Specifications or Rating of Power Capacitor Bank
Capacitor Bank Definition
A capacitor bank is defined as a group of capacitors used to store and release electrical energy in a power system, helping to improve power quality.
System Voltage Tolerance
Capacitor banks must operate smoothly at up to 110% of the rated peak phase voltage and 120% of the rated RMS phase voltage.
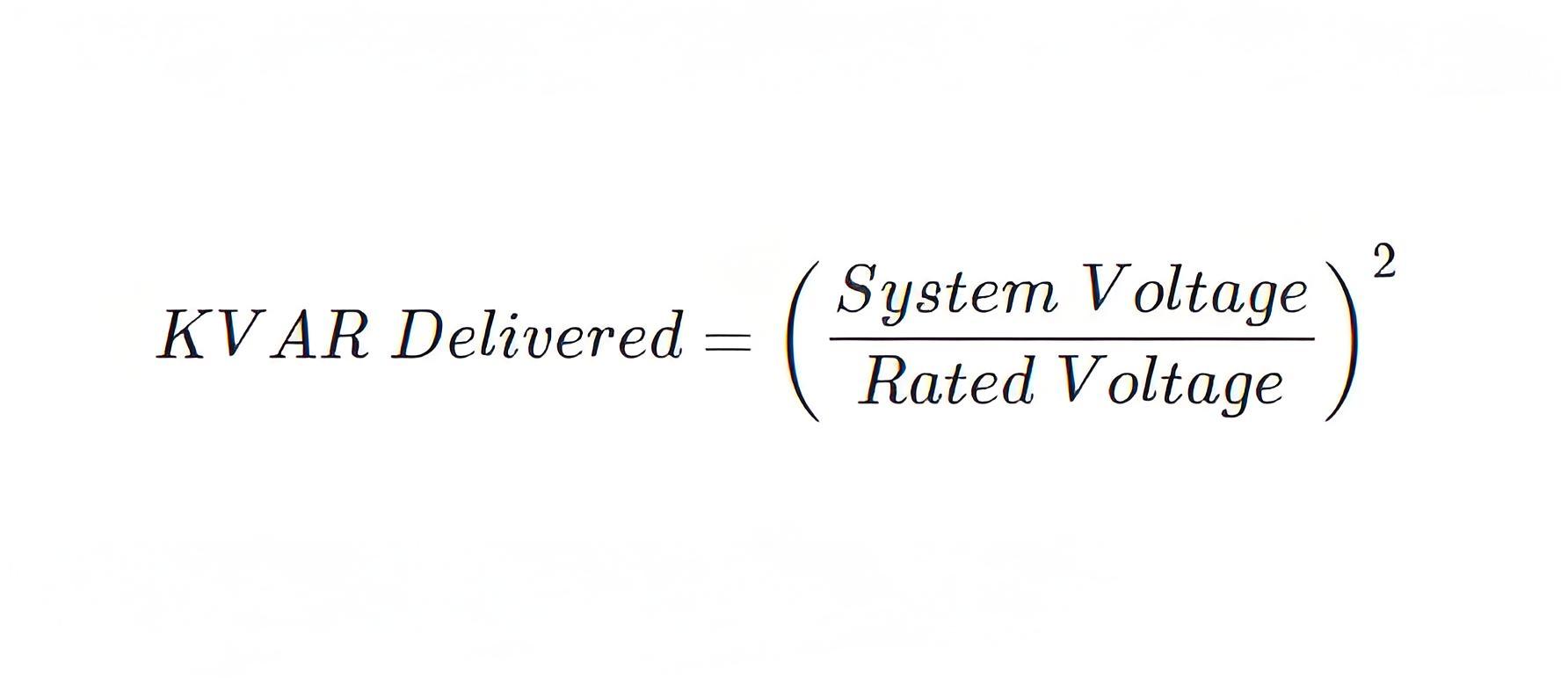
KVAR Rating
Capacitor unit are normally rated with its KVAR ratings. Standard capacitor unit available at market, are typically rated with either of following KVAR rating.50 KVAR, 100 KVAR, 150 KVAR, 200 KVAR, 300 KVAR and 400 KVAR.The KVAR delivered to the power system depends upon the system voltage by the following formula.
Temperature Rating of a Capacitor Bank
These are mainly two cause of farming heat on a capacitor bank.
Outdoor type capacitor bank are generally installed at open space where sunlight strikes on the capacitor unit directly. Capacitor can also absorb heat from the nearly furnace for which it is installed.
Production of heat in the capacitor unit is also initiated from the VAR delivering by the unit.
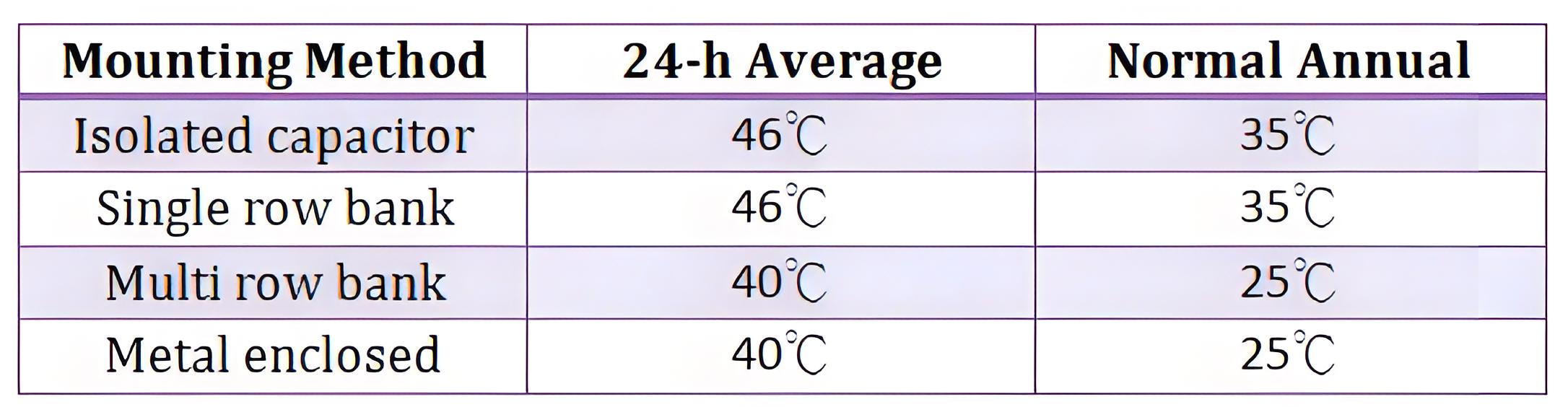
Hence, for radiation of these heats, there should be sufficient arrangement. The maximum allowable ambient temperatures in which a capacitor bank should be operated are given below in tabular form,
Heat Management
Proper ventilation and spacing are necessary to manage heat from external and internal sources to maintain capacitor bank efficiency.
To ensure proper ventilation, there should be adequate spacing between capacitor units. Sometimes, forced airflow can be used to speed up heat dissipation from the bank.
Capacitor Bank Unit or Capacitor Unit
Capacitor bank units or simply called capacitor units are manufactured in either single phase or three phase configuration.
Single Phase Capacitor Unit
Single phase capacitor units are designed either double bushing or single bushing.
Double Bushing Capacitor Unit
Here, the terminal of the both ends of capacitor assembly are come out from the metallic casing of the unit through two bushing. The entire capacitor assembly, this is series parallel combination of required number of capacitive elements is immersed in insulating fluid casing. Hence, there will be an insulated separation between conducting part of the capacitor element assembly go through bushing, there will be no connection between conductor and casing. That is why double bushing capacitor unit is known as dead tank capacitor unit.
Single Bushing Capacitor Unit
In this case casing of the unit is used as second terminal of assembly of capacitor element. Here single bushing is used to terminal one end of the assembly and its other terminal is internally connected to the metallic casing. This is possible because except terminal, all other conducting portion of the capacitor assembly is insulated from the casing.
Three Bushing Capacitor Unit
A three phase capacitor unit has three bushings to terminate 3 phase respectively. There is no neutral terminal in 3 phase capacitor unit.
BIL or Basic Insulation Level of Capacitor Unit
Like other electrical equipments a capacitor bank has also to with stand different voltage conditions, like power frequency over voltages and lightening and switching over voltages.
So Basic Insulation Level must be specified on every capacitor unit rating plate.
Internal Discharge Device
Capacitor units usually have an internal discharge device that quickly reduces residual voltage to a safe level, typically 50 V or less, within a specified time. The discharge period is part of the unit’s rating.
Transient Over Current Rating
Power capacitor may undergo over current situating during switching operation. So the capacitor unit must be rated for allowable short circuit current for specified time period.So, a capacitor unit should be rated with all the above mentioned parameters.
So a power capacitor unit can be rated as follows,
Nominal system voltage in KV.
System power frequency in Hz.
Temperature class with allowable maximum and minimum temperature in oC.
Rated voltage per unit in KV.
Rated output in KVAR.
Rated capacitance in µF.
Rated current in Amp.
Rated insulation level (Nominal voltage/Impulse voltage).
Discharge time/voltage in second/voltage.
Fusing arrangement either internally fused or externally fused or fuseless.
Number of bushing, double/single/triple bushing.
Number of phase. Single phase or three phase.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













