How to Measure Electrical Energy?
How to Measure Electrical Energy?
Electrical Energy Definition
Electrical energy is defined as the product of electrical power and time, measured in joules (J).
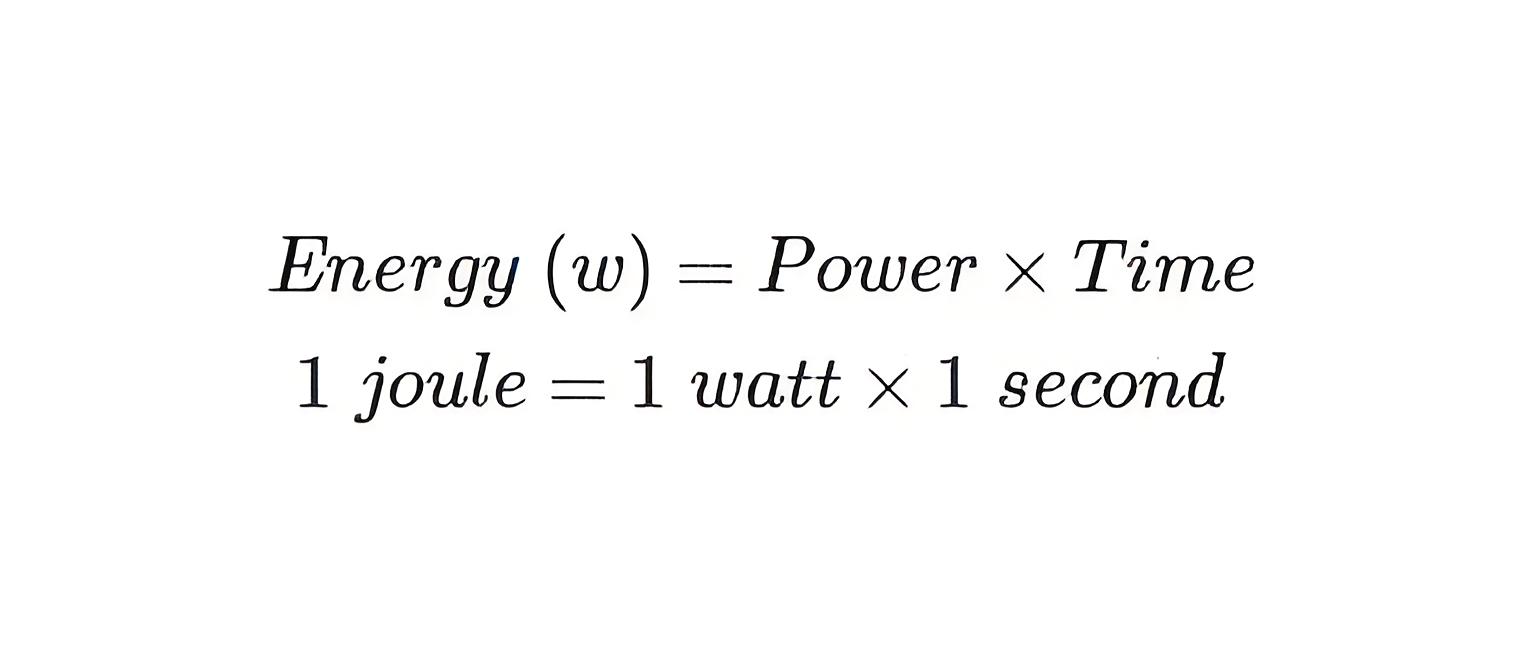
E is the electrical energy in joules (J)
P is the electrical power in watts (W)
t is the time in seconds (s)
Electrical energy and power are closely related concepts. Electrical power is the amount of electrical current that flows through a circuit due to a certain voltage difference across it. Electrical power is also the rate at which electrical energy is delivered or consumed by a device or a system. Electrical power is measured in watts (W), which are equivalent to joules per second (J/s). Mathematically, we can write:
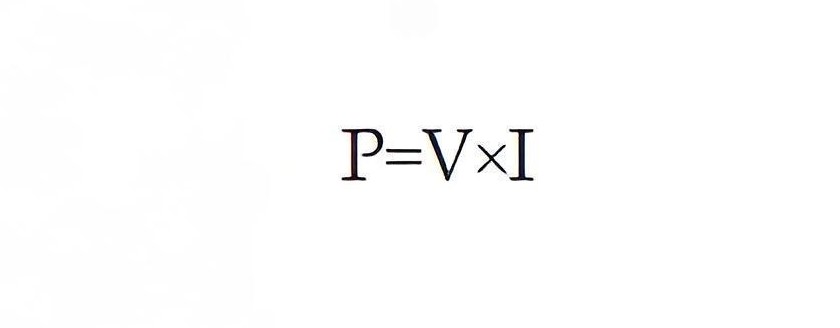
P is the electrical power in watts (W)
V is the voltage difference in volts (V)
I is the electrical current in amperes (A)
Electrical Energy Measure
An energy meter is a device that measures the amount of electric energy consumed by a residence, a business, or an electrically powered device.
It measures the total power consumed over a time interval and is calibrated in billing units, the most common one being the kilowatt-hour (kWh). Energy meters are used in domestic and industrial AC circuits for measuring power consumption.
Type of Energy Meter
Electromechanical meters
Electronic meters
Smart meters
Single-phase meters
Three-phase meters
Electrical Energy Consumption Calculate
To calculate electrical energy consumption, we need to multiply the electrical power by the time duration for which it is consumed. The formula for calculating electrical energy consumption is:
E is the electrical energy consumption in joules (J) or watt-hours (Wh)
P is the electrical power in watts (W)
t is the time duration in seconds (s) or hours (h)
The unit of electrical energy consumption depends on the unit of time used in the formula. If we use seconds, then the unit of electrical energy consumption is joules (J). If we use hours, then the unit of electrical energy consumption is watt-hours (Wh).
However, as mentioned before, the watt-hour is a very small unit for practical purposes, so we usually use larger units such as kilowatt-hours (kWh), megawatt-hour (MWh), or gigawatt-hour (GWh).
To convert between different units of electrical energy consumption, we can use the following conversion factors:
1 kWh = 1,000 Wh = 3.6 MJ
1 MWh = 1,000 kWh = 3.6 GJ
1 GWh = 1,000 MWh = 3.6 TJ
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













