What is an Oscillator Transducer?
What is an Oscillator Transducer?
Oscillator Transducer Definition
An oscillator transducer is a device that converts force, pressure, or displacement into a measurable voltage.
Working Principle
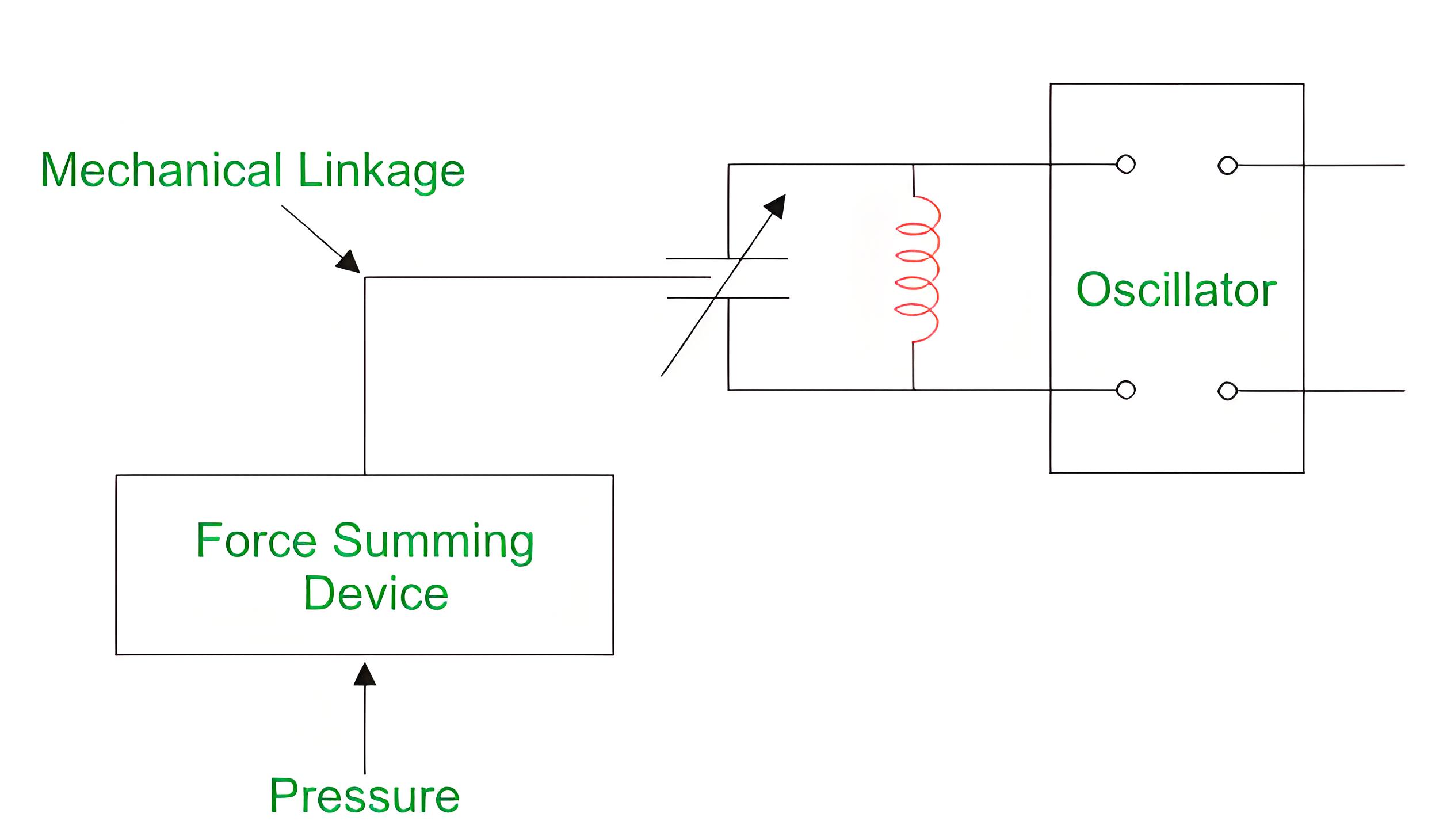
The quantity to be measured like pressure is applied to the force summing device which transfers this pressure to mechanical linkage.
Mechanical linkage responds according to the magnitude of the pressure.
Mechanical linkage drives the dielectric medium inside the capacitor.
The movement of the dielectric medium inside the capacitor tends to change the capacitance.
Frequency of oscillator depends on capacitance and inductance. In case of change of any of these quantities the frequency changes.
The output of oscillator is a modulated output and can be modulated and calibrated in terms of pressure or force applied.
Components
Mechanical linkae: This links the input quantity to the oscillator transducer by actuating it. It may include gears or other linkage systems.
Oscillator: As we know oscillator are used to generate desired frequency. The oscillator used here consists of LC tank/circuit. The output frequency is generated according to the input source.
Frequency Modulator: This component modifies the oscillator’s output frequency for telemetry purposes, ensuring it is suitable for transmission.
Force Summing Member: This is used to change the capacitance or inductance of an LC oscillator circuit. It transfers the pressure to mechanical linkage.
Advantages
This transducer can measure both dynamic and static phenomena, making it versatile for different applications.
This transducer is very useful for telemetry applications.
Disadvantages
This transducer has very hunted temperature range.
It has a poor thermal stability.
It has a low accuracy and therefore is used only in low accuracy applications.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













