What is a Gunn Diode Oscillator?
What is a Gunn Diode Oscillator?
Gunn Diode Oscillator
A Gunn Diode Oscillator (also known as a Gunn oscillators or transferred electron device oscillator) are a cheap source of microwave power and comprise of Gunn diode or transferred electron device (TED) as their major component. They perform a similiar funciton as Reflex Klystron Oscillators.
In Gunn oscillators, the Gunn diode will be placed in a resonant cavity. A Gunn oscillator is comprised of two major components: (i) A DC bias and (ii) A tuning circuit.
How a Gunn Diode Works as an Oscillator DC Bias
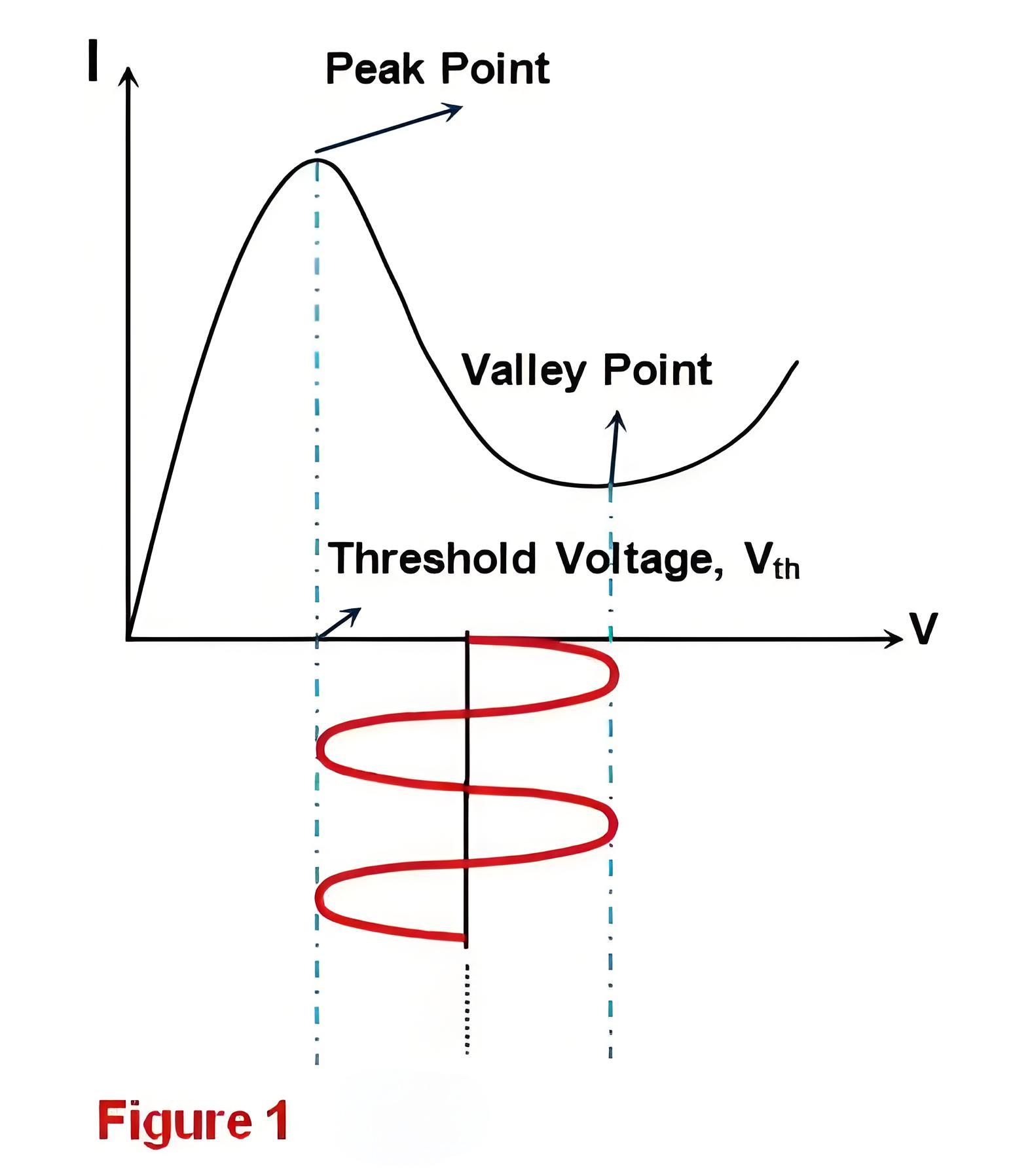
In a Gunn diode, as the applied DC bias increases, the current initially rises until it reaches the threshold voltage. Beyond this point, the current decreases as the voltage continues to increase up to the breakdown voltage. The span from the peak to the valley in this behavior forms what is known as the negative resistance region.
The Gunn diode’s ability to show negative resistance, combined with its timing properties, allows it to function as an oscillator. This occurs because the negative resistance counteracts any actual resistance within the circuit, enabling optimal current flow.
This leads to the generation of continuous oscillations as long as the DC bias is maintained, though the amplitude of these oscillations is confined within the boundaries of the negative resistance region.
Tuning Circuit
In the case of Gunn oscillators, the oscillation frequency primarily depends on the middle active layer of the gunn diode. However the resonant frequency can be tuned externally either by mechanical or by electrical means. In the case of electronic tuning circuit, the control can be brought about by using a waveguide or microwave cavity or varactor diode or YIG sphere.
Here the diode is mounted inside the cavity in such a way that it cancels the loss resistance of the resonator, producing oscillations. On the other hand, in the case of mechanical tuning, the size of the cavity or the magnetic field (for YIG spheres) is varied mechanically by the means of, say, an adjusting screw, inorder to tune the resonant frequency.
These types of oscillators are used to generate microwave frequencies ranging from 10 GHz to few THz, as decided by the dimensions of the resonant cavity. Usually the coaxial and microstrip/planar based oscillator designs have low power factor and are less stable in terms of temperature.
On the other hand, the waveguide and the dielectric resonator stabilized circuit designs have greater power factor and can be made thermally stable, quite easily.Figure 2 shows a coaxial resonator based Gunn oscillator which is used to generate the frequencies ranging from 5 to 65 GHz. Here as the applied voltage Vb is varied, the Gunn diode induced fluctuations travel along the cavity to get reflected from its other end and reach back their starting point after time t given by
Where, l is the length of the cavity and c is the speed of light. From this, the equation for the resonant frequency of the Gunn oscillator can be deduced as
where, n is the number of half-waves which can fit into the cavity for a given frequency. This n ranges from 1 to l/ct d where td is the time taken by the gunn diode to respond to the changes in the applied voltage.
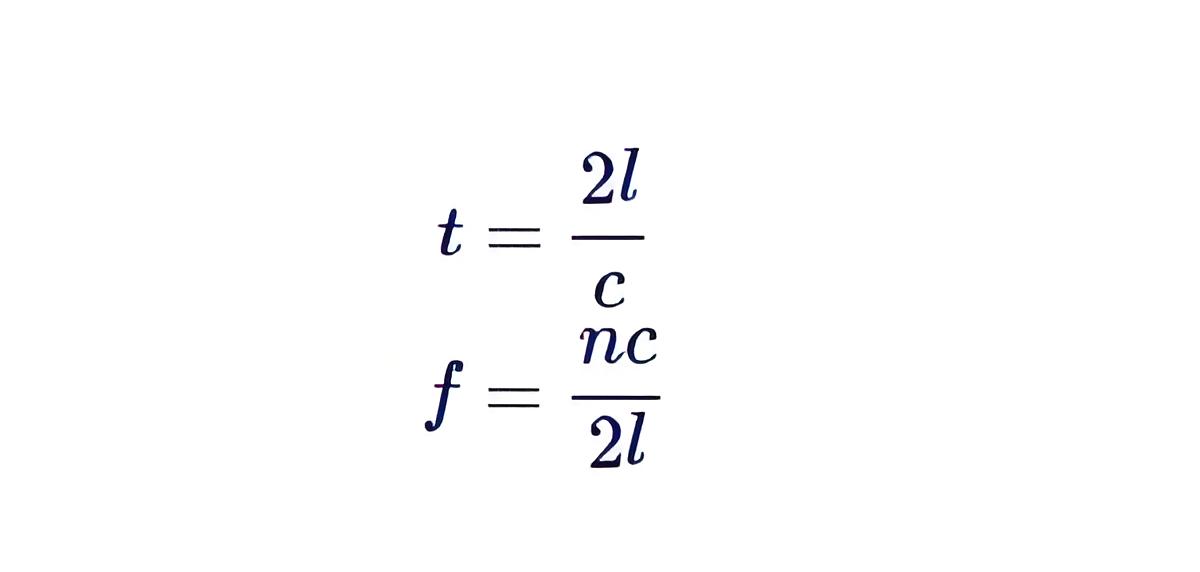
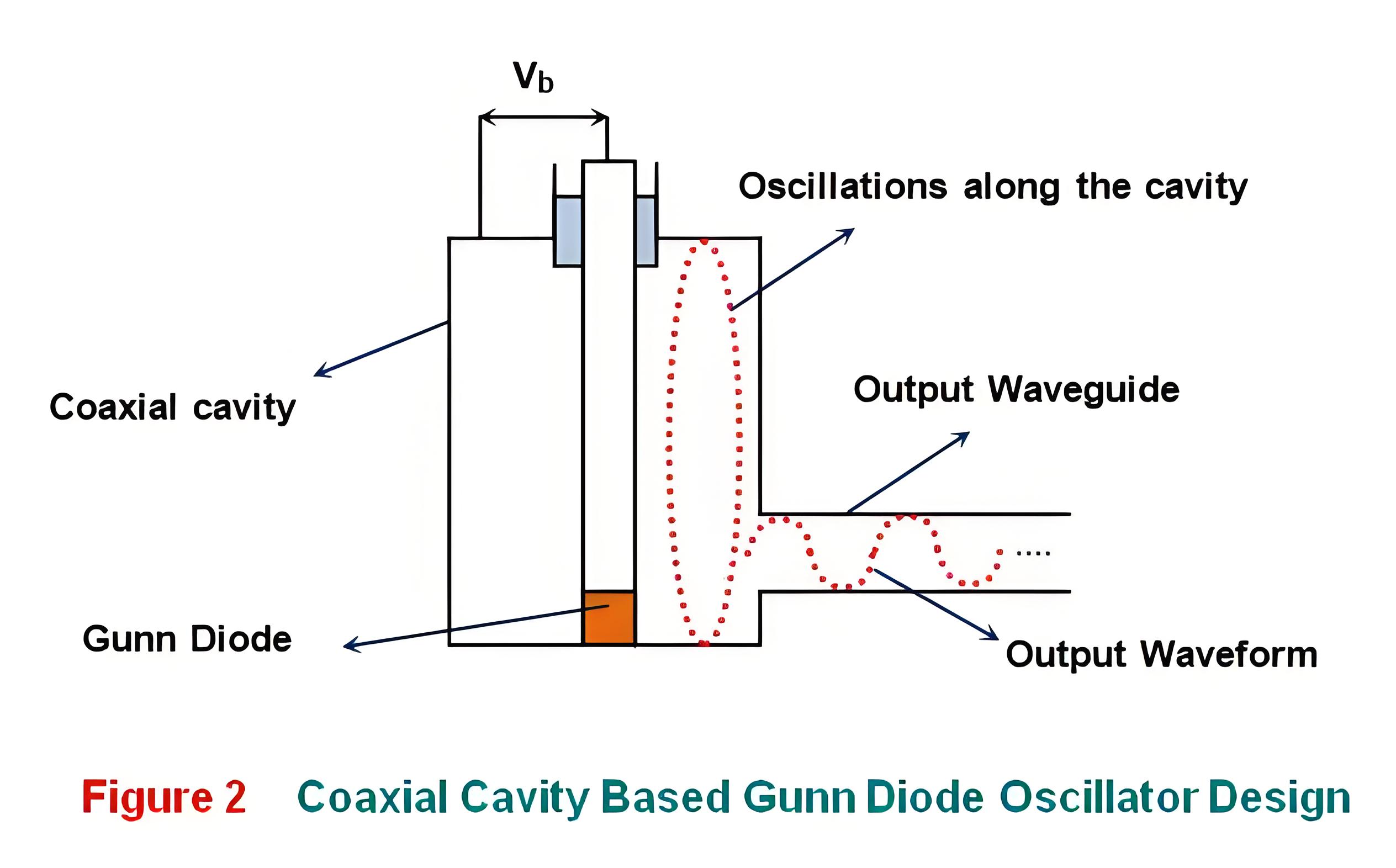
Here the oscillations are initiated when the loading of the resonator is slightly higher than the maximum negative resistance of the device. Next, these oscillations grow interms of amplitude until the average negative resistance of the gunn diode becomes equal to the resistance of the resonator after which one can get sustained oscillations.
Further, these kind of relaxation oscillators have a large capacitor connected across the gunn diode so as to avoid burning-out of the device due to the large amplitude signals.Lastly, it is to be noted that the Gunn diode oscillators are extensively used as radio transmitters and receivers, velocity-detecting sensors, parametric amplifiers, radar sources, traffic monitoring sensors, motion detectors, remote vibration detectors, rotational speed tachometers, moisture content monitors, microwave transceivers (Gunnplexers) and in the case of automatic door openers, burglar alarms, police radars, wireless LANs, collision avoidance systems, anti-lock brakes, pedestrian safety systems, etc.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













