents.
Loss Measurement Methods
Losses of a shunt reactor should be measured at rated voltage and frequency. For high voltage reactors, measure losses at a lower voltage and then scale up by multiplying the loss by the square of the ratio of rated current to the current at the test voltage.
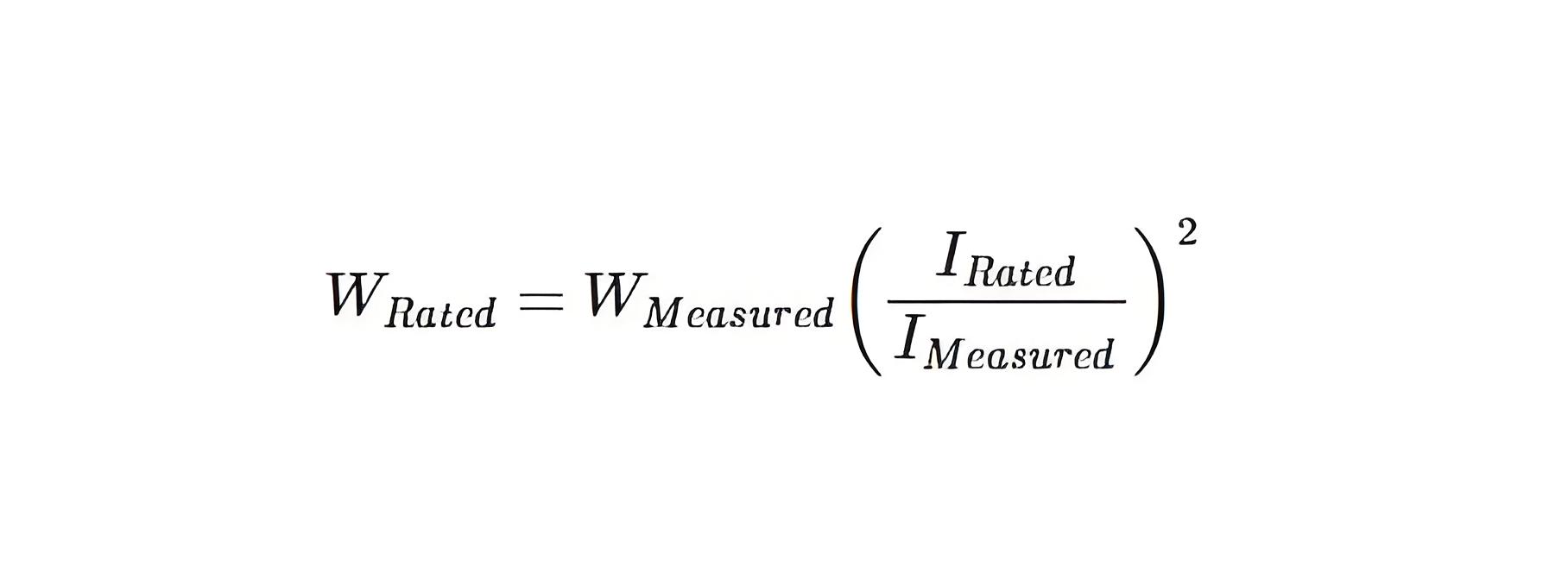
As the power factor of the shunt reactor is very low, loss measurement of shunt reactor by conventional wattmeter is not very reliable, instead of bridge method of measurement may be adopted for better accuracy.
This test can not segregate the losses in various parts of the reactor. To avoid, correction of test result for a reference temperature, it is preferable to take the measurement when the average temperature of the winding becomes equal to the reference temperature.
Operating Conditions
Must handle continuous voltage without overheating, ensuring it operates within safe temperature limits.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













