What is Double Beam Oscilloscope?
What is Double Beam Oscilloscope?
Double Beam Oscilloscope Definition
A double beam oscilloscope uses two electron beams to display signals on a single screen simultaneously.
Construction
There are two individual vertical input channels for the two electron beams from different sources. Each channel has its own attenuator and pre-amplifier, allowing independent control of each beam’s amplitude.
The two channels can have either common or independent time base circuits for different sweep rates. Each beam passes through its own channel for vertical deflection before crossing a single set of horizontal plates. A sweep generator drives the horizontal amplifier, providing a common horizontal deflection for both beams across the screen.
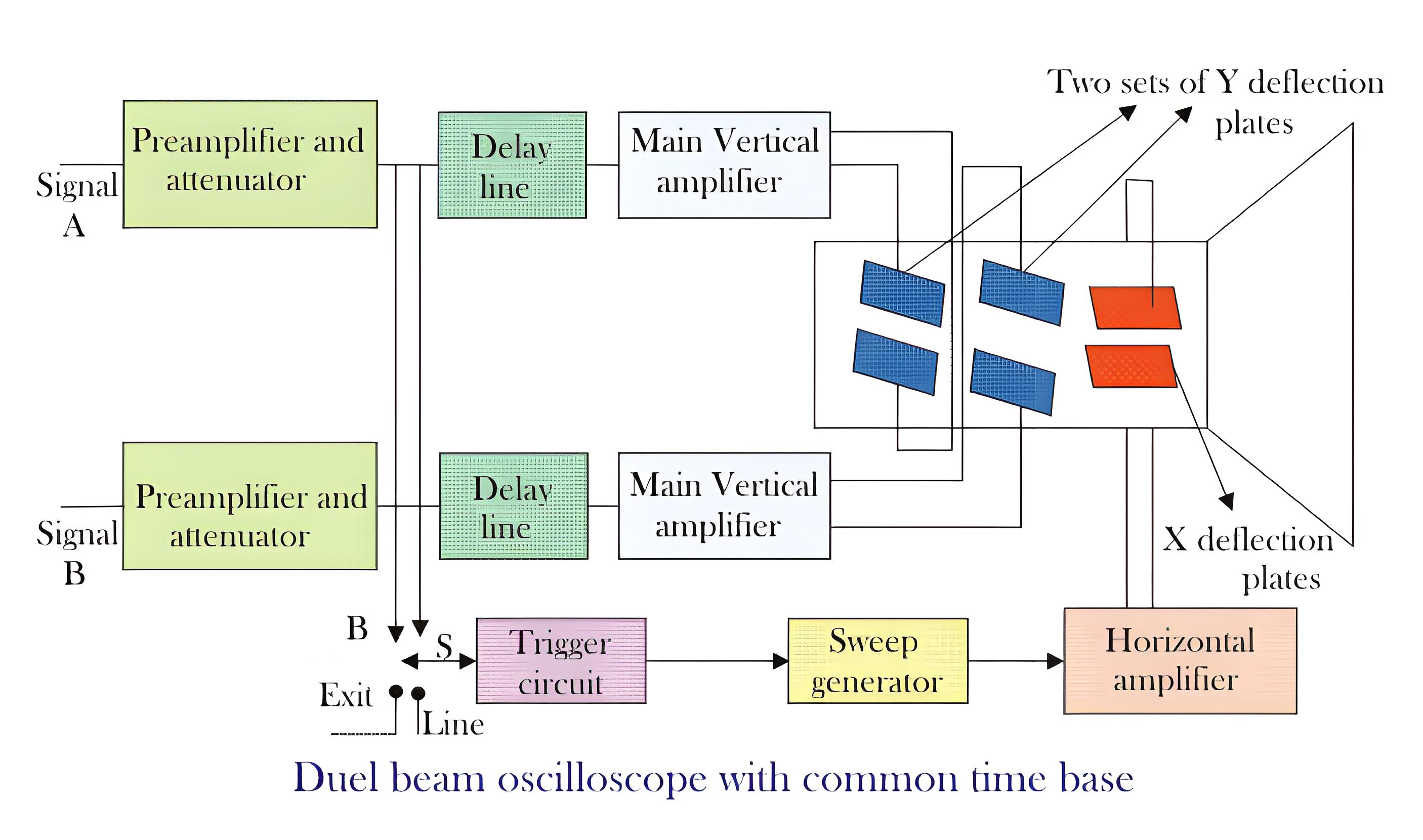
A dual beam oscilloscope generates two electron beams within the cathode ray tube using either a double electron gun tube or a split beam method. Each beam’s brightness and focus are controlled separately. However, using two tubes increases the oscilloscope’s size and weight, making it bulky.
The other method is the split beam tube, which uses a single electron gun. A horizontal splitter plate between the Y deflection plate and the last anode isolates the two channels. The potential of the splitter plate is the same as the last anode. Since the single beam is split into two, the resulting beams are only half as bright as the original. This is a disadvantage at high frequencies. To improve brightness, two sources can be used in the last anode instead of one.
Time Base Circuits
These oscilloscopes can have common or independent time base circuits, allowing different sweep rates.
Split Beam Method
In this method, a single electron gun is used, but the beam is split into two, resulting in reduced brightness.
Dual Beam vs. Dual Trace
The dual beam oscilloscope has two different electron gun which passes through two completely separate vertical channels, where as dual trace oscilloscope has single electron beam which get split into two and passes through two separate channels.
Dual trace CRO cannot switch quickly between the traces so it cannot capture two fast transient events whereas dual beam CRO there is no question of switching.
The brightness of the two displayed beam has drastically different as it operated at widely spaced sweep speeds. On the other hand, dual trace brightness of the resultant display is same.
The brightness of the displayed beam of the dual trace is half of the brightness of dual beam CRO.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













