What is a Digital Frequency Meter?
What is a Digital Frequency Meter?
Digital Frequency Meter Definition
A digital frequency meter is defined as an instrument that accurately measures and displays the frequency of periodic electrical signals.
Function
It counts and displays the number of events occurring within a set time interval, resetting after each interval.
Operating Principle
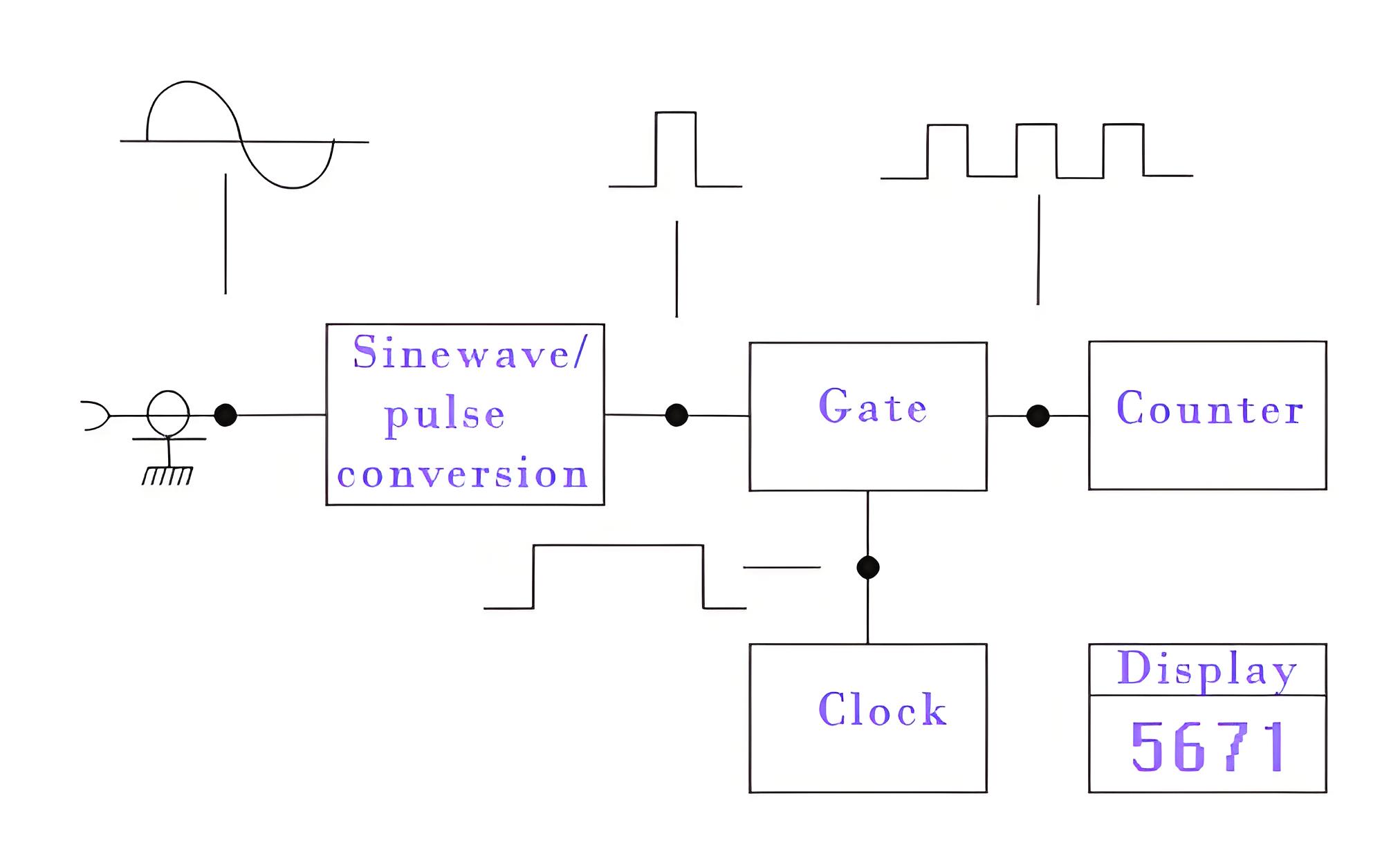
A frequency meter converts the sinusoidal voltage of the frequency into unidirectional pulses. The input signal’s frequency is displayed as a count, averaged over intervals of 0.1, 1.0, or 10 seconds, which repeat sequentially. As the ring counting units reset, pulses pass through the time-base gate and enter the main gate, which opens for a set interval. The time base gate stops a divider pulse from opening the main gate during the display interval. The main gate acts as a switch: when open, pulses pass through; when closed, the flow of pulses is blocked.
The main gate is controlled by a flip-flop. An electronic counter at the gate output counts the pulses passing through while the gate is open. When the flip-flop receives the next divider pulse, the counting interval ends, and further pulses are blocked. The count is displayed on a screen using ring counting units, each coupled to a numeric indicator for the digital display. When the reset pulse generator is triggered, the ring counters reset automatically, and the process starts again.
The range of modern digital frequency meter is between the range from104 to 109 hertz. The possibility of relative measurement error ranges between from 10-9 to 10-11 hertz and a sensitivity of 10-2 volt.
Measurement Range
Modern digital frequency meters measure from ten thousand to one billion hertz with high accuracy and sensitivity.
Applications
For testing radio equipment
Measuring the temperature, pressure, and other physical values.
Measuring vibration, strain
Measuring transducers
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













