Transient Stability in Power System
Transient Stability Definition
Transient stability is the power system’s ability to return to a stable state after significant disturbances like faults or sudden changes in load.
Swing Equation
The swing equation helps determine how changes in load affect a generator’s stability by analyzing the dynamics between mechanical and electromagnetic forces.
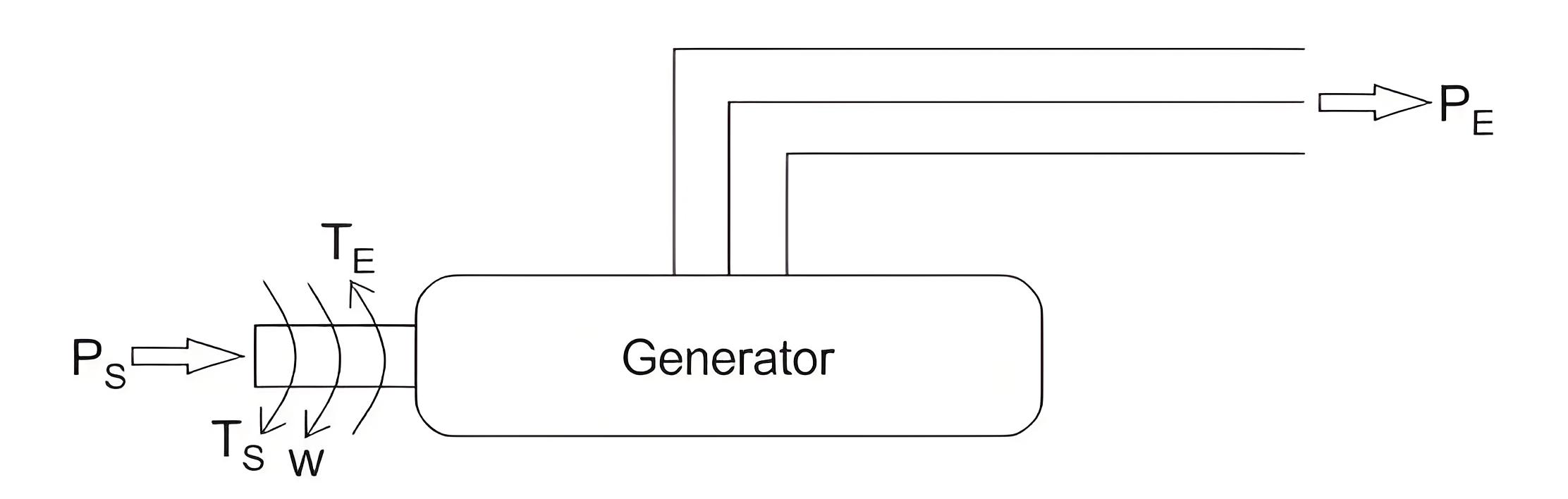
Here for the sake of understanding, we consider the case where a synchronous generator is suddenly applied with an increased amount of electromagnetic load, which leads to instability by making PE less than PS as the rotor undergoes deceleration. Now the increased amount of the accelerating power required to bring the machine back to a stable condition is given by,
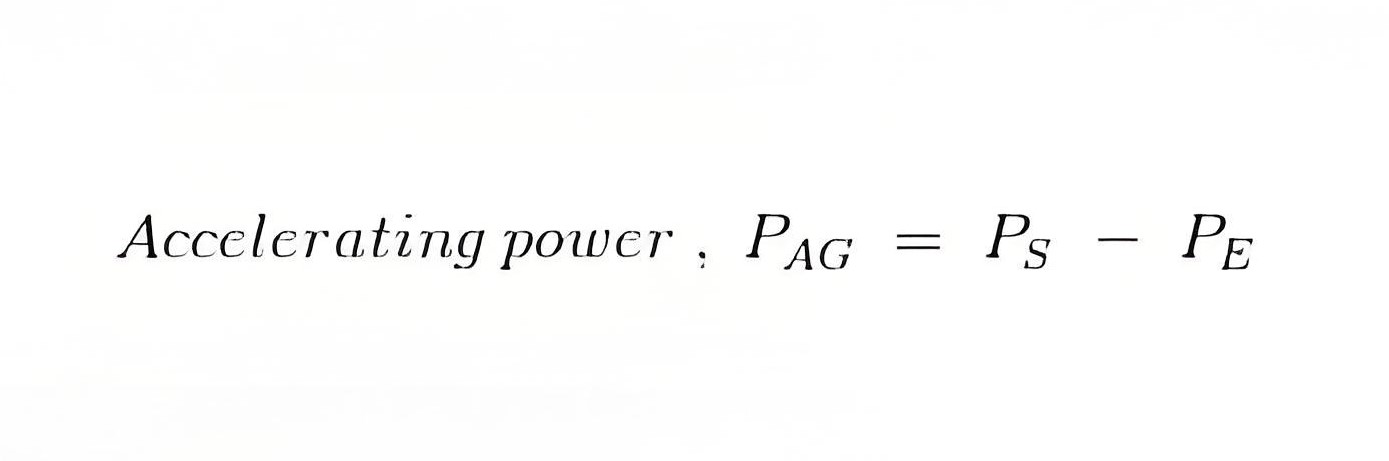
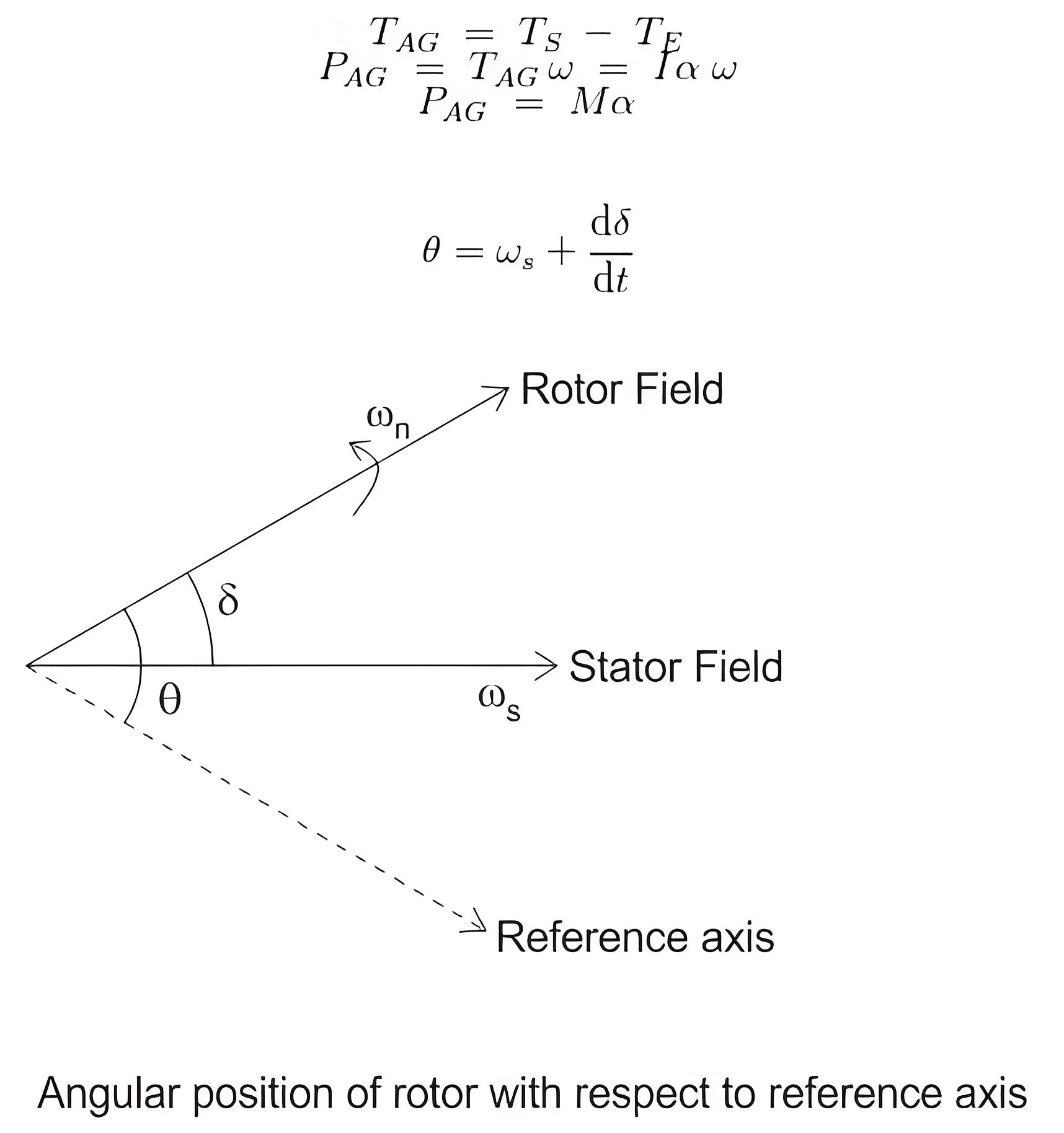
The formula for the accelerating torque is as follows:
Now we know that(since T = current × angular acceleration)Furthermore, angular momentum, M = Iω
But since on loading the angular displacement θ varies continuously with time, as shown in the figure below, we can write. This is known as the swing equation for transient stability in power system.
Importance of Stability
Maintaining transient stability is crucial for preventing system failures and ensuring reliable power delivery.
Instability Consequences
Without proper transient stability, power systems can experience failures, leading to blackouts and other reliability issues.
Stability Assessment
Initial studies focus on the system’s response to the first swing post-disturbance to predict its ability to regain and maintain stability.
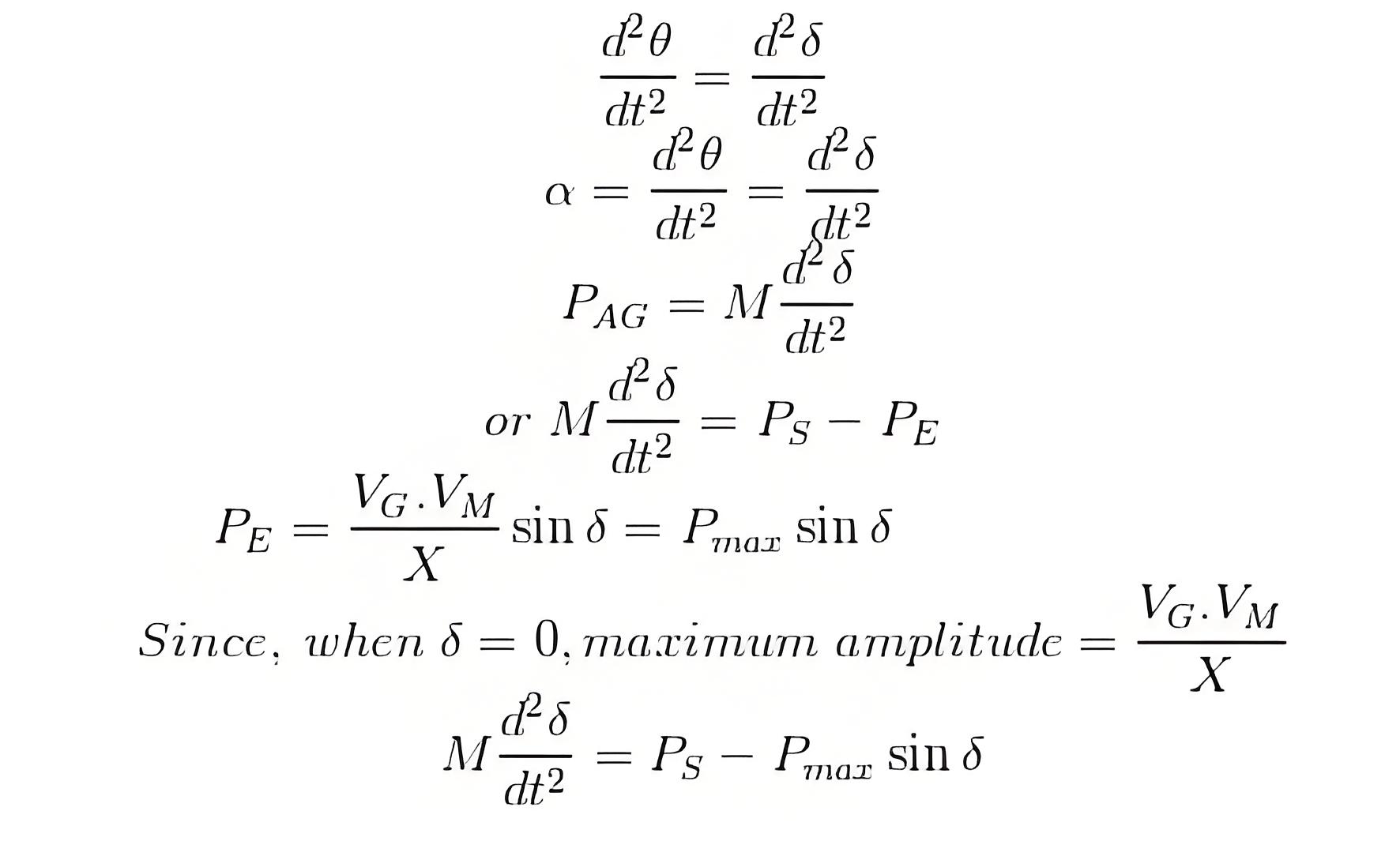
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.