Protection System Power System
Power System Protection Definition
Power system protection is defined as the methods and technologies used to detect and isolate faults in an electrical power system to prevent damage to other parts of the system.
Circuit Breakers
These devices are crucial for automatically disconnecting the faulted part of the system, ensuring the stability and safety of the remaining electrical grid.
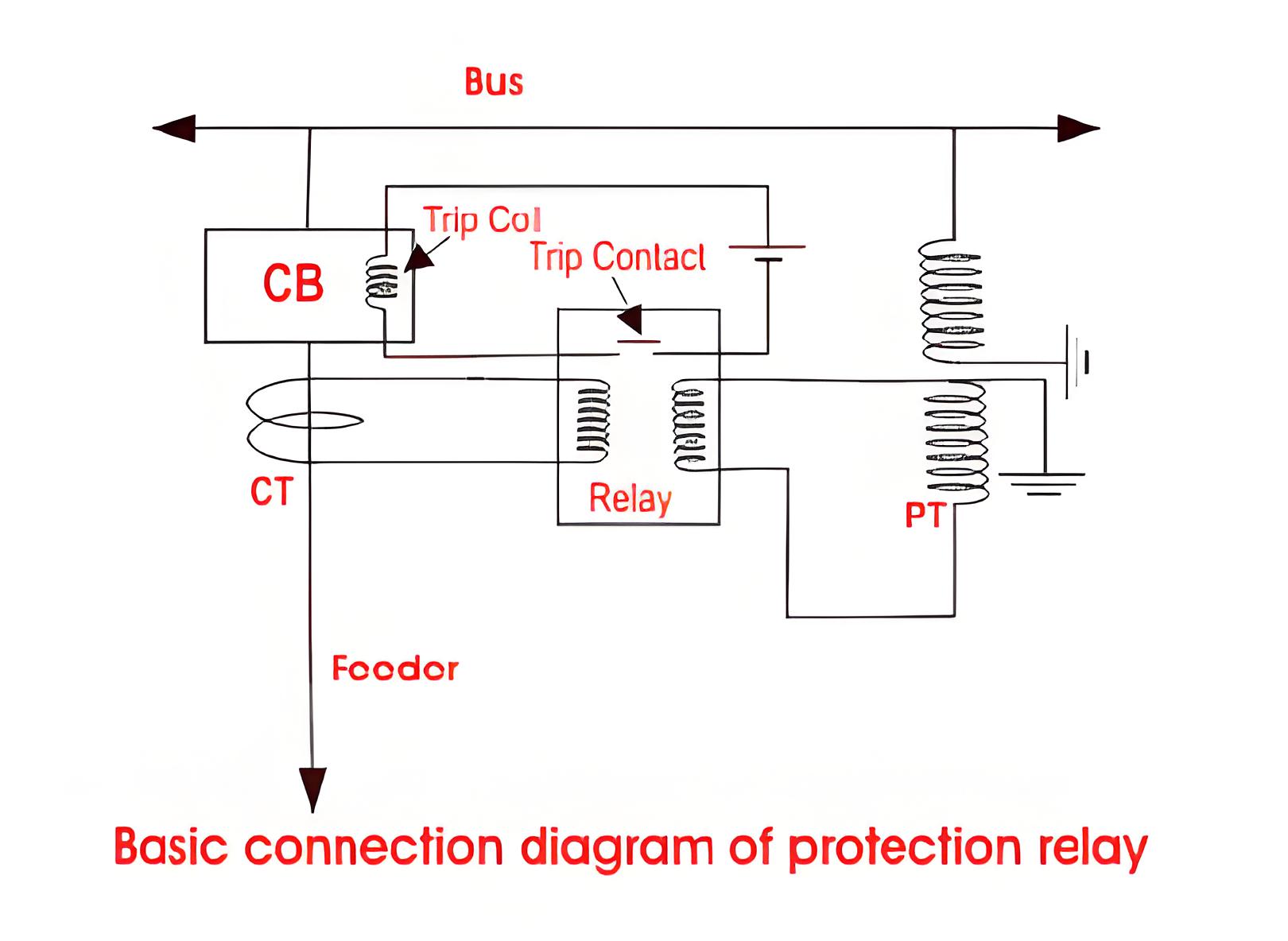
Protection Relays
Protection relays monitor the electrical network and initiate the tripping of circuit breakers when they detect anomalies, critical for mitigating damage during faults.
Functional Requirements
The most important requisite of protective relay is reliability. They remain inoperative for a long time before a fault occurs; but if a fault occurs, the relays must respond instantly and correctly.
Selectivity
The relay must be operated in only those conditions for which relays are commissioned in the electrical power system. There may be some typical condition during fault for which some relays should not be operated or operated after some definite time delay hence protection relay must be sufficiently capable to select appropriate condition for which it would be operated.
Sensitivity
The relaying equipment must be sufficiently sensitive so that it can be operated reliably when level of fault condition just crosses the predefined limit.
Speed
Protective relays must operate quickly and be well-coordinated. Proper coordination ensures that a fault in one part of the system doesn’t unnecessarily affect a healthy part. Relays in the healthy area should not trip faster than those in the faulted area to avoid disrupting the stable sections. If a fault relay fails to act due to a defect, the next relay should operate to secure the system without being overly quick, which might lead to unnecessary interruptions, or too slow, risking equipment damage.
Important Elements for Power System Protection
Switchgear
Consists of mainly bulk oil circuit breaker, minimum oil circuit breaker, SF6 circuit breaker, air blast circuit breaker and vacuum circuit breaker etc. Different operating mechanisms such as solenoid, spring, pneumatic, hydraulic etc. are employed in the circuit breaker. Circuit breaker is the main part of protection system in power system and it automatically isolate the faulty portion of the system by opening its contacts.
Protective Gear
Consists of mainly power system protection relays like current relays, voltage relays, impedance relays, power relays, frequency relays, etc. based on operating parameter, definite time relays, inverse time relays, stepped relays etc. as per operating characteristic, logic wise such as differential relays, over fluxing relays etc. During fault the protection relay gives trip signal to the associated circuit breaker for opening its contacts.
Station Battery
Circuit breakers in the electrical power system operate on DC (Direct Current) from station batteries. These batteries store DC power, allowing circuit breakers to function even during a complete power failure. Referred to as the heart of the electrical substation, station batteries accumulate energy when AC power is available and provide essential power to trip the circuit breaker if AC power fails.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













