What is a Transmission Tower?
What is a Transmission Tower?
Transmission Tower Definition
A transmission tower is defined as a tall structure used to support overhead power lines, transporting high-voltage electricity from generating stations to substations.
Transmission Tower Parts
A power transmission tower is essential for power transmission systems and consists of several parts:
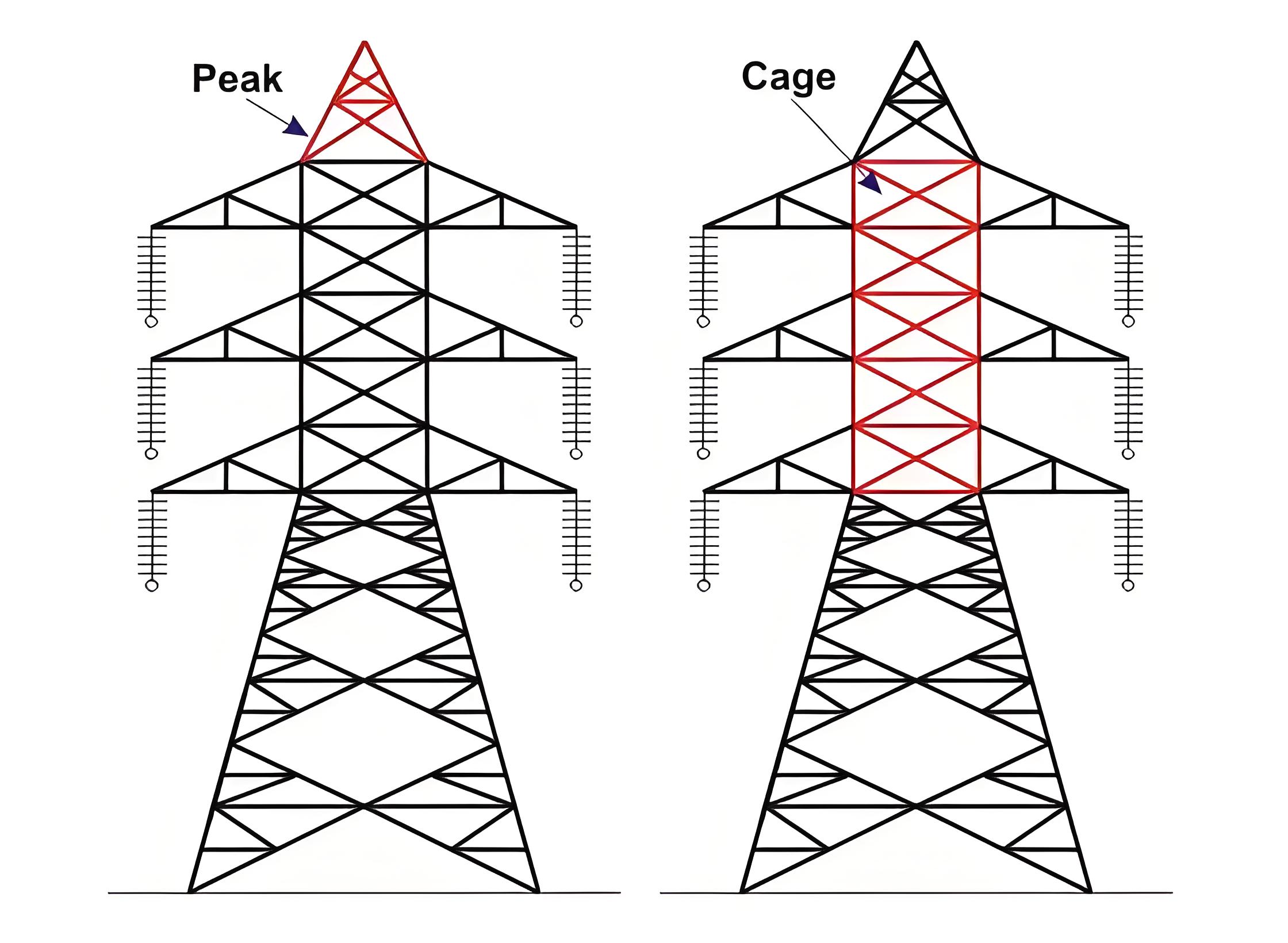
The peak of the transmission tower
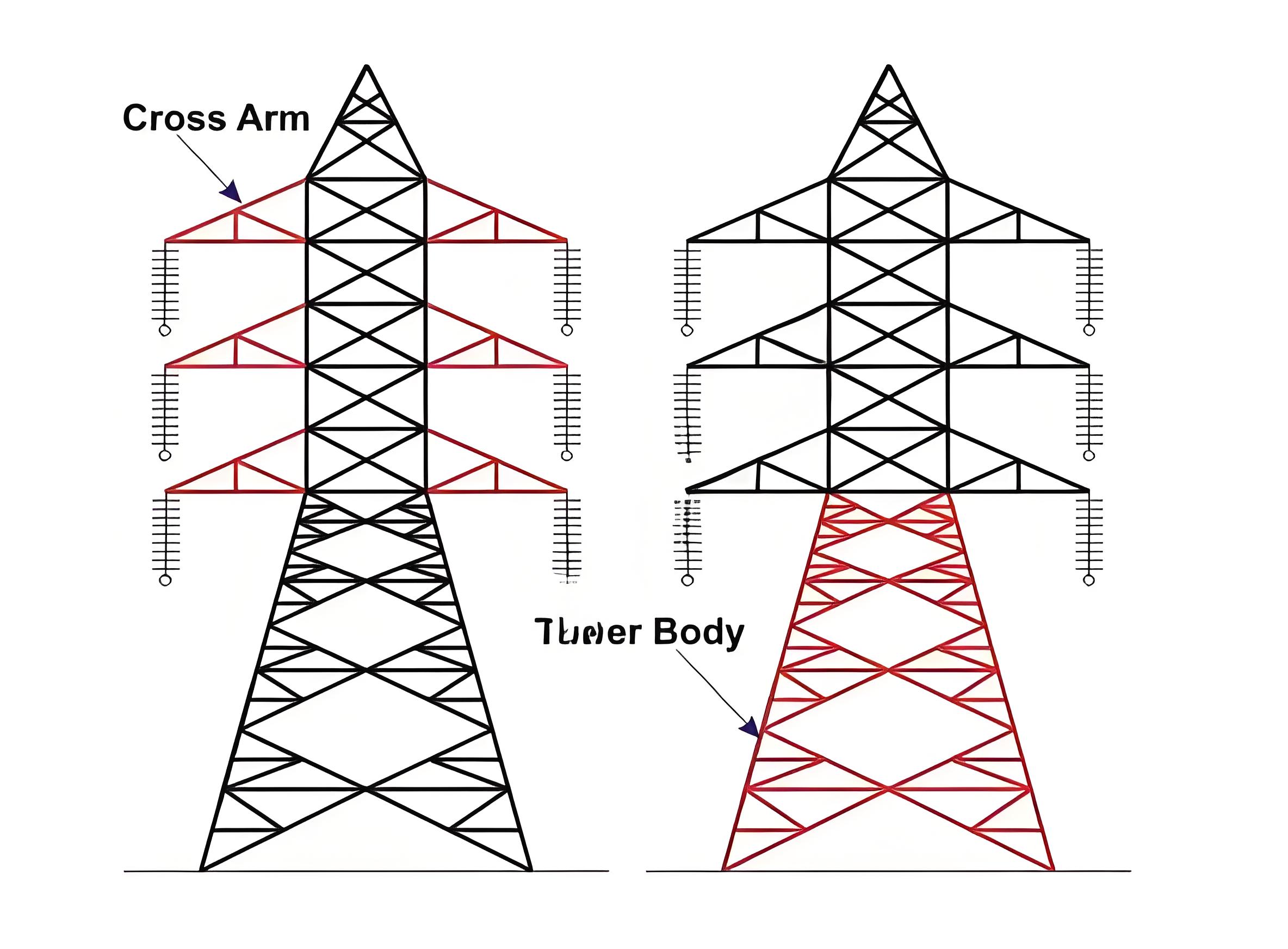
The cross arm of the transmission tower
The boom of transmission tower
Cage of transmission tower
Transmission Tower Body
Leg of transmission tower
Stub/Anchor Bolt and Baseplate assembly of the transmission tower.
These parts have been described below. Note that the construction of these towers is not a simple task, and there is a tower erection methodology behind building these high voltage transmission towers.
Design Importance
Transmission towers must support heavy conductors and withstand natural disasters, requiring robust engineering in civil, mechanical, and electrical fields.
Parts of a Transmission Tower
Key parts include the peak, cross arm, boom, cage, body, legs, and baseplate assembly, each playing a crucial role in the tower’s function.
Cross Arm of Transmission Tower
The cross arms hold the transmission conductors. Their size depends on the transmission voltage, configuration, and stress distribution angle.
Cage of Transmission Tower
The portion between tower body and peak is known as cage of transmission tower. This portion of the tower holds the cross arms.
Transmission Tower Body
The tower body extends from the bottom cross arms to the ground and is vital for maintaining the ground clearance of the bottom conductor of the transmission line.
Transmission Tower Design
During design of transmission tower the following points to be considered in mind
The minimum ground clearance of the lowest conductor point above the ground level.
The length of the insulator string.
The minimum clearance to be maintained between conductors and between conductor and tower.
The location of a ground wire with respect to outermost conductors.
The midspan clearance required from considerations of the dynamic behavior of the conductor and lightning protection of the power line.
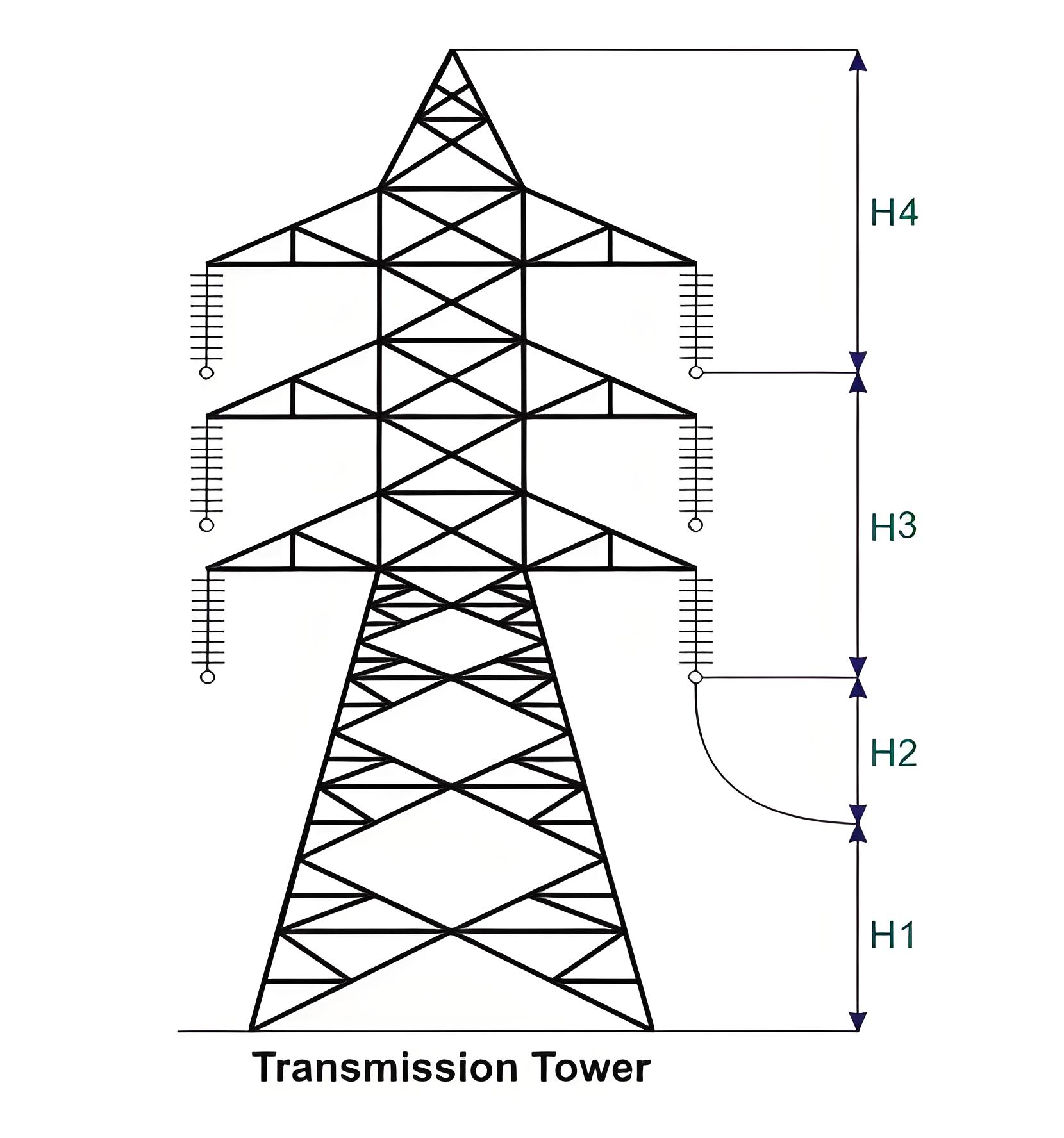
To determine the actual transmission tower height by considering the above points, we have divided the total height of the tower into four parts:
Minimum permissible ground clearance (H1)
Maximum sag of the overhead conductor (H2)
Vertical spacing between the top and bottom conductors (H3)
Vertical clearance between the ground wire and top conductor (H4)
Higher voltage transmission lines require greater ground clearance and vertical spacing. Therefore, high-voltage towers have higher ground clearance and larger spacing between conductors.
Types of Electrical Transmission Towers
According to different considerations, there are different types of transmission towers.
The transmission line goes as per available corridors. Due to the unavailability of the shortest distance straight corridor transmission line has to deviate from its straightway when obstruction comes. In the total length of a long transmission line, there may be several deviation points. According to the angle of deviation, there are four types of transmission tower
A – type tower – angle of deviation 0o to 2o.
B – type tower – angle of deviation 2o to 15o.
C – type tower – angle of deviation 15o to 30o.
D – type tower – angle of deviation 30o to 60o.
As per the force applied by the conductor on the cross arms, the transmission towers can be categorized in another way
Tangent suspension tower and it is generally A – type tower.
Angle tower or tension tower or sometime it is called section tower. All B, C and D types of transmission towers come under this category.
Apart from the above-customized type of tower, the tower is designed to meet special usages listed below:
These are called special type tower
River crossing tower
Railway/ Highway crossing tower
Transposition tower
Based on numbers of circuits carried by a transmission tower, it can be classisfied as
Single circuit tower
Double circuit tower
Multi circuit tower.
Transmission Tower Design
Design considerations include ground clearance, conductor spacing, insulator length, ground wire location, and midspan clearance, which are vital for safe and efficient operation.

The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













